C7-2 56Gb/s PAM4 and NRZ SerDes Transceivers in 40nm CMOS
... 4. Here, we present a full-rate purely-linear NRZ CDR/DEMUX operating at 56Gb/s. After pre-amplification and equalization, the input data goes through a static divided-by-2 circuit to slow down the high-speed data by a factor of 2. The data transitions are still preserved but split into two interlea ...
... 4. Here, we present a full-rate purely-linear NRZ CDR/DEMUX operating at 56Gb/s. After pre-amplification and equalization, the input data goes through a static divided-by-2 circuit to slow down the high-speed data by a factor of 2. The data transitions are still preserved but split into two interlea ...
Chapter 10
... • Uses a complex algorithm to sort the packets that make up the different conversations on an interface • Automatically allocates bandwidth to all types of network traffic – prioritizes delay-sensitive packets so that high-volume conversations don’t consume all of the available bandwidth. – Low-volu ...
... • Uses a complex algorithm to sort the packets that make up the different conversations on an interface • Automatically allocates bandwidth to all types of network traffic – prioritizes delay-sensitive packets so that high-volume conversations don’t consume all of the available bandwidth. – Low-volu ...
Lesson 5 - The Data Link Layer
... receiver at the other end of the link. Many link -layer protocols have been designed for point -to -point links;PPP (the point-to-point protocol) and HDLC are two such protocols. The second type of link, a broadcast link, can have multiple sending and receiving nodes all connected to the same, singl ...
... receiver at the other end of the link. Many link -layer protocols have been designed for point -to -point links;PPP (the point-to-point protocol) and HDLC are two such protocols. The second type of link, a broadcast link, can have multiple sending and receiving nodes all connected to the same, singl ...
TTCN-3 Based Automation Framework for LTE UE Protocol Stack
... • Encodes and decodes the RRC messages which are defined in EUTRA_RRC_ASN1_Definitions. • The default technique for encoding and decoding is as per RRC standard 36.331 is “PER-BASICUNALIGNED: 2002”. L2 Layer Stubs • PDCP, RLC and MAC header encapsulation and de-capsulation of messages and PDUs are s ...
... • Encodes and decodes the RRC messages which are defined in EUTRA_RRC_ASN1_Definitions. • The default technique for encoding and decoding is as per RRC standard 36.331 is “PER-BASICUNALIGNED: 2002”. L2 Layer Stubs • PDCP, RLC and MAC header encapsulation and de-capsulation of messages and PDUs are s ...
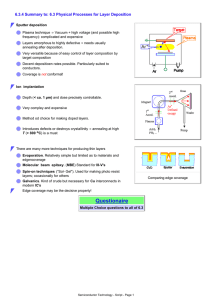
6.3.4 Summary to: 6.3 Physical Processes for Layer Deposition
... 6.3.4 Summary to: 6.3 Physical Processes for Layer Deposition Sputter deposition Plasma technique ⇒ Vacuum + high voltage (and possible high frequency): complicated and expensive Layers amorphous to highly defective ⇒ needs usually annealing after deposition. Very versatile because of easy control o ...
... 6.3.4 Summary to: 6.3 Physical Processes for Layer Deposition Sputter deposition Plasma technique ⇒ Vacuum + high voltage (and possible high frequency): complicated and expensive Layers amorphous to highly defective ⇒ needs usually annealing after deposition. Very versatile because of easy control o ...
CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming
... Can operate selectively - does not copy all frames (must look at data-link headers). Extends the network beyond physical length limitations. ...
... Can operate selectively - does not copy all frames (must look at data-link headers). Extends the network beyond physical length limitations. ...
Chapter 8 Hardware Address & Frame Type Identification
... network node by using the unique hardware address of destination node network interface card on each machine looks at the destination field of every packet. If the destination address in the frame matches the computer’s physical address, the frame is sent to the operating system of the computer; o ...
... network node by using the unique hardware address of destination node network interface card on each machine looks at the destination field of every packet. If the destination address in the frame matches the computer’s physical address, the frame is sent to the operating system of the computer; o ...
Rr.destination
... Networks in Distributed Systems Distributed System is simply a collection of components that communicate to solve a problem Why should programmers of distributed systems know about networks? ...
... Networks in Distributed Systems Distributed System is simply a collection of components that communicate to solve a problem Why should programmers of distributed systems know about networks? ...
Slides
... Networks in Distributed Systems Distributed System is simply a collection of components that communicate to solve a problem Why should programmers of distributed systems know about networks? ...
... Networks in Distributed Systems Distributed System is simply a collection of components that communicate to solve a problem Why should programmers of distributed systems know about networks? ...
Using Argus Audit Trails to Enhance IDS Analysis
... network using libpcap, collects network data into audit trails. This engine can output the data to a file or to a socket. – Argus client: Reads audit data from a file or from a socket. There are a number of clients available for various purposes. ...
... network using libpcap, collects network data into audit trails. This engine can output the data to a file or to a socket. – Argus client: Reads audit data from a file or from a socket. There are a number of clients available for various purposes. ...
IP address - ECS Networking
... ¡ Hosts learn IP → Ethernet address mappings § ARP responses are stored in ARP tables § ARP requests are stored in ARP tables (whether ...
... ¡ Hosts learn IP → Ethernet address mappings § ARP responses are stored in ARP tables § ARP requests are stored in ARP tables (whether ...
network terminology
... Hardware device that uses IP addresses to determine paths for data; forwards packets ...
... Hardware device that uses IP addresses to determine paths for data; forwards packets ...
Slide 1
... How many bits (and which ones) of the IP address are used for Network address, and for Host ? Depends on the LAN: e.g. only 4 devices we may only use 2 bits. Subnet mask specifies which bits are used for Host name: Full Network Address ...
... How many bits (and which ones) of the IP address are used for Network address, and for Host ? Depends on the LAN: e.g. only 4 devices we may only use 2 bits. Subnet mask specifies which bits are used for Host name: Full Network Address ...
Presentation - Incotex Group
... Collection, processing, storage and displaying of data on the consumption of the energy from meters. Data grouping according to object initial basis. Calculation of energy granting-consumption imbalance. Consumer load control by remote disconnection (restriction) – connection of power supply. Univer ...
... Collection, processing, storage and displaying of data on the consumption of the energy from meters. Data grouping according to object initial basis. Calculation of energy granting-consumption imbalance. Consumer load control by remote disconnection (restriction) – connection of power supply. Univer ...
Accompanying slides for Project 5
... Routing packets (2) Route Reply packets: Used to give route information to the sources Send by destinations back to the sources Flooded through the network until they are ...
... Routing packets (2) Route Reply packets: Used to give route information to the sources Send by destinations back to the sources Flooded through the network until they are ...
Part I: Introduction
... len service fragment 16-bit identifier flgs offset time to upper Internet layer live checksum ...
... len service fragment 16-bit identifier flgs offset time to upper Internet layer live checksum ...
Network Devices - courses.psu.edu
... TCP port 20 – FTP data transfer TCP port 21 – FTP control port TCP port 23 – Telnet TCP port 25 – SMTP TCP & UDP port 53 – DNS TCP (port 80) – HTTP Web services TCP & UDP port 123 – Network Time Protocol (NTP) TCP port 110 – Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3) TCP port 119 – Network News Transport ...
... TCP port 20 – FTP data transfer TCP port 21 – FTP control port TCP port 23 – Telnet TCP port 25 – SMTP TCP & UDP port 53 – DNS TCP (port 80) – HTTP Web services TCP & UDP port 123 – Network Time Protocol (NTP) TCP port 110 – Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3) TCP port 119 – Network News Transport ...
ppt - Stanford Crypto group
... server; tells server its port number. The ACK bit is not set while establishing the connection but will be set on the remaining packets ...
... server; tells server its port number. The ACK bit is not set while establishing the connection but will be set on the remaining packets ...
Slide 1
... Sender inserts SYN character occurs at start and end of large block of data Receiver recognises bit pattern of SYN & sets its clock to sample signal in the middle of each bit ...
... Sender inserts SYN character occurs at start and end of large block of data Receiver recognises bit pattern of SYN & sets its clock to sample signal in the middle of each bit ...
A repeater is a network device used to regenerate a signal
... In digital systems, the basic unit of bandwidth is bits per second (bps). Bandwidth is the measure of how many bits of information can flow from one place to another in a given amount of time. Although bandwidth can be described in bps, a larger unit of measurement is generally used. Network bandwid ...
... In digital systems, the basic unit of bandwidth is bits per second (bps). Bandwidth is the measure of how many bits of information can flow from one place to another in a given amount of time. Although bandwidth can be described in bps, a larger unit of measurement is generally used. Network bandwid ...
MAC Protocols
... Link Layer Services (more) Flow Control: pacing between adjacent sending and receiving nodes Error Detection: errors caused by signal attenuation, noise. receiver detects presence of errors: • signals sender for retransmission or drops frame Error Correction: receiver identifies and c ...
... Link Layer Services (more) Flow Control: pacing between adjacent sending and receiving nodes Error Detection: errors caused by signal attenuation, noise. receiver detects presence of errors: • signals sender for retransmission or drops frame Error Correction: receiver identifies and c ...