Elementary Data Structures
... Insertions are at the rear of the queue and removals are at the front of the queue ...
... Insertions are at the rear of the queue and removals are at the front of the queue ...
Retrieval2
... •Sometimes they don’t even do insertions immediately! •Instead they keep a log with all deletions (and additions), and periodically (i.e., every night, weekend), the log is traversed to update the database. The technique is called Differential Databases. •Deleting cases is part of the general proble ...
... •Sometimes they don’t even do insertions immediately! •Instead they keep a log with all deletions (and additions), and periodically (i.e., every night, weekend), the log is traversed to update the database. The technique is called Differential Databases. •Deleting cases is part of the general proble ...
1 Elementary Data Structures The Stack ADT (§4.2.1) Applications of
... Auxiliary data structure for algorithms Component of other data structures Elementary Data Structures ...
... Auxiliary data structure for algorithms Component of other data structures Elementary Data Structures ...
TREES - Simpson College
... the bits in the keys If we have larger keys – the height increases. One way to overcome this deficiency is using a multiway radix tree searching. The branching is not according to 1 bit, but rather according to several bits (most often 2) If m bits are examined at a time – the search is speede ...
... the bits in the keys If we have larger keys – the height increases. One way to overcome this deficiency is using a multiway radix tree searching. The branching is not according to 1 bit, but rather according to several bits (most often 2) If m bits are examined at a time – the search is speede ...
Algorithm Design CS 515 Fall 2014 Sample Midterm Questions – Solutions
... • Delete(x): delete key x from the structure if it is there. • Next(x): return a pointer to the smallest key in the structure that is larger than x (or a NIL pointer if x is the largest key in the structure). You may refer to structures and algorithms we have described in class in describing Insert ...
... • Delete(x): delete key x from the structure if it is there. • Next(x): return a pointer to the smallest key in the structure that is larger than x (or a NIL pointer if x is the largest key in the structure). You may refer to structures and algorithms we have described in class in describing Insert ...
Tree Introduction
... Binary Tree Application: Animal Game • Purpose: guess an animal using a sequence of questions – Internal nodes contain yes/no questions – Leaf nodes are animals – Initially, tree contains a single animal (e.g., a “cat”) stored in the root node 1. Start at root. 2. If internal node ask yes/no ques ...
... Binary Tree Application: Animal Game • Purpose: guess an animal using a sequence of questions – Internal nodes contain yes/no questions – Leaf nodes are animals – Initially, tree contains a single animal (e.g., a “cat”) stored in the root node 1. Start at root. 2. If internal node ask yes/no ques ...
SCSX1005_SEMIII_DS
... In linked representation of binary trees, instead of arrays, pointers are used to connect the various nodes of the tree. Hence each node of the binary tree consists of three parts namely, the info, left and right. The info part stores the data, left part stores the address of the left child and the ...
... In linked representation of binary trees, instead of arrays, pointers are used to connect the various nodes of the tree. Hence each node of the binary tree consists of three parts namely, the info, left and right. The info part stores the data, left part stores the address of the left child and the ...
Pclec06
... The major disadvantage of hash organisation is that sequential organisation is not convenient because the records are not stored in primary key sequence. But highly concurrent environments doing random access are suitable for using hash organisation. The basis of a hash file is an addressing algorit ...
... The major disadvantage of hash organisation is that sequential organisation is not convenient because the records are not stored in primary key sequence. But highly concurrent environments doing random access are suitable for using hash organisation. The basis of a hash file is an addressing algorit ...
Trees
... A tree is a connected undirected graph with no simple circuits A tree is a connected graph with n-1 edges ...
... A tree is a connected undirected graph with no simple circuits A tree is a connected graph with n-1 edges ...
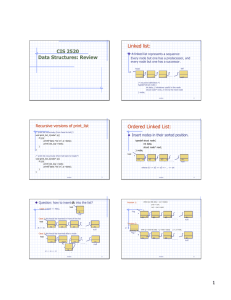
CIS 2520 Data Structures: Review Linked list: Ordered Linked List:
... z with the larger height, and let x be the child of y with the larger height. To rebalance the subtree rooted at z, we must perform a restructuring ...
... z with the larger height, and let x be the child of y with the larger height. To rebalance the subtree rooted at z, we must perform a restructuring ...
Index Structures for Files Multi-Level Indexes Multi
... It is hard to think of a major general-purpose file system that is not built around B-tree design They were invented by two researchers at Boeing, R. Bayer and E. McCreight in 1972 ...
... It is hard to think of a major general-purpose file system that is not built around B-tree design They were invented by two researchers at Boeing, R. Bayer and E. McCreight in 1972 ...
Tree - UMass CS !EdLab
... public Object getData(); //returns the data element at this node. public void setData(Object myElement); //sets data element to myElement public void setLeftChild(BinaryNodeInterface myLeft); //set left child to myLeft public void setRightChild(BinaryNodeInterface myRight); //set right child to myRi ...
... public Object getData(); //returns the data element at this node. public void setData(Object myElement); //sets data element to myElement public void setLeftChild(BinaryNodeInterface myLeft); //set left child to myLeft public void setRightChild(BinaryNodeInterface myRight); //set right child to myRi ...
B-tree
In computer science, a B-tree is a tree data structure that keeps data sorted and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree is a generalization of a binary search tree in that a node can have more than two children (Comer 1979, p. 123). Unlike self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data. B-trees are a good example of a data structure for external memory. It is commonly used in databases and filesystems.