FALSE MEMORIES False Memories
... In the lost-in-the-mall study, implantation of a false memory occurred when another individual, usually a family member, claimed that the event happened. Corroboration of an event by another person can be a powerful technique for instilling a false memory. In fact, merely claiming to have seen a per ...
... In the lost-in-the-mall study, implantation of a false memory occurred when another individual, usually a family member, claimed that the event happened. Corroboration of an event by another person can be a powerful technique for instilling a false memory. In fact, merely claiming to have seen a per ...
Zhang Yufeng - USD Biology
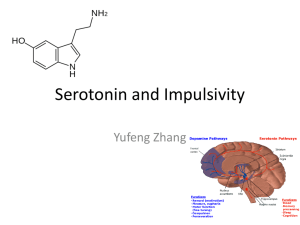
... • Rewards wait error gradually increased, and 5HT neural activity ceased before the rats ceased waiting for possible future rewards • When an expected water reward was suddenly omitted for several continuous trials, 5-HT neural activity also dropped ...
... • Rewards wait error gradually increased, and 5HT neural activity ceased before the rats ceased waiting for possible future rewards • When an expected water reward was suddenly omitted for several continuous trials, 5-HT neural activity also dropped ...
Text - Reading`s CentAUR
... order of the presentation of the blocks was randomized, as was the order of presentation of the scenarios within each block. Participants were reminded of the task instructions between each training block in order to compensate for potential memory difficulties. 2.4.2 Mental Imagery Instructions. Th ...
... order of the presentation of the blocks was randomized, as was the order of presentation of the scenarios within each block. Participants were reminded of the task instructions between each training block in order to compensate for potential memory difficulties. 2.4.2 Mental Imagery Instructions. Th ...
Memory - Home | Quincy College
... • Spacing effect • People tend to remember information longer when they acquire it via distributed practice (i.e., various sessions spaced over time) rather than via massed practice (session crammed together all at once) • A good night’s sleep, which includes plenty of REM stage sleep, aids in memor ...
... • Spacing effect • People tend to remember information longer when they acquire it via distributed practice (i.e., various sessions spaced over time) rather than via massed practice (session crammed together all at once) • A good night’s sleep, which includes plenty of REM stage sleep, aids in memor ...
PSY504 - VU LMS - Virtual University
... The information processing approach, unlike the stimulus-response model of behaviorism, looks at how input is transformed into output. In other words, what happens between sensation and behavior is amore important question for cognitive psychologists than just which sensation produced which behavior ...
... The information processing approach, unlike the stimulus-response model of behaviorism, looks at how input is transformed into output. In other words, what happens between sensation and behavior is amore important question for cognitive psychologists than just which sensation produced which behavior ...
Memory - Macmillan Learning
... our memories define us. Each of us has a unique identity that is intricately tied to the things we have thought, felt, done, and experienced. Memories are the residue of those events, the enduring changes that experience makes in our brains and leaves behind when it passes. If an experience passes w ...
... our memories define us. Each of us has a unique identity that is intricately tied to the things we have thought, felt, done, and experienced. Memories are the residue of those events, the enduring changes that experience makes in our brains and leaves behind when it passes. If an experience passes w ...
Domain-general mechanisms of complex working memory span
... manipulate information in coordination with ongoing processing that is the very hallmark of WM (Baddeley and Hitch, 1974; Miller et al., 1960) and that distinguishes the complex working memory span (CWMS) tasks that yield the strongest correlations with complex cognition from other measures of short ...
... manipulate information in coordination with ongoing processing that is the very hallmark of WM (Baddeley and Hitch, 1974; Miller et al., 1960) and that distinguishes the complex working memory span (CWMS) tasks that yield the strongest correlations with complex cognition from other measures of short ...
Goldstein - Chapter 9
... Caption: These pictures represent images that Kosslyn’s (1978) participants created, which filled different portions of their visual field. (a) Imagine elephant and rabbit, so elephant fills the field. (b) Imagine rabbit and fly, so rabbit fills the field. Reaction times indicate how long it took pa ...
... Caption: These pictures represent images that Kosslyn’s (1978) participants created, which filled different portions of their visual field. (a) Imagine elephant and rabbit, so elephant fills the field. (b) Imagine rabbit and fly, so rabbit fills the field. Reaction times indicate how long it took pa ...
Testing Promotes Long-Term Learning via Stabilizing Activation
... at short retention intervals, it produced significantly higher learning performance than an equal amount of restudying when the retention interval was longer than one day (Wheeler et al. 2003; Karpicke and Roediger 2008; Toppino and Cohen 2009). These results suggest that the efficiency of testing o ...
... at short retention intervals, it produced significantly higher learning performance than an equal amount of restudying when the retention interval was longer than one day (Wheeler et al. 2003; Karpicke and Roediger 2008; Toppino and Cohen 2009). These results suggest that the efficiency of testing o ...
How does imagery in interactive consumption lead to false memory
... the misleading theme emerges due to its relative recency compared to the original theme encountered during consumption. This subjective feeling of familiarity is exacerbated due to elaboration and imagery which should lead to more remember judgments. In particular, the remember judgments should be t ...
... the misleading theme emerges due to its relative recency compared to the original theme encountered during consumption. This subjective feeling of familiarity is exacerbated due to elaboration and imagery which should lead to more remember judgments. In particular, the remember judgments should be t ...
1 A test of the relation between working memory capacity and
... relationship between processing resource capacity and individual differences in the strength of island effects for different island types, as predicted by the capacity-based theory. Sections 4 and 5 present the results of those two studies. Because neither study reveals any evidence of a relationshi ...
... relationship between processing resource capacity and individual differences in the strength of island effects for different island types, as predicted by the capacity-based theory. Sections 4 and 5 present the results of those two studies. Because neither study reveals any evidence of a relationshi ...
Cognitive control - Translational Neuromodeling Unit
... feels intense anxiety and washes his hands until they bleed. wikipedia.org ...
... feels intense anxiety and washes his hands until they bleed. wikipedia.org ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... input system as one of modules, such as sensory systems (Fodor, 1983). In contrast, Chomsky claimed that it is too narrow to regard the ‘language module’ solely as an input system and that it is, rather, a ‘central system’ (Chomsky, 1986), although the central system is not modular in Fodor’s model ...
... input system as one of modules, such as sensory systems (Fodor, 1983). In contrast, Chomsky claimed that it is too narrow to regard the ‘language module’ solely as an input system and that it is, rather, a ‘central system’ (Chomsky, 1986), although the central system is not modular in Fodor’s model ...
An Account of Associative Learning in Memory Recall
... increase, since this does not shed much additional light on distinguishing between the different theories of list recall, we do not focus on it much in this paper. The study’s authors interpret these results as being supportive of an associative account of list learning, as do we. To preview our app ...
... increase, since this does not shed much additional light on distinguishing between the different theories of list recall, we do not focus on it much in this paper. The study’s authors interpret these results as being supportive of an associative account of list learning, as do we. To preview our app ...
Clinical, imaging, lesion, and genetic approaches toward a model of
... circuits. These basal ganglia thalamocortical circuits involve the same general brain regions (basal ganglia, thalamus, and cortex), but differ in projection zones within each of these regions and in the set of behaviors they support. These behaviors range from skeletal and eye movements to cognitiv ...
... circuits. These basal ganglia thalamocortical circuits involve the same general brain regions (basal ganglia, thalamus, and cortex), but differ in projection zones within each of these regions and in the set of behaviors they support. These behaviors range from skeletal and eye movements to cognitiv ...
Cognitive Psychology
... The information processing approach, unlike the stimulus-response model of behaviorism, looks at how input is transformed into output. In other words, what happens between sensation and behavior is amore important question for cognitive psychologists than just which sensation produced which behavior ...
... The information processing approach, unlike the stimulus-response model of behaviorism, looks at how input is transformed into output. In other words, what happens between sensation and behavior is amore important question for cognitive psychologists than just which sensation produced which behavior ...