External Memory Techniques for Isosurface Extraction in Scientific
... simpler and more space-efficient in practice (where the corner structure is not implemented, which may result in non-optimal I/O cost for the stabbing queries in the worst case). Rather than fetching only the active cells into main memory as in I/O-filter [8, 9], this method fetches the set of activ ...
... simpler and more space-efficient in practice (where the corner structure is not implemented, which may result in non-optimal I/O cost for the stabbing queries in the worst case). Rather than fetching only the active cells into main memory as in I/O-filter [8, 9], this method fetches the set of activ ...
linked lists in python - KSU Web Home
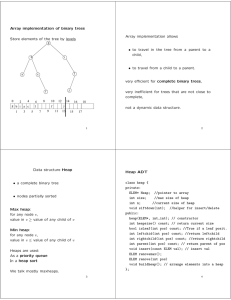
... items, each of which is stored in a node. Each node in a stack includes a data block and one or more links. A stack has only one end: the top of the stack. The main characteristics of a stack are: • Nodes can only be inserted at the top of the stack (TOS) • Nodes can only be removed from the top of ...
... items, each of which is stored in a node. Each node in a stack includes a data block and one or more links. A stack has only one end: the top of the stack. The main characteristics of a stack are: • Nodes can only be inserted at the top of the stack (TOS) • Nodes can only be removed from the top of ...
Indexing Mixed Types for Approximate Retrieval
... tree for the string collection is to use their q-grams. Given a string s and an integer q, the set of q-grams of s, denoted Gq (s), is obtained by sliding a window of length q from left to right over the characters of string s. If the number of remaining characters in the window is smaller than q, w ...
... tree for the string collection is to use their q-grams. Given a string s and an integer q, the set of q-grams of s, denoted Gq (s), is obtained by sliding a window of length q from left to right over the characters of string s. If the number of remaining characters in the window is smaller than q, w ...
Linked List - MHS Comp Sci
... The actual implementation of which is left to the specific data structure As for the Iterator and ListIterator Interfaces, we will discuss these shortly The List Interface requires you implement a Size and an Add Behavior ...
... The actual implementation of which is left to the specific data structure As for the Iterator and ListIterator Interfaces, we will discuss these shortly The List Interface requires you implement a Size and an Add Behavior ...