A Fast Contention-Friendly Binary Search Tree
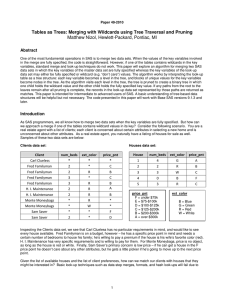
... Removing such a node is likely to cause much more contention than removing a less frequently accessed one. In order to prevent this, only nodes that are marked as deleted and have at least one of their children as an empty subtree are removed. Marked deleted nodes can ...
... Removing such a node is likely to cause much more contention than removing a less frequently accessed one. In order to prevent this, only nodes that are marked as deleted and have at least one of their children as an empty subtree are removed. Marked deleted nodes can ...
Chapter2
... Let n be the number of elements in the stack The space used is O(n) Each operation runs in time O(1) ...
... Let n be the number of elements in the stack The space used is O(n) Each operation runs in time O(1) ...
Fundamental Data Structures
... become its parent. This way we can build up a hierarchy of nodes of any depth. It is never possible to add a parent node because the constraint that each node has at most one parent would be violated. The node manipulation is usually relative to the current node. We can modify or remove the current ...
... become its parent. This way we can build up a hierarchy of nodes of any depth. It is never possible to add a parent node because the constraint that each node has at most one parent would be violated. The node manipulation is usually relative to the current node. We can modify or remove the current ...
Functional Pearl Trouble Shared is Trouble Halved
... Before we tackle optimal bracketing, let us first look at a related but simpler problem, in which each recursive call depends only on the immediate segments. ...
... Before we tackle optimal bracketing, let us first look at a related but simpler problem, in which each recursive call depends only on the immediate segments. ...
Geometric Data Structures
... and the remainder is partitioned into 2 equal sets. – The 2 sets are partitioned into sets above & below – Construct the tree recursively ...
... and the remainder is partitioned into 2 equal sets. – The 2 sets are partitioned into sets above & below – Construct the tree recursively ...
Advanced Data Structure
... Case II : Removing a node with a single child Replace the removed node with its child Case III : Removing a node with 2 children Replace the removed node with the minimum element in the right subtree (or maximum element in the left subtree) This may create a hole again Apply Case I or II Som ...
... Case II : Removing a node with a single child Replace the removed node with its child Case III : Removing a node with 2 children Replace the removed node with the minimum element in the right subtree (or maximum element in the left subtree) This may create a hole again Apply Case I or II Som ...
Efficient Differential Timeslice Computation
... simply computing either incrementalTimeslice or decrementalTimeslice is more efficient than computing differentialTimeslice. Rather, the solution should require only a few disk accesses. Also observe that using the temporal proximity among the three times tx−1 , tx , and tx+1 as the basis for comput ...
... simply computing either incrementalTimeslice or decrementalTimeslice is more efficient than computing differentialTimeslice. Rather, the solution should require only a few disk accesses. Also observe that using the temporal proximity among the three times tx−1 , tx , and tx+1 as the basis for comput ...
TITLE BYLINE Synonym Definition Discussion
... Assuming that x is divisible, and that x can be sent in N blocks of size n/N (assuming for simplicity that N divides n) better performance can be achieved. By pipelining through the path, such that the blocks are sent one after another, the root is busy for N consecutive rounds. The ith processor, i ...
... Assuming that x is divisible, and that x can be sent in N blocks of size n/N (assuming for simplicity that N divides n) better performance can be achieved. By pipelining through the path, such that the blocks are sent one after another, the root is busy for N consecutive rounds. The ith processor, i ...