Week_Two_2_ppt
... Allows various types of network hardware and software to communicate. Allows changes in one layer from affecting other layers, so it doesn’t hamper development. ...
... Allows various types of network hardware and software to communicate. Allows changes in one layer from affecting other layers, so it doesn’t hamper development. ...
6LoWPAN adaptation layer (cont.)
... Dynamic MANET On-demand for 6LoWPAN Routing Like AODV, DYMO performs route discovery and maintenance by using RREQ, RREP and RERR messages. Unlike AODV, the DYMO protocol does not use local repair although it uses Hello message to keep track of the link connectivity. However, DYMO cannot be ...
... Dynamic MANET On-demand for 6LoWPAN Routing Like AODV, DYMO performs route discovery and maintenance by using RREQ, RREP and RERR messages. Unlike AODV, the DYMO protocol does not use local repair although it uses Hello message to keep track of the link connectivity. However, DYMO cannot be ...
投影片 1
... • The FileSystem is a tree-based view of all the directories mounted in the QualNet Developer IDE. • The Inspector displays the scenario's global, node and link topology settings in a hierarchical tree format. ...
... • The FileSystem is a tree-based view of all the directories mounted in the QualNet Developer IDE. • The Inspector displays the scenario's global, node and link topology settings in a hierarchical tree format. ...
Solutions - PolyU
... b) The learning rate should be small so that the change in the weights will not be very large in successive iterations. The key point is we want to have small change in weights for each iteration so that eventually, we will reach the bottom of a valley. If the learning rate is very large, the change ...
... b) The learning rate should be small so that the change in the weights will not be very large in successive iterations. The key point is we want to have small change in weights for each iteration so that eventually, we will reach the bottom of a valley. If the learning rate is very large, the change ...
Protocols Notes
... determine the path for packets from source to destination when a router receives a packet, inspects the destination address looks up that address in a routing table based on the contents of the table, forwards the packet to another router (or to its final destination if possible) Routing Infor ...
... determine the path for packets from source to destination when a router receives a packet, inspects the destination address looks up that address in a routing table based on the contents of the table, forwards the packet to another router (or to its final destination if possible) Routing Infor ...
Internet & Web Protocols
... determine the path for packets from source to destination when a router receives a packet, inspects the destination address looks up that address in a routing table based on the contents of the table, forwards the packet to another router (or to its final destination if possible) Routing Infor ...
... determine the path for packets from source to destination when a router receives a packet, inspects the destination address looks up that address in a routing table based on the contents of the table, forwards the packet to another router (or to its final destination if possible) Routing Infor ...
1.01 - BRAUDE
... Responsible for delivering the data or the messages between the two nodes Divide the data in packets at the sender side Re-assemble packets at the receiver side Third task: error free data transmission ...
... Responsible for delivering the data or the messages between the two nodes Divide the data in packets at the sender side Re-assemble packets at the receiver side Third task: error free data transmission ...
IP Network Addressing
... In the Capture box, select/check Local Area Connection. This should post an IP address. Configure Wireshark to read only packets destined to your IP address as follows: Capture Filter: host
We want to capture and display packets in real-time. Optionally you may turn off MAC name
tr ...
... In the Capture box, select/check Local Area Connection. This should post an IP address. Configure Wireshark to read only packets destined to your IP address as follows: Capture Filter: host
Internet Secure Protocols
... almost (but not quite) as safe as a node disconnected from the net. Internal routers should not advertise paths to such nodes to the outside. Filter routes learned from the outside: ...
... almost (but not quite) as safe as a node disconnected from the net. Internal routers should not advertise paths to such nodes to the outside. Filter routes learned from the outside: ...
COEN 351
... almost (but not quite) as safe as a node disconnected from the net. Internal routers should not advertise paths to such nodes to the outside. Filter routes learned from the outside: ...
... almost (but not quite) as safe as a node disconnected from the net. Internal routers should not advertise paths to such nodes to the outside. Filter routes learned from the outside: ...
Chapter 2 - William Stallings, Data and Computer
... – Typically, a unique address is associated with each end system and each intermediate system (eg router). This refers to a network-level address – The network-level address is used to route a PDU through a network or networks to a system indicated by a network level address in the PDU. – Once data ...
... – Typically, a unique address is associated with each end system and each intermediate system (eg router). This refers to a network-level address – The network-level address is used to route a PDU through a network or networks to a system indicated by a network level address in the PDU. – Once data ...
Securing TCP/IP
... (the “next hop”) to help it along toward its ultimate destination. IP is responsible for ensuring that systems can identify the next hop in an efficient manner so that all network traffic eventually reaches its ultimate destination. It’s important to note that the IP protocol itself does not provide ...
... (the “next hop”) to help it along toward its ultimate destination. IP is responsible for ensuring that systems can identify the next hop in an efficient manner so that all network traffic eventually reaches its ultimate destination. It’s important to note that the IP protocol itself does not provide ...
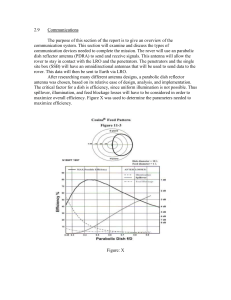
Communications
... a diameter of ten wavelengths and a feed diameter of one wavelength is 80%, with a corresponding focal length to diameter ratio of 0.45. At 8 GHz, the free space wavelength was calculated to be 0.0375 meters, so the dish diameter will be 0.375 meters and feed diameter will be 0.0375 meters. Thus, th ...
... a diameter of ten wavelengths and a feed diameter of one wavelength is 80%, with a corresponding focal length to diameter ratio of 0.45. At 8 GHz, the free space wavelength was calculated to be 0.0375 meters, so the dish diameter will be 0.375 meters and feed diameter will be 0.0375 meters. Thus, th ...
Automotive CAN Engli..
... – transmitter transmits particular bits using NRZ (not return to zero) coding – if there is a sequence of 5 consecutive bits of the same level, one bit of the opposite level is ...
... – transmitter transmits particular bits using NRZ (not return to zero) coding – if there is a sequence of 5 consecutive bits of the same level, one bit of the opposite level is ...
MPLS
... and to meet policy requirements imposed by the network operator Traffic Engineering ensure available spare link capacity for re-routing traffic on failure In case of single failure the network traffic is spread across network backup links The LSPs are created independently, specifying different path ...
... and to meet policy requirements imposed by the network operator Traffic Engineering ensure available spare link capacity for re-routing traffic on failure In case of single failure the network traffic is spread across network backup links The LSPs are created independently, specifying different path ...
Remote Access
... • Two common types of VPNs include: – Remote-access VPN or virtual private dial-up network (VPDN): user-to-LAN connection used by remote users – Site-to-site VPN: multiple sites can connect to other sites over the Internet ...
... • Two common types of VPNs include: – Remote-access VPN or virtual private dial-up network (VPDN): user-to-LAN connection used by remote users – Site-to-site VPN: multiple sites can connect to other sites over the Internet ...
Week_Three_Network_ppt - Computing Sciences
... Terminal screen: 4 Kbytes Simple e-mail: 10 Kbytes Simple web page: 50 Kbytes High-quality image: 50,000 Kbytes Database backup: 1,000,000 Kbytes or more ...
... Terminal screen: 4 Kbytes Simple e-mail: 10 Kbytes Simple web page: 50 Kbytes High-quality image: 50,000 Kbytes Database backup: 1,000,000 Kbytes or more ...
Energy Efficient Protocols for Low Duty Cycle Wireless
... basestation). Third, a cell covers a small area (<10m) and the cell density(i.e. number of sensors per cell) can have a large spatial variation and small time variation. That is, one cell may have a few hundreds of sensors while another cell only has a few number of sensors. Finally, reliability (lo ...
... basestation). Third, a cell covers a small area (<10m) and the cell density(i.e. number of sensors per cell) can have a large spatial variation and small time variation. That is, one cell may have a few hundreds of sensors while another cell only has a few number of sensors. Finally, reliability (lo ...
Slide 1
... Domain name resolvers (DNRs) are the bottom layer of servers which the ISPs hit with a domain name to resolve. If the DNR server has a match for the domain name in its IP address table cache, then the DNR server can resolve the domain name into an IP address. If not, then the DNR server hits the reg ...
... Domain name resolvers (DNRs) are the bottom layer of servers which the ISPs hit with a domain name to resolve. If the DNR server has a match for the domain name in its IP address table cache, then the DNR server can resolve the domain name into an IP address. If not, then the DNR server hits the reg ...