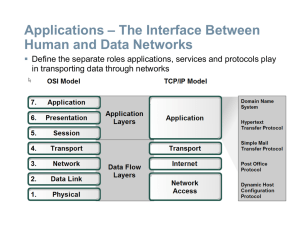
Internet Model
... the end office is known as the local loop. In the United States alone there are about 20,000 local central offices. The concentration of the area code and the first three digits of the telephone number uniquely specify a local central office, which is why the rate structure uses this information. If ...
... the end office is known as the local loop. In the United States alone there are about 20,000 local central offices. The concentration of the area code and the first three digits of the telephone number uniquely specify a local central office, which is why the rate structure uses this information. If ...
Towards meticulous data plane monitoring
... a tagging mechanism if action of the flow rule matched erroneously is same as the action of expected flow rule. This will result in same path but different flow rule match. Moreover, in OpenFlow, if one adds any nonoverlapping rule through the command line utility of the switch e.g., ovs-ofctl then ...
... a tagging mechanism if action of the flow rule matched erroneously is same as the action of expected flow rule. This will result in same path but different flow rule match. Moreover, in OpenFlow, if one adds any nonoverlapping rule through the command line utility of the switch e.g., ovs-ofctl then ...
Application Layer Functionality and Protocols
... Testing the Network Layer Describe the general purpose of the ping command, trace the steps of its operation in a network, and use the ping command to determine if the IP protocol is operational on a local host ...
... Testing the Network Layer Describe the general purpose of the ping command, trace the steps of its operation in a network, and use the ping command to determine if the IP protocol is operational on a local host ...
50 Ohm Driver Manual
... 50 ohms and thus preserve the pulse shape of the signal. The source of the driving pulse will normally be from a NI interface card. Four isolated inputs are also provided. (Black BNCs) Commercial 250ma line driver amps THS6022 are used as the drivers and HCPL-0900 digital isolators provide fast isol ...
... 50 ohms and thus preserve the pulse shape of the signal. The source of the driving pulse will normally be from a NI interface card. Four isolated inputs are also provided. (Black BNCs) Commercial 250ma line driver amps THS6022 are used as the drivers and HCPL-0900 digital isolators provide fast isol ...
PPT
... Whenever you are near any node, give it a (new) packet for the destination. On average should have data for every possible destination ...
... Whenever you are near any node, give it a (new) packet for the destination. On average should have data for every possible destination ...
The OSI Reference Model
... Serves as an outline of rules for how protocols can be used to allow communication between computers. Each layer has its own function and provides support to other layers. ...
... Serves as an outline of rules for how protocols can be used to allow communication between computers. Each layer has its own function and provides support to other layers. ...
WPAN - Feng Xia
... – Ad hoc peer-to-peer networking – Security – Low power consumption – Low cost – Designed to meet the demanding requirements of portable consumer imaging and multimedia applications ...
... – Ad hoc peer-to-peer networking – Security – Low power consumption – Low cost – Designed to meet the demanding requirements of portable consumer imaging and multimedia applications ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 2. What is the difference between a packet and a frame? 3. List the key services provided by the session layer. 4. What are the major classifications of transmission media? 5. What is differential coding? 6. List the three basic encoding or modulation techniques for transforming digital data into an ...
... 2. What is the difference between a packet and a frame? 3. List the key services provided by the session layer. 4. What are the major classifications of transmission media? 5. What is differential coding? 6. List the three basic encoding or modulation techniques for transforming digital data into an ...
What is a Network?
... would correlate to the OSI model in order to communicate via the Internet. In this model, there are four layers, including: •Ethernet (Physical/Data Link Layers) •IP/IPX (Network Layer) •TCP/SPX (Transport Layer) •HTTP, FTP, Telnet, SMTP, and DNS (Session/Presentation/Application Layers). Assuming y ...
... would correlate to the OSI model in order to communicate via the Internet. In this model, there are four layers, including: •Ethernet (Physical/Data Link Layers) •IP/IPX (Network Layer) •TCP/SPX (Transport Layer) •HTTP, FTP, Telnet, SMTP, and DNS (Session/Presentation/Application Layers). Assuming y ...
Chapter 13 slides
... • Allows partitioning total responsibility for message transmission and reception among various layers. • Modularity allows integration of a new module at a particular layer with minimal changes to the other layers. • It might appear that a potential downside to layering might be a performance penal ...
... • Allows partitioning total responsibility for message transmission and reception among various layers. • Modularity allows integration of a new module at a particular layer with minimal changes to the other layers. • It might appear that a potential downside to layering might be a performance penal ...
Introduction
... incoming packet streams onto one outgoing link it is possible that the switch will receive packets faster than the shared link can accommodate in this case, the switch is forced to buffer these packets in its memory should a switch receive packets faster than it can send them for an extended p ...
... incoming packet streams onto one outgoing link it is possible that the switch will receive packets faster than the shared link can accommodate in this case, the switch is forced to buffer these packets in its memory should a switch receive packets faster than it can send them for an extended p ...
Data Communications
... WANs and LANs. The types of LAN can be dissimilar and a selective choice can be made dynamically based on the cheapest and fastest way to route a data packet. b. Needed when two networks use the same transport layer but have different network layers. c. Network layer. Gateways a. It is a specialised ...
... WANs and LANs. The types of LAN can be dissimilar and a selective choice can be made dynamically based on the cheapest and fastest way to route a data packet. b. Needed when two networks use the same transport layer but have different network layers. c. Network layer. Gateways a. It is a specialised ...
Slide - Microsoft Research
... • Decision Plane must be modular/extensible – Isolation: each group specifies the decision logic used to control traffic among the group – Device heterogeneity: vendor ships decision logic that leverages their cool new feature along with the router Grand Vision: 4D must arbitrate access to resources ...
... • Decision Plane must be modular/extensible – Isolation: each group specifies the decision logic used to control traffic among the group – Device heterogeneity: vendor ships decision logic that leverages their cool new feature along with the router Grand Vision: 4D must arbitrate access to resources ...
ppt
... Demultiplexing: delivering the data in a transportlayer segment to the correct application process Multiplexing: gathering data at the source host from different application processes, enveloping data with header information to create segments and passing the segments to the network layer ...
... Demultiplexing: delivering the data in a transportlayer segment to the correct application process Multiplexing: gathering data at the source host from different application processes, enveloping data with header information to create segments and passing the segments to the network layer ...
lecture20
... “best effort” service, UDP segments may be: lost delivered out-of-order to app connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
... “best effort” service, UDP segments may be: lost delivered out-of-order to app connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
Introduction of Electronic Commerce
... • Open System: different network systems supporting the functions of a related layer can exchange data ...
... • Open System: different network systems supporting the functions of a related layer can exchange data ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) ISSN: , PP: 60-63 www.iosrjournals.org
... The camera acquires bulk image data; therefore, it is a good module to demonstrate the effectiveness of the system. It compresses and transfers the image from the camera to the serial port. The communication with the camera is established over an RS232 communication protocol using an asynchronous pa ...
... The camera acquires bulk image data; therefore, it is a good module to demonstrate the effectiveness of the system. It compresses and transfers the image from the camera to the serial port. The communication with the camera is established over an RS232 communication protocol using an asynchronous pa ...