Data Communication Network
... ◦ Each packet contains a portion of user data plus some control info ...
... ◦ Each packet contains a portion of user data plus some control info ...
Document
... – But this is all done on top of IP, which is connectionless, so we’ll need to implement quite a bit of extra logic in TCP to get the connection-oriented characteristics out of an underlying connectionless medium ...
... – But this is all done on top of IP, which is connectionless, so we’ll need to implement quite a bit of extra logic in TCP to get the connection-oriented characteristics out of an underlying connectionless medium ...
experiment number 9 random access memory for combinational logic
... locations are accessed by addresses. The word length and number of addresses depend on the size of a particular RAM. Data words can be read from or written into a RAM by accessing it with the desired address. RAM is a volatile memory device, meaning that it must be powered whenever data is to be wri ...
... locations are accessed by addresses. The word length and number of addresses depend on the size of a particular RAM. Data words can be read from or written into a RAM by accessing it with the desired address. RAM is a volatile memory device, meaning that it must be powered whenever data is to be wri ...
b) simplex channels.
... 4) Packets offer an alternative to dedicating a channel for the entire length of a message. This increases utilization and availability of a channel by allowing packets from several sources to access and share a single channel. 5) The use of packets presents a productive way to use a communication c ...
... 4) Packets offer an alternative to dedicating a channel for the entire length of a message. This increases utilization and availability of a channel by allowing packets from several sources to access and share a single channel. 5) The use of packets presents a productive way to use a communication c ...
wireless
... These slides contain material developed by Lili Qiu for CS386W at UT Austin and by J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross ...
... These slides contain material developed by Lili Qiu for CS386W at UT Austin and by J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross ...
Speed Communications for Selected Applications with UDP For
... in reliable data transfer, but it does introduce substantial overhead. Additional overhead is introduced in the TCP header. TCP places a somewhat complex packet header in front of the application’s content when sending data and removes the header from the packet before delivering a received TCP pack ...
... in reliable data transfer, but it does introduce substantial overhead. Additional overhead is introduced in the TCP header. TCP places a somewhat complex packet header in front of the application’s content when sending data and removes the header from the packet before delivering a received TCP pack ...
Comparison and Contrast between the OSI and TCP/IP Model
... It takes the information into individual packets Provide a signaling service for the remote node Transport protocols mark packets with sequencing information To acknowledge the receipt of a packet Provide multiple application processes to access the network by using individual local addresses to det ...
... It takes the information into individual packets Provide a signaling service for the remote node Transport protocols mark packets with sequencing information To acknowledge the receipt of a packet Provide multiple application processes to access the network by using individual local addresses to det ...
Improving Performance of ALM Systems with Bayesian
... excessive congestion possible: packet delay and loss protocols needed for reliable data transfer, congestion control Q: How to provide circuit-like behavior? bandwidth guarantees needed for audio/video apps still an unsolved problem ...
... excessive congestion possible: packet delay and loss protocols needed for reliable data transfer, congestion control Q: How to provide circuit-like behavior? bandwidth guarantees needed for audio/video apps still an unsolved problem ...
The Network Layer - Murdoch University
... at the bottom layer. Note that the OSI model itself is not a network architecture because it does not specify the exact services and protocols to be used in each layer. It just tells what each layer should do. However, ISO has also produced standards for all the layers, although these are not part o ...
... at the bottom layer. Note that the OSI model itself is not a network architecture because it does not specify the exact services and protocols to be used in each layer. It just tells what each layer should do. However, ISO has also produced standards for all the layers, although these are not part o ...
cross_ip - cs.wisc.edu
... – Packets are read out one at a time in round robin order • Insures packet order is preserved ...
... – Packets are read out one at a time in round robin order • Insures packet order is preserved ...
Lecture 1 - Lane Department of Computer Science and Electrical
... Interfaces – how does one layer evoke the services of another layer Think API, function calls, etc ...
... Interfaces – how does one layer evoke the services of another layer Think API, function calls, etc ...
Link Layer - UNM Computer Science
... • encapsulate datagram into frame, adding header, trailer • implement channel access if shared medium, • ‘physical addresses’ used in frame headers to identify source, dest • different from IP address! ...
... • encapsulate datagram into frame, adding header, trailer • implement channel access if shared medium, • ‘physical addresses’ used in frame headers to identify source, dest • different from IP address! ...
A(t)
... 3. Close circuit (“tear down”). Originally, a circuit was an end-to-end physical wire. Nowadays, a circuit is like a virtual private wire: each call has its own private, guaranteed data rate from end-to-end. ...
... 3. Close circuit (“tear down”). Originally, a circuit was an end-to-end physical wire. Nowadays, a circuit is like a virtual private wire: each call has its own private, guaranteed data rate from end-to-end. ...
IT 141: Information Systems I
... periods. Each section is called an octet, because in binary it is represented by 8 bits. It can be assigned by ISPs or system managers. Assigned IP addresses are semi-permanent and stay the same every time you boot your computer. (Static IP addresses) It can also be obtained through DHCP (Dynami ...
... periods. Each section is called an octet, because in binary it is represented by 8 bits. It can be assigned by ISPs or system managers. Assigned IP addresses are semi-permanent and stay the same every time you boot your computer. (Static IP addresses) It can also be obtained through DHCP (Dynami ...
16.36: Communication Systems Engineering Lecture 1: Introduction Eytan Modiano
... It is responsible for routing and flow control between networks, so looks like a network layer to the end-to-end transport layer ...
... It is responsible for routing and flow control between networks, so looks like a network layer to the end-to-end transport layer ...
wret2104_1_LAN
... the traffic to keep local traffic local, yet allow connectivity to other parts. Keeps track on MAC address on each side ...
... the traffic to keep local traffic local, yet allow connectivity to other parts. Keeps track on MAC address on each side ...
B is the correct answer
... B is the correct answer Segment is in transport layer Packet is in network layer Frame is in data link layer ...
... B is the correct answer Segment is in transport layer Packet is in network layer Frame is in data link layer ...
Circuit Switching
... single link shared by many packets over time packets queued and transmitted as fast as possible stations connects to local node at own speed nodes buffer data if required to equalize rates ...
... single link shared by many packets over time packets queued and transmitted as fast as possible stations connects to local node at own speed nodes buffer data if required to equalize rates ...
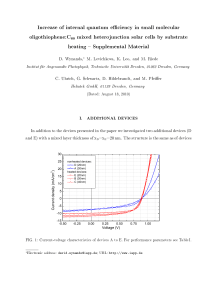
Increase of internal quantum efficiency in small
... To separate the absorption of active absorber layers from absorption within transport layers and metal contact, we use a transfer-matrix-formalism to model the device optically [1]. Values of the optical constants n and k were derived by tting transmission and re ection spectra of thin lm layers o ...
... To separate the absorption of active absorber layers from absorption within transport layers and metal contact, we use a transfer-matrix-formalism to model the device optically [1]. Values of the optical constants n and k were derived by tting transmission and re ection spectra of thin lm layers o ...
Windows Server 2008 - St. Mary's Ryken High School
... • Manages the mechanics of ongoing conversations such as identifying which side can transmit data when and for how long • Checkpointing is performed at this layer – Example: keeping the audio in sync with video Copyright © 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. ...
... • Manages the mechanics of ongoing conversations such as identifying which side can transmit data when and for how long • Checkpointing is performed at this layer – Example: keeping the audio in sync with video Copyright © 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. ...
Switching and Forwarding
... • Typically wait full RTT for connection setup before sending first data packet. • While the connection request contains the full address for destination, each data packet contains only a small identifier, making the per-packet header overhead small. • If a switch or a link in a connection fails, th ...
... • Typically wait full RTT for connection setup before sending first data packet. • While the connection request contains the full address for destination, each data packet contains only a small identifier, making the per-packet header overhead small. • If a switch or a link in a connection fails, th ...