The HV-tree: a Memory Hierarchy Aware Version Index
... at an unprecedented speed, the existing structures are no longer capable of handling the data in terms of both scalability and efficiency. Wal-Mart’s data warehouse was 70 terabytes in 2001 [19], and it became over 1,000 Terabytes in 2007. The Sloan Digital Sky Survey project [1] captures images tha ...
... at an unprecedented speed, the existing structures are no longer capable of handling the data in terms of both scalability and efficiency. Wal-Mart’s data warehouse was 70 terabytes in 2001 [19], and it became over 1,000 Terabytes in 2007. The Sloan Digital Sky Survey project [1] captures images tha ...
PPT - WSU EECS - Washington State University
... than on the special cases. We distinguish between the is-a relationship and the has-a relationship. The is-a relationship represents inheritance. ...
... than on the special cases. We distinguish between the is-a relationship and the has-a relationship. The is-a relationship represents inheritance. ...
Document
... record in the file. Frequently, one wants to find all the records whose values in a certain attribute (which is not the searchkey of the primary index) satisfy some condition. Example 1: In the account database stored sequentially by account number, we may want to find all accounts in a ...
... record in the file. Frequently, one wants to find all the records whose values in a certain attribute (which is not the searchkey of the primary index) satisfy some condition. Example 1: In the account database stored sequentially by account number, we may want to find all accounts in a ...
7. Full-Text Indexes in External Memory
... particular, they introduce two index structures for two and three level memory hierarchy (that use main memory and one/two levels of external storage), and present experimental and analytical results for these. These additional index structures are much smaller in terms of space compared to the text ...
... particular, they introduce two index structures for two and three level memory hierarchy (that use main memory and one/two levels of external storage), and present experimental and analytical results for these. These additional index structures are much smaller in terms of space compared to the text ...
child
... Consider the set of formulas from variables x1, x2, ..., xn and operators ^, V and ~ The value of a variable is either TRUE or FALSE. The expression is defined as : (1) A variable is an expression (2) If x and y are expressions, then ~x, x^y, x v y are expressions (3) Parenthesis can be used to alte ...
... Consider the set of formulas from variables x1, x2, ..., xn and operators ^, V and ~ The value of a variable is either TRUE or FALSE. The expression is defined as : (1) A variable is an expression (2) If x and y are expressions, then ~x, x^y, x v y are expressions (3) Parenthesis can be used to alte ...
Spatial data structures: Octrees and kD
... Octree Node Data Structure • What needs to be stored in a node? – Children pointers (at most eight) – Parent pointer - useful for moving about the tree – Extents of cube - can be inferred from tree structure, but easier to just store it – List of pointers to the contents of the cube • Contents migh ...
... Octree Node Data Structure • What needs to be stored in a node? – Children pointers (at most eight) – Parent pointer - useful for moving about the tree – Extents of cube - can be inferred from tree structure, but easier to just store it – List of pointers to the contents of the cube • Contents migh ...
document
... – Sometimes data are inserted into a data structure but there is no available space. – This situation is called overflow – Example: In linked list overflow occurs when • AVAIL= NULL and • There is an insertion operation Underflow: – Situation: • Want to delete data from data structure that is empty. ...
... – Sometimes data are inserted into a data structure but there is no available space. – This situation is called overflow – Example: In linked list overflow occurs when • AVAIL= NULL and • There is an insertion operation Underflow: – Situation: • Want to delete data from data structure that is empty. ...
Cache-Oblivious Priority Queue and Graph Algorithm Applications
... – We have touched all cells within distance r from q. Thus, if there is a point within distance r from q, we already found it – If there is no such point, then the p’ provides a (1+eps)approximate solution • Running time: – All cells C seen so far (except maybe for the last one) have diameter > eps* ...
... – We have touched all cells within distance r from q. Thus, if there is a point within distance r from q, we already found it – If there is no such point, then the p’ provides a (1+eps)approximate solution • Running time: – All cells C seen so far (except maybe for the last one) have diameter > eps* ...
ppt
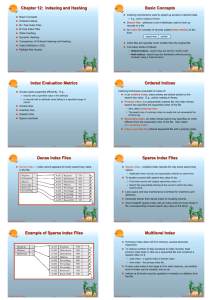
... Dense indices – deletion of search-key is similar to file record deletion. Sparse indices – if an entry for the search key exists in the index, it is deleted by replacing the entry in the index with the next searchkey value in the file (in search-key order). If the next search-key value already ...
... Dense indices – deletion of search-key is similar to file record deletion. Sparse indices – if an entry for the search key exists in the index, it is deleted by replacing the entry in the index with the next searchkey value in the file (in search-key order). If the next search-key value already ...
Example of Sparse Index Files
... " Dense indices – if the search-key value does not appear in the ...
... " Dense indices – if the search-key value does not appear in the ...
Indexing and Hashing
... Dense Index Files ! Dense index — Index record appears for every search-key value ...
... Dense Index Files ! Dense index — Index record appears for every search-key value ...
B-tree
In computer science, a B-tree is a tree data structure that keeps data sorted and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree is a generalization of a binary search tree in that a node can have more than two children (Comer 1979, p. 123). Unlike self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data. B-trees are a good example of a data structure for external memory. It is commonly used in databases and filesystems.