CSE 326: Data Structures Lecture #7 Branching Out
... • Each node has (up to) M-1 keys: – subtree between two keys x and y contains leaves with values v such that 3 7 12 21 xv
... • Each node has (up to) M-1 keys: – subtree between two keys x and y contains leaves with values v such that 3 7 12 21 xv
Basic Tree Terminologies, their Representation and
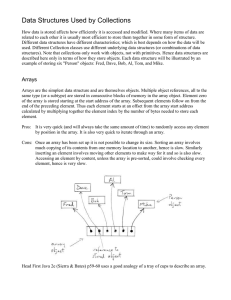
... LPTR – pointing to the left child node RPTR – pointing to the right child node INFO – actual value In linked representation, a node has two pointers fields and one information field. Each of pointer field contains the address of left or right child node. An information field contains the actual data ...
... LPTR – pointing to the left child node RPTR – pointing to the right child node INFO – actual value In linked representation, a node has two pointers fields and one information field. Each of pointer field contains the address of left or right child node. An information field contains the actual data ...
Chapter08
... WHILE (deck not empty) Pop the deckStack Check for Aces While (There are playStacks to check) If(can place card) Push card onto playStack Else push card onto usedStack Does implementation matter at this point? ...
... WHILE (deck not empty) Pop the deckStack Check for Aces While (There are playStacks to check) If(can place card) Push card onto playStack Else push card onto usedStack Does implementation matter at this point? ...
Red-Black tree
... memory. However, remember word size and memory. Note this works both ways: a single bit could mean the incursion of an extra cost. However, a node may well have excess space because it doesn't take up a full word size and so no cost to store the extra bit. ...
... memory. However, remember word size and memory. Note this works both ways: a single bit could mean the incursion of an extra cost. However, a node may well have excess space because it doesn't take up a full word size and so no cost to store the extra bit. ...
Bulk-Loading the ND-Tree in Non-ordered Discrete Data Spaces, Best Paper Award, 13th International Conference, DASFAA 2008 (pp. 156-172), New Delhi, India, Hyun-Jeon Seik, Gang Qian, Qiang Zhu, Alexander R. Oswald and Sakti Pramanik.
... ND-tree, which utilizes special properties of an NDDS, was proposed recently to support efficient similarity queries in NDDSs [16,18]. A conventional tupleloading (TL) algorithm was introduced to load vectors/tuples into the tree one by one. However, such a TL method may take too long when building an ...
... ND-tree, which utilizes special properties of an NDDS, was proposed recently to support efficient similarity queries in NDDSs [16,18]. A conventional tupleloading (TL) algorithm was introduced to load vectors/tuples into the tree one by one. However, such a TL method may take too long when building an ...
Binary trees
... deque, or throw an Overflow exception if the deque is full. pushRight(c): add character c as the right-most character in the deque, or throw an Overflow exception if the deque is full. peekLeft(): return the left-most character in the deque, or throw an Underflow exception if the deque is empty. pee ...
... deque, or throw an Overflow exception if the deque is full. pushRight(c): add character c as the right-most character in the deque, or throw an Overflow exception if the deque is full. peekLeft(): return the left-most character in the deque, or throw an Underflow exception if the deque is empty. pee ...
Trees
... These have many applications, some of which we will discuss. The most obvious is storing hierarchical structures, such as genealogies, file structures, and organizational structures. The root (which corresponds to a single data element) is at the top, and the branches are arranged below the root and ...
... These have many applications, some of which we will discuss. The most obvious is storing hierarchical structures, such as genealogies, file structures, and organizational structures. The root (which corresponds to a single data element) is at the top, and the branches are arranged below the root and ...
First-Solutions - Philadelphia University Jordan
... C) If the following elements are inserted to the data structure in this order (15, 20, 77, 60 and 40) these elements should be stored in the data structure in the following order (15, 20, 40, 60 and 77) knowing that it is a linear data structure. Ordered list D) If the following elements are inserte ...
... C) If the following elements are inserted to the data structure in this order (15, 20, 77, 60 and 40) these elements should be stored in the data structure in the following order (15, 20, 40, 60 and 77) knowing that it is a linear data structure. Ordered list D) If the following elements are inserte ...
Binary Search Trees
... The binary-search-tree property allows us to print out all the keys in a binary search tree in sorted order by a simple recursive algorithm, called an inorder tree walk. This algorithm is so named because the key of the root of a subtree is printed between the values in its left subtree and those ...
... The binary-search-tree property allows us to print out all the keys in a binary search tree in sorted order by a simple recursive algorithm, called an inorder tree walk. This algorithm is so named because the key of the root of a subtree is printed between the values in its left subtree and those ...
Lecture 8 Data Structures (DAT037)
... 3. We can recreate a tree from only one of the traversals 4. We can’t recreate a tree from any combinaKon of two traversals ...
... 3. We can recreate a tree from only one of the traversals 4. We can’t recreate a tree from any combinaKon of two traversals ...
I/O-E cient Dynamic Point Location in Monotone Planar Subdivisions
... in O((log N ) log log N ) time (worst-case), insertions in O((log N ) log log N ) time (amortized), and deletions in O(log2 N ) time (amortized). Both structures store the edges of the subdivision in an interval tree [13] constructed on their x-projection (as rst suggested in [15]) and use this str ...
... in O((log N ) log log N ) time (worst-case), insertions in O((log N ) log log N ) time (amortized), and deletions in O(log2 N ) time (amortized). Both structures store the edges of the subdivision in an interval tree [13] constructed on their x-projection (as rst suggested in [15]) and use this str ...
B-tree
In computer science, a B-tree is a tree data structure that keeps data sorted and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree is a generalization of a binary search tree in that a node can have more than two children (Comer 1979, p. 123). Unlike self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data. B-trees are a good example of a data structure for external memory. It is commonly used in databases and filesystems.