DS-T2 - PESIT South
... queue has same method but with a major difference. In Priority queue items are ordered by key value so that item with the lowest value of key is at front and item with the highest value of key is at rear or vice versa. So we're assigned priority to item based on its key value. Lower the value, highe ...
... queue has same method but with a major difference. In Priority queue items are ordered by key value so that item with the lowest value of key is at front and item with the highest value of key is at rear or vice versa. So we're assigned priority to item based on its key value. Lower the value, highe ...
Tree: A New Overlay with Deterministic Bounds
... solutions are either heuristics, or provide expected bounds under certain assumptions, or amortized bounds but at the expense of increasing the memory size per node. In particular, in BATON [13], a decentralized overlay is provided with load balancing based on data migration. However, their O(log n) ...
... solutions are either heuristics, or provide expected bounds under certain assumptions, or amortized bounds but at the expense of increasing the memory size per node. In particular, in BATON [13], a decentralized overlay is provided with load balancing based on data migration. However, their O(log n) ...
MS.BHUMIKA PATEL
... (A) Write a program to create an array for 10 numbers where the value for 10 numbers are given by user and find out average of element in array. Display like: Average of 10 numbers=/10=.
[NOTE: Create User define function for calculate average]
(B) Write a program to create an array for ...
... (A) Write a program to create an array for 10 numbers where the value for 10 numbers are given by user and find out average of element in array. Display like: Average of 10 numbers=
Ternary Tree Optimalization for n-gram Indexing - CEUR
... To search words “AB AC AB” is necessary to find first word in first part of data structure named word tree. When the first word is found, reference to the second part of the data structure n-gram tree is stored. Then the second word “AC” is found in the word tree with result 3. The stored root index ...
... To search words “AB AC AB” is necessary to find first word in first part of data structure named word tree. When the first word is found, reference to the second part of the data structure n-gram tree is stored. Then the second word “AC” is found in the word tree with result 3. The stored root index ...
Balanced Binary Search Trees
... • Each node stores its height. This is inherently a DATA STRUCTURE AUGMENTATION procedure, similar to augmenting subtree size. Alternatively, one can just store dif ference in heights. A good animation applet for AVL trees is available at this link. To compare Binary Search Trees and AVL balancing ...
... • Each node stores its height. This is inherently a DATA STRUCTURE AUGMENTATION procedure, similar to augmenting subtree size. Alternatively, one can just store dif ference in heights. A good animation applet for AVL trees is available at this link. To compare Binary Search Trees and AVL balancing ...
Accountable systems or how to catch a liar?
... Accountable systems or how to catch a liar? Jinyang Li (with slides from authors of SUNDR and PeerReview) ...
... Accountable systems or how to catch a liar? Jinyang Li (with slides from authors of SUNDR and PeerReview) ...
k - Current students
... insertions and removals. This can be accomplished with a data structure called a heap, which enables to perform both insertions and removals in logarithmic time. The idea is to store the elements in a binary tree instead of a sequence. ...
... insertions and removals. This can be accomplished with a data structure called a heap, which enables to perform both insertions and removals in logarithmic time. The idea is to store the elements in a binary tree instead of a sequence. ...
CSCI 210 Data Structures & Algorithms
... Can use const if array elements are not to be modified, e.g. int findmax ( const int x [ ] , int size ); Do not include the array size within the brackets when defining an array parameter. This is because the array name is the base address of the array, and the size is already ...
... Can use const if array elements are not to be modified, e.g. int findmax ( const int x [ ] , int size ); Do not include the array size within the brackets when defining an array parameter. This is because the array name is the base address of the array, and the size is already ...
Q2,3 Sample Solutions
... (a) [4 marks] The idea is to use the algorithm to find the median in deterministic linear time (CLRS, Sec. 9.3) to find the median of the given set of numbers. In linear time, using the median as the “pivot” the set can be partitioned into three groups (=, < and >) of numbers that are equal to, less ...
... (a) [4 marks] The idea is to use the algorithm to find the median in deterministic linear time (CLRS, Sec. 9.3) to find the median of the given set of numbers. In linear time, using the median as the “pivot” the set can be partitioned into three groups (=, < and >) of numbers that are equal to, less ...
CS-240 Data Structures
... max heap - item stored in each node has a key/priority that is >= the priority of the items stored in each of its children min heap - item stored in each node has a key/priority that is <= the priority of the items stored in each of its children ...
... max heap - item stored in each node has a key/priority that is >= the priority of the items stored in each of its children min heap - item stored in each node has a key/priority that is <= the priority of the items stored in each of its children ...
Trees - Intro - Dr. Manal Helal Moodle Site
... Exercise: Perform each of the reverse depth-first traversals on the tree: ...
... Exercise: Perform each of the reverse depth-first traversals on the tree: ...
Chapter 9
... many types of balanced binary search trees that guarantee a worst case search / insert / delete time of O(log n). An AVL tree is a binary search tree in which the heights of the left and right subtrees of every node differ by at most 1. Recursive definition: An AVL tree is a binary search tree in wh ...
... many types of balanced binary search trees that guarantee a worst case search / insert / delete time of O(log n). An AVL tree is a binary search tree in which the heights of the left and right subtrees of every node differ by at most 1. Recursive definition: An AVL tree is a binary search tree in wh ...
Spatial Data Structures
... root node. Root node has two entries unless it is a leaf node. • R-tree is not unique, rectangles depend on how objects are inserted and deleted from the tree. • Problem is that to find some object you might have to go through several rectangles or whole database. Snehal Thakkar ...
... root node. Root node has two entries unless it is a leaf node. • R-tree is not unique, rectangles depend on how objects are inserted and deleted from the tree. • Problem is that to find some object you might have to go through several rectangles or whole database. Snehal Thakkar ...
EE2204 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHM
... 2.1 .1 Implementation of List ADT 1. Array Implementation 2. Linked List Implementation 3. Cursor Implementation. Array Implementation of List Array is a collection of specific number of data stored in a consecutive memory locations. * Insertion and Deletion operation are expensive as it requires mo ...
... 2.1 .1 Implementation of List ADT 1. Array Implementation 2. Linked List Implementation 3. Cursor Implementation. Array Implementation of List Array is a collection of specific number of data stored in a consecutive memory locations. * Insertion and Deletion operation are expensive as it requires mo ...
Chapter 10-11 File Systems
... disk I/O is done in units of blocks blocks are all the same size disks have no external fragmentation blocks may have internal fragmentation packing data into blocks -- may eliminate internal (block) fragmentation but may make data more difficult to locate packing data into bytes – unrelated to curr ...
... disk I/O is done in units of blocks blocks are all the same size disks have no external fragmentation blocks may have internal fragmentation packing data into blocks -- may eliminate internal (block) fragmentation but may make data more difficult to locate packing data into bytes – unrelated to curr ...
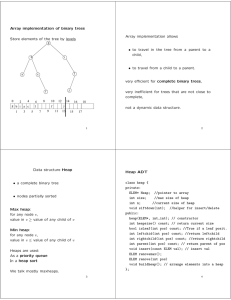
csci 210: Data Structures Priority Queues and Heaps
... • Priorities are not necessarily unique: there can be several elements with same priority • Examples: store a collection of company records • compare by number of employees • compare by earnings • The priority is not necessarily a field in the object itself. It can be a function computed based on th ...
... • Priorities are not necessarily unique: there can be several elements with same priority • Examples: store a collection of company records • compare by number of employees • compare by earnings • The priority is not necessarily a field in the object itself. It can be a function computed based on th ...
B-tree
In computer science, a B-tree is a tree data structure that keeps data sorted and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree is a generalization of a binary search tree in that a node can have more than two children (Comer 1979, p. 123). Unlike self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data. B-trees are a good example of a data structure for external memory. It is commonly used in databases and filesystems.