TITLE BYLINE Synonym Definition Discussion
... rounds. The cost of this pipelined broadcast algorithms is (N +p−2)(α+ Nn )β. Minimizing this yields a best possible cost of XXX Likewise the fixed degree balanced binary tree and Fibonacci tree can be pipelined. Upon receiving a new block each not in a fixed sequence sends this block to its childre ...
... rounds. The cost of this pipelined broadcast algorithms is (N +p−2)(α+ Nn )β. Minimizing this yields a best possible cost of XXX Likewise the fixed degree balanced binary tree and Fibonacci tree can be pipelined. Upon receiving a new block each not in a fixed sequence sends this block to its childre ...
iterators
... index i that keeps track of the cursor doubly-linked list L storing the elements, with sentinels for header and trailer pointer p to node containing the last element returned (or the header if this is a new iterator). ...
... index i that keeps track of the cursor doubly-linked list L storing the elements, with sentinels for header and trailer pointer p to node containing the last element returned (or the header if this is a new iterator). ...
Data Structures: Lists
... requires: list L is not empty. input: none results: the current element is removed from the list. If the resulting list is empty current is set to NULL. If successor of the deleted element exists it is made the new current element otherwise first element is made the new current element. output: none ...
... requires: list L is not empty. input: none results: the current element is removed from the list. If the resulting list is empty current is set to NULL. If successor of the deleted element exists it is made the new current element otherwise first element is made the new current element. output: none ...
1 of 5
... New nodes can be added and removed only at the top Similar to a pile of dishes Last-in, first-out (LIFO) Bottom of stack indicated by a link member to NULL Constrained version of a linked list Adds a new node to the top of the stack ...
... New nodes can be added and removed only at the top Similar to a pile of dishes Last-in, first-out (LIFO) Bottom of stack indicated by a link member to NULL Constrained version of a linked list Adds a new node to the top of the stack ...
Keyword Search On Spatial Databases
... node splitting. We modify the standard AdjustTree method to also maintain the signatures of the modified nodes. That is, if a new bit is set to 1 in a node N, then it must be also set to 1 for N’s ancestors. Finally, we assume that all tree related algorithms have implicit access to the root node of ...
... node splitting. We modify the standard AdjustTree method to also maintain the signatures of the modified nodes. That is, if a new bit is set to 1 in a node N, then it must be also set to 1 for N’s ancestors. Finally, we assume that all tree related algorithms have implicit access to the root node of ...
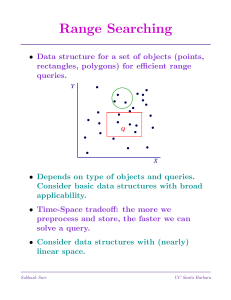
Range Searching
... • Next, each canonical set is searched using the y-tree for range [ylo, yhi]. We locate ylo; then read off points until yhi reached. • Since each set is searched for the same key, ylo, we can improve the search to O(1) per set. • In effect, we do the first search in O(log n) time, but then use that ...
... • Next, each canonical set is searched using the y-tree for range [ylo, yhi]. We locate ylo; then read off points until yhi reached. • Since each set is searched for the same key, ylo, we can improve the search to O(1) per set. • In effect, we do the first search in O(log n) time, but then use that ...
ViST: A Dynamic Index Method for Querying XML Data by Tree
... /A[B/C]/B/D, the two nodes under the branch are the same: B. In this case, the tree isomorphism problem can not be avoided by enforcing sibling orders, since the two nodes are identical. As a result, the preorder sequences of XML data trees that contain such a branch can have two possible forms. In ...
... /A[B/C]/B/D, the two nodes under the branch are the same: B. In this case, the tree isomorphism problem can not be avoided by enforcing sibling orders, since the two nodes are identical. As a result, the preorder sequences of XML data trees that contain such a branch can have two possible forms. In ...
Singly-linked List
... If data is entered in sorted order, the tree becomes a list. This degeneration loses the O(log2 n) behaviour. How can we get around this? ...
... If data is entered in sorted order, the tree becomes a list. This degeneration loses the O(log2 n) behaviour. How can we get around this? ...
09_Lecture
... Let P be a set of points in the plane stored in a 2-dim range tree and let a 2-dim range R defined by the two intervals [x, x‘], [y, y‘] be given. The all k points of P falling into the range R can be reported as follows: 1. Determine the O(log n) umbrella nodes for the range [x, x‘], i.e. determine ...
... Let P be a set of points in the plane stored in a 2-dim range tree and let a 2-dim range R defined by the two intervals [x, x‘], [y, y‘] be given. The all k points of P falling into the range R can be reported as follows: 1. Determine the O(log n) umbrella nodes for the range [x, x‘], i.e. determine ...
B-tree
In computer science, a B-tree is a tree data structure that keeps data sorted and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree is a generalization of a binary search tree in that a node can have more than two children (Comer 1979, p. 123). Unlike self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data. B-trees are a good example of a data structure for external memory. It is commonly used in databases and filesystems.