Dynamic FM-Index for a Collection of Texts with
... Sequence-based indices allow to search efficiently for any substring within the text. Classical examples of such sequence-based indices are the suffix tree and the suffix array. The problem with these indices is that they require space several times the text size in addition to the text itself. Thus ...
... Sequence-based indices allow to search efficiently for any substring within the text. Classical examples of such sequence-based indices are the suffix tree and the suffix array. The problem with these indices is that they require space several times the text size in addition to the text itself. Thus ...
pq - Green Cedars
... •Definition: a heap is a complete binary tree, represented as an array, in which every node satisfies the heap condition. The largest key is the 1st position of the array. Recall that a complete binary tree is constructed by placing one node (the root) and proceeding down the page and from left to r ...
... •Definition: a heap is a complete binary tree, represented as an array, in which every node satisfies the heap condition. The largest key is the 1st position of the array. Recall that a complete binary tree is constructed by placing one node (the root) and proceeding down the page and from left to r ...
space-efficient data structures for collections of textual data
... compressed form) a “semi-index”: a succinct data structure that supports operations on the document tree at speed comparable with an in-memory deserialized object. After describing the general technique, we focus on the JSON format: our experiments show that avoiding the full loading and parsing ste ...
... compressed form) a “semi-index”: a succinct data structure that supports operations on the document tree at speed comparable with an in-memory deserialized object. After describing the general technique, we focus on the JSON format: our experiments show that avoiding the full loading and parsing ste ...
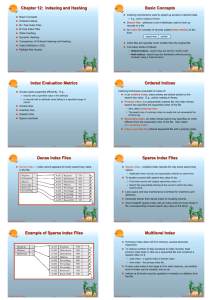
Example of Sparse Index Files
... and the entries in the node and a sibling fit into a single node, then " Redistribute the pointers between the node and a sibling such that both have more than the minimum number of entries. ...
... and the entries in the node and a sibling fit into a single node, then " Redistribute the pointers between the node and a sibling such that both have more than the minimum number of entries. ...
ppt
... Redistribute the pointers between the node and a sibling such that both have more than the minimum number of entries. ...
... Redistribute the pointers between the node and a sibling such that both have more than the minimum number of entries. ...
Pointers and Linked Lists
... The constant NULL is actually the number 0, but we prefer to think of it and spell it as NULL. That makes it clear that you mean this special-purpose value that you can assign to pointer variables. The definition of the identifier NULL is in a number of the standard libraries, such as and ...
... The constant NULL is actually the number 0, but we prefer to think of it and spell it as NULL. That makes it clear that you mean this special-purpose value that you can assign to pointer variables. The definition of the identifier NULL is in a number of the standard libraries, such as