CS 291 Special Topics on Network Security
... Architecture (Layer); Algorithm; Protocol Why it is built this way? Is it good/the best to build it this way? What if I build it? Network Usage, Management, Analysis How to use the networking service? Application Development Existing Network Applications/Tools ...
... Architecture (Layer); Algorithm; Protocol Why it is built this way? Is it good/the best to build it this way? What if I build it? Network Usage, Management, Analysis How to use the networking service? Application Development Existing Network Applications/Tools ...
071008
... host with the specified name at port 13 on that host getInputStream() is called on the socket to get a byte stream that reads from the socket An InputStreamReader wraps the byte stream and a BufferedReader wraps the InputStreamReader The BufferedReader reads all characters sent by the server using r ...
... host with the specified name at port 13 on that host getInputStream() is called on the socket to get a byte stream that reads from the socket An InputStreamReader wraps the byte stream and a BufferedReader wraps the InputStreamReader The BufferedReader reads all characters sent by the server using r ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
Lecture note 5
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
Link Layer - Computer Sciences User Pages
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
Secure Efficient Distance Vector Routing for Mobile Wireless Ad Hoc
... not meet application requirements for reasons such as security, cost, or quality. Examples of applications for ad hoc networks range from military operations and emergency disaster relief, to community networking and interaction between attendees at a meeting or students during a lecture. In these a ...
... not meet application requirements for reasons such as security, cost, or quality. Examples of applications for ad hoc networks range from military operations and emergency disaster relief, to community networking and interaction between attendees at a meeting or students during a lecture. In these a ...
Chapter 1
... • Used to connect routers to external networks, usually over a larger geographical distance. • The Layer 2 encapsulation can be different types (PPP, Frame Relay, HDLC (High-Level Data Link Control) ). • Similar to LAN interfaces, each WAN interface has its own IP address and subnet mask, making it ...
... • Used to connect routers to external networks, usually over a larger geographical distance. • The Layer 2 encapsulation can be different types (PPP, Frame Relay, HDLC (High-Level Data Link Control) ). • Similar to LAN interfaces, each WAN interface has its own IP address and subnet mask, making it ...
Serial over Ethernet Device Server User`s Manual
... devices. It provides a convenient and economical solution not only to protect your current hardware investment, but also to ensure future network expandability. With Serial over Ethernet Server, users can centralize serial devices and distribute the management hosts at the same time. Serial over Eth ...
... devices. It provides a convenient and economical solution not only to protect your current hardware investment, but also to ensure future network expandability. With Serial over Ethernet Server, users can centralize serial devices and distribute the management hosts at the same time. Serial over Eth ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
What is Sockets
... used to transmitting data to remote host return: the number of bytes that has been delivered or -1. sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call) buf: a pointer to the data location buf_len: the data length to_addr: the socket address of the destination. to_len: the “to_addr” structure lengt ...
... used to transmitting data to remote host return: the number of bytes that has been delivered or -1. sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call) buf: a pointer to the data location buf_len: the data length to_addr: the socket address of the destination. to_len: the “to_addr” structure lengt ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
Internetworking Technology Overview
... The seven OSI layers use various forms of control information to communicate with their peer layers in other computer systems. This control information consists of specific requests and instructions that are exchanged between peer OSI layers. Control information typically takes one of two forms: he ...
... The seven OSI layers use various forms of control information to communicate with their peer layers in other computer systems. This control information consists of specific requests and instructions that are exchanged between peer OSI layers. Control information typically takes one of two forms: he ...
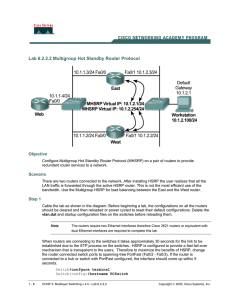
Lab 6.2.2.2 Multigroup Hot Standby Router Protocol
... Configure the East and West routers. Router(config)#hostname West West(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 West(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 West(config-if)#no shutdown West(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/1 West(config-if)#ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 West(config-if)#no shut ...
... Configure the East and West routers. Router(config)#hostname West West(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 West(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 West(config-if)#no shutdown West(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/1 West(config-if)#ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 West(config-if)#no shut ...
Lect03
... • A single computer can be running several applications (email, FTP, HTTP and others). • TCP is application to application (port to port) protocol, IP is computer to computer protocol. • TCP uses port numbers to identify different application running on a single computer. • A port is a 16-bit number ...
... • A single computer can be running several applications (email, FTP, HTTP and others). • TCP is application to application (port to port) protocol, IP is computer to computer protocol. • TCP uses port numbers to identify different application running on a single computer. • A port is a 16-bit number ...
slides
... Payload Type (7 bits): Indicates type of encoding currently being used. If sender changes encoding in middle of conference, sender informs the receiver through this payload type field. ...
... Payload Type (7 bits): Indicates type of encoding currently being used. If sender changes encoding in middle of conference, sender informs the receiver through this payload type field. ...
Chapter 5 - Department of Computer Engineering
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
How to connect an Epson POS printer with
... Each has a different set of features and a different way of setting them up. ...
... Each has a different set of features and a different way of setting them up. ...
Table of Contents - HP Enterprise Group
... 2.6.3 Rear Panel ............................................................................................................ 2-23 2.6.4 Power System ....................................................................................................... 2-23 2.6.5 Cooling System .................... ...
... 2.6.3 Rear Panel ............................................................................................................ 2-23 2.6.4 Power System ....................................................................................................... 2-23 2.6.5 Cooling System .................... ...
Notes
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
... “Taking Turns” MAC protocols channel partitioning MAC protocols: share channel efficiently and fairly at high load inefficient at low load: delay in channel access, 1/N bandwidth allocated even if only 1 active node! Random access MAC protocols efficient at low load: single node can fully uti ...
Ipv4-mapped Ipv6 Address Dest. 1.2.3.4 Dest.
... • IPv6 Mobility is based on core features of IPv6 – The base IPv6 was designed to support Mobility – Mobility is not an “Add-on” features • All IPv6 Networks are IPv6-Mobile Ready • All IPv6 nodes are IPv6-Mobile Ready • All IPv6 LANs / Subnets are IPv6 Mobile Ready ...
... • IPv6 Mobility is based on core features of IPv6 – The base IPv6 was designed to support Mobility – Mobility is not an “Add-on” features • All IPv6 Networks are IPv6-Mobile Ready • All IPv6 nodes are IPv6-Mobile Ready • All IPv6 LANs / Subnets are IPv6 Mobile Ready ...
Chapter6 (Delivery, Forwarding, and Routing of IP Packets)
... U (Up) : indicating the router’s running G (Gateway) : meaning that the destination is another network H (Host-specific) : indicating that the entry in the destination is a host-specific address D (Added by redirection) : indicating that routing information for this destination has been added to the ...
... U (Up) : indicating the router’s running G (Gateway) : meaning that the destination is another network H (Host-specific) : indicating that the entry in the destination is a host-specific address D (Added by redirection) : indicating that routing information for this destination has been added to the ...
The Network Layer - London South Bank University
... a) RIP is based on distance vector routing, which uses the BellmanFord algorithm for calculating the routing table. b) RIP treats all network equals; the cost of passing thru a network is the same: one hop count per network. c) Each router/node maintains a vector (table) of minimum distances to ever ...
... a) RIP is based on distance vector routing, which uses the BellmanFord algorithm for calculating the routing table. b) RIP treats all network equals; the cost of passing thru a network is the same: one hop count per network. c) Each router/node maintains a vector (table) of minimum distances to ever ...
Link Layer - Gordon College
... PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) Old-fashioned Ethernet 802.11 wireless LAN ...
... PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) Old-fashioned Ethernet 802.11 wireless LAN ...