MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS 1 Matrix Transformations
... some portion of a cone. The angle of rotation, which is measured in the base of the cone, is described as ‘clockwise’ or ‘anti-clockwise’ in relation to a viewpoint that is along the axis of rotation looking towards the origin. y ...
... some portion of a cone. The angle of rotation, which is measured in the base of the cone, is described as ‘clockwise’ or ‘anti-clockwise’ in relation to a viewpoint that is along the axis of rotation looking towards the origin. y ...
Theorem: (Fisher`s Inequality, 1940) If a (v,b,r,k,λ) – BIBD exists with
... efficient (faster and less expensive) to test large groups of these samples together for the attribute. It is desirable to then use the results of these pooled tests to deduce which of the samples had the attribute. Note that a negative result ensures that none of the samples were positive, while a ...
... efficient (faster and less expensive) to test large groups of these samples together for the attribute. It is desirable to then use the results of these pooled tests to deduce which of the samples had the attribute. Note that a negative result ensures that none of the samples were positive, while a ...
Approximating sparse binary matrices in the cut
... Therefore, an approximation up to cut norm 41 · n is trivial in this case, and can be done by one cut ...
... Therefore, an approximation up to cut norm 41 · n is trivial in this case, and can be done by one cut ...
2016 HS Algebra 2 Unit 3 Plan - Matrices
... A. Add, subtract, and multiply matrices. B. Use addition, subtraction, and multiplication of matrices to solve real-world problems. C. Calculate the determinant of 2 x 2 and 3 x 3 matrices. D. Calculate the inverse of a 2 x 2 matrix. E. Solve systems of equations by using inverses and determinants o ...
... A. Add, subtract, and multiply matrices. B. Use addition, subtraction, and multiplication of matrices to solve real-world problems. C. Calculate the determinant of 2 x 2 and 3 x 3 matrices. D. Calculate the inverse of a 2 x 2 matrix. E. Solve systems of equations by using inverses and determinants o ...
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM)
... unique invertible Hermitian matrix J with complex entries such that [x, y] = < x, Jy >, where <. , . > denotes the Euclidean inner product on ℂn , with an additional assumption on J, that is, J2 = I, to present the results with much algebraic ease. Thus an indefinite inner product space is a general ...
... unique invertible Hermitian matrix J with complex entries such that [x, y] = < x, Jy >, where <. , . > denotes the Euclidean inner product on ℂn , with an additional assumption on J, that is, J2 = I, to present the results with much algebraic ease. Thus an indefinite inner product space is a general ...
ABC`s Of Math
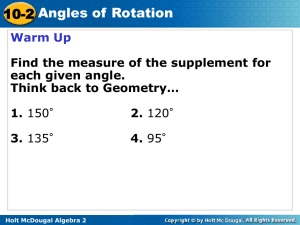
... • Rotation : Is a transformation that turns a line or a shape around a line point . This point is called the center of rotation . Rotation are usually measurement in the counter clockwise directions. • Reflection : Is one kind of transformation. When you hear the word “Reflection” you may think of a ...
... • Rotation : Is a transformation that turns a line or a shape around a line point . This point is called the center of rotation . Rotation are usually measurement in the counter clockwise directions. • Reflection : Is one kind of transformation. When you hear the word “Reflection” you may think of a ...