WHY NEED NETWORKING? NETWORKING NETWORK
... Communications protocols are rules established to govern the way data are transmitted in a computer network. ...
... Communications protocols are rules established to govern the way data are transmitted in a computer network. ...
ppt - Zoo
... autonomous systems organized roughly hierarchical backbone links at 100 Gbps Software: datagram switching with virtual circuit support at backbone layered network architecture • use end-to-end arguments to determine the services provided by each layer ...
... autonomous systems organized roughly hierarchical backbone links at 100 Gbps Software: datagram switching with virtual circuit support at backbone layered network architecture • use end-to-end arguments to determine the services provided by each layer ...
lecture8
... - Different services • E.g., degree of reliability - Different interfaces • E.g., length of the packet that can be transmitted, address format - Different protocols • E.g., routing protocols ...
... - Different services • E.g., degree of reliability - Different interfaces • E.g., length of the packet that can be transmitted, address format - Different protocols • E.g., routing protocols ...
Communications and networking Early technology:
... • routers exchange information frequently about routes – which nets each knows about and number of hops to reach them ...
... • routers exchange information frequently about routes – which nets each knows about and number of hops to reach them ...
Static Routing Protocols - IT246
... Load the CD Software. Go to page 303, section 7-4 in the textbook Follow along with the activity. Record all the results from your actions. Go to page 309, section 7-5 in the textbook Follow along with the activity. Record all the results from your actions. Submit a report when you have completed th ...
... Load the CD Software. Go to page 303, section 7-4 in the textbook Follow along with the activity. Record all the results from your actions. Go to page 309, section 7-5 in the textbook Follow along with the activity. Record all the results from your actions. Submit a report when you have completed th ...
08-Application File
... and address in cache it will return the IP address. Note: addresses will time out in cache at an interval determined by the administrator (typically 2 days) • Otherwise a request will be made to a higher level server or a root server which may have to refer the request down to its sub-domain servers ...
... and address in cache it will return the IP address. Note: addresses will time out in cache at an interval determined by the administrator (typically 2 days) • Otherwise a request will be made to a higher level server or a root server which may have to refer the request down to its sub-domain servers ...
CHAPTER 3 Classes of Attack
... the subnet broadcast adress – Affected Windows NT systems respond to each broadcast – Creating a flood of UDP datagrams on the network ...
... the subnet broadcast adress – Affected Windows NT systems respond to each broadcast – Creating a flood of UDP datagrams on the network ...
PowerPoint - ECSE - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
... √ Flat addresses (eg: Ethernet) do not explicitly acknowledge the possibility of indirect connectivity: it assumes all nodes are directly connected to each other. This fundamentally limits scalability. √ Token passing and polling are two examples of “taking turns” method of MAC layer protocol de ...
... √ Flat addresses (eg: Ethernet) do not explicitly acknowledge the possibility of indirect connectivity: it assumes all nodes are directly connected to each other. This fundamentally limits scalability. √ Token passing and polling are two examples of “taking turns” method of MAC layer protocol de ...
ppt - UCL Computer Science
... sending on link as frames • How to demarcate frame boundaries, given only a bit-oriented physical layer? • Reserve a sequence of bits as “end-offrame” marker – e.g., at end of frame, sender sends “000000”; receiver ends frame upon receipt of “000000” ...
... sending on link as frames • How to demarcate frame boundaries, given only a bit-oriented physical layer? • Reserve a sequence of bits as “end-offrame” marker – e.g., at end of frame, sender sends “000000”; receiver ends frame upon receipt of “000000” ...
Internet Protocol (IP):
... Design a network protocol that can operate over and bridge multiple different kinds of packet networks | Why this problem statement? ...
... Design a network protocol that can operate over and bridge multiple different kinds of packet networks | Why this problem statement? ...
Chapter 2 Networking Standards and the OSI Model
... ■ Application layer —Roughly equivalent to the Application, Presentation, and Session layers of the OSI Model. Applications gain access to the network through this layer, via protocols such as the File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) ...
... ■ Application layer —Roughly equivalent to the Application, Presentation, and Session layers of the OSI Model. Applications gain access to the network through this layer, via protocols such as the File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) ...
module05-datalinkV2
... Switched networks • Some data link technologies can be used to build complete networks, with their own addressing, routing, and forwarding mechanisms. These networks are often called switched networks. • At the IP layer, a switched network may like a point-topoint link or like a broadcast link ...
... Switched networks • Some data link technologies can be used to build complete networks, with their own addressing, routing, and forwarding mechanisms. These networks are often called switched networks. • At the IP layer, a switched network may like a point-topoint link or like a broadcast link ...
Undergraduate Curriculum SIGCOMM 2002 Education Workshop Russell J Clark College of Computing
... why needed, standards, specifications, evolution • Layering Abstraction service interface, encapsulation, modular design • Performance Issues protocol overhead, bandwidth vs propagation delay, effect of error rate • Network Programming Issues API’s (e.g. sockets), data representation, reliability, s ...
... why needed, standards, specifications, evolution • Layering Abstraction service interface, encapsulation, modular design • Performance Issues protocol overhead, bandwidth vs propagation delay, effect of error rate • Network Programming Issues API’s (e.g. sockets), data representation, reliability, s ...
APP-G
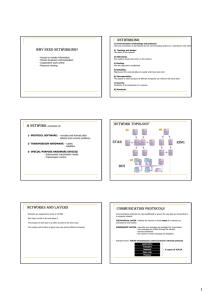
... Assignment may be temporary: Address “leased” to a client for a limited time. SENS supports DHCP client, server and relay agent operation ...
... Assignment may be temporary: Address “leased” to a client for a limited time. SENS supports DHCP client, server and relay agent operation ...
Lecture 2 - Lane Department of Computer Science and Electrical
... Services – what can each layer do Interface – the mechanism to evoke the services of a layer from an adjacent layer Protocol – the rules or policies for how layers interact with each other ...
... Services – what can each layer do Interface – the mechanism to evoke the services of a layer from an adjacent layer Protocol – the rules or policies for how layers interact with each other ...
CCNA 1 Module 10 Routing Fundamentals and Subnets
... A routed protocol allows the router to forward data between nodes on different networks. In order for a protocol to be routable, it must provide the ability to assign a network number and a host number to each individual device. These protocols also require a network mask in order to differentiate t ...
... A routed protocol allows the router to forward data between nodes on different networks. In order for a protocol to be routable, it must provide the ability to assign a network number and a host number to each individual device. These protocols also require a network mask in order to differentiate t ...
VoIPpresentation
... WHAT IS VoIP? Voice-over-IP technology transfers voice signals in data packets over IP networks in real-time. It uses some other protocols like TCP, Internet Protocol (IP), User Datagram Protocol (UDP), Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP), RTCP or RTCP-XR. Some of the benefits using VoIP: • Cost Sav ...
... WHAT IS VoIP? Voice-over-IP technology transfers voice signals in data packets over IP networks in real-time. It uses some other protocols like TCP, Internet Protocol (IP), User Datagram Protocol (UDP), Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP), RTCP or RTCP-XR. Some of the benefits using VoIP: • Cost Sav ...
Internet protocol suite

The Internet protocol suite is the computer networking model and set of communications protocols used on the Internet and similar computer networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP, because among many protocols, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) is the accepted and most widely used protocol in Internet. Often also called the Internet model, it was originally also known as the DoD model, because the development of the networking model was funded by DARPA, an agency of the United States Department of Defense.TCP/IP provides end-to-end connectivity specifying how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination. This functionality is organized into four abstraction layers which are used to sort all related protocols according to the scope of networking involved. From lowest to highest, the layers are the link layer, containing communication technologies for a single network segment (link); the internet layer, connecting hosts across independent networks, thus establishing internetworking; the transport layer handling host-to-host communication; and the application layer, which provides process-to-process application data exchange.The TCP/IP model and related protocol models are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).