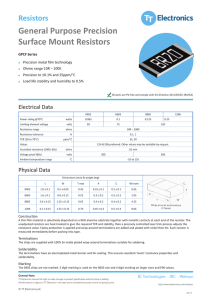
General Purpose Precision Surface Mount Resistors
... GPCF resistors are ideally suited for handling by automatic methods due to their rectangular shape and the small dimensional tolerances. Electrical connection to a ceramic substrate or to a printed circuit board can be made by reflow or wave soldering of wraparound terminations. Wrap-around terminat ...
... GPCF resistors are ideally suited for handling by automatic methods due to their rectangular shape and the small dimensional tolerances. Electrical connection to a ceramic substrate or to a printed circuit board can be made by reflow or wave soldering of wraparound terminations. Wrap-around terminat ...
InternetOverview
... establishment (which can add delay) simple: no connection state at sender, receiver small segment header no congestion control: UDP can blast away as fast as desired ...
... establishment (which can add delay) simple: no connection state at sender, receiver small segment header no congestion control: UDP can blast away as fast as desired ...
Research Mission
... – Coherence: amplitude and phase about the frequencies held in common between two signals ...
... – Coherence: amplitude and phase about the frequencies held in common between two signals ...
VLAN - CA, Inc.
... • Virtual channel (VC) is a single connection between two ATM devices • The channel is given a unique identifier, called a Virtual Channel Identifier (VCI) ...
... • Virtual channel (VC) is a single connection between two ATM devices • The channel is given a unique identifier, called a Virtual Channel Identifier (VCI) ...
Network Control Plane
... and, speed and RA = requesting agent, aka client (e.g., IP router, ATM switch) efficiency gains ...
... and, speed and RA = requesting agent, aka client (e.g., IP router, ATM switch) efficiency gains ...
1.01 - BRAUDE
... TCP = Transport Control Protocol A reliable end-to-end byte stream over an unreliable internetwork Independent of network architecture, topology, speed Robust in the face of many kinds of failures Defined in RFC's 793, 1122, 1323 A machine that supports TCP must have a single "TCP entity" ...
... TCP = Transport Control Protocol A reliable end-to-end byte stream over an unreliable internetwork Independent of network architecture, topology, speed Robust in the face of many kinds of failures Defined in RFC's 793, 1122, 1323 A machine that supports TCP must have a single "TCP entity" ...
Unit 3- Mobile Network layer
... A MN may not use ARP if it is using a FA COA. It needs to use the address of the FA as the destination address. If it is using a collocated COA, then it uses ARP to locate the default router using its COA as source. Note that if the ‘R’ bit is set is uses the FA address as the destination address. F ...
... A MN may not use ARP if it is using a FA COA. It needs to use the address of the FA as the destination address. If it is using a collocated COA, then it uses ARP to locate the default router using its COA as source. Note that if the ‘R’ bit is set is uses the FA address as the destination address. F ...
WP1 – D1.1 - PlanetData
... provide me all temperature sensors that have shown higher than 30 degrees Use ontological schemas fro queries, internally map to the appropriate sensors Query rewritten and dispatched to the appropriate GSN instances Return query results URL ...
... provide me all temperature sensors that have shown higher than 30 degrees Use ontological schemas fro queries, internally map to the appropriate sensors Query rewritten and dispatched to the appropriate GSN instances Return query results URL ...
Network Virtualization for QoS-Aware Resource Management
... with strict bandwidth guarantees, however, they are not scalable, while those based on DiffServ (i.e., packet scheduling, traffic profiling, admission control) provide only probabilistic QoS guarantees, however, in a scalable manner. Packet scheduling algorithms are used for traffic prioritization w ...
... with strict bandwidth guarantees, however, they are not scalable, while those based on DiffServ (i.e., packet scheduling, traffic profiling, admission control) provide only probabilistic QoS guarantees, however, in a scalable manner. Packet scheduling algorithms are used for traffic prioritization w ...
File Systems
... Extent-based file systems allocate disk blocks in extents An extent is a contiguous block of disks ...
... Extent-based file systems allocate disk blocks in extents An extent is a contiguous block of disks ...
The OSI Model - La Salle University
... This suite includes the File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Telnet, the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), e-mail protocols, and sometimes others. Although TCP fits well into the Transport layer of OSI and IP into the Network layer, the other programs fit rather loosely (but not neatly within a layer) ...
... This suite includes the File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Telnet, the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), e-mail protocols, and sometimes others. Although TCP fits well into the Transport layer of OSI and IP into the Network layer, the other programs fit rather loosely (but not neatly within a layer) ...
Chapter 2 - Chabot College
... protocol field to identify the network-layer protocol. – ISDN: a set of digital services that transmits voice and data over existing phone lines. – Link Access Procedure, Balanced (LAPB): For packet-switched networks used to encapsulate packets at Layer 2 of the X.25 stack. Provides reliability and ...
... protocol field to identify the network-layer protocol. – ISDN: a set of digital services that transmits voice and data over existing phone lines. – Link Access Procedure, Balanced (LAPB): For packet-switched networks used to encapsulate packets at Layer 2 of the X.25 stack. Provides reliability and ...
CDD-564/LEN
... Header Decompression Option Header compression reduces the bandwidth required for Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) by as much as 60%. Example: A G.729 voice codec, operating at 8 kbps, requires 32 kbps bandwidth once encapsulated into an IP/UDP/RTP frame. With IP/UDP/RTP header compression, the s ...
... Header Decompression Option Header compression reduces the bandwidth required for Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) by as much as 60%. Example: A G.729 voice codec, operating at 8 kbps, requires 32 kbps bandwidth once encapsulated into an IP/UDP/RTP frame. With IP/UDP/RTP header compression, the s ...
Information-Centric Networking for Machine-to
... These operations are significantly improved if the system state is known. In RTSE, large volumes of raw synchrophasor measurement data are collected by geographically distributed PMUs, strategically deployed in the power grid infrastructure to ensure full grid state observability. The UTCsynchroniz ...
... These operations are significantly improved if the system state is known. In RTSE, large volumes of raw synchrophasor measurement data are collected by geographically distributed PMUs, strategically deployed in the power grid infrastructure to ensure full grid state observability. The UTCsynchroniz ...
QoS Networking Requirements
... • Lack of symmetry: • protocols such as TCP (ideally) require symmetric QoS ...
... • Lack of symmetry: • protocols such as TCP (ideally) require symmetric QoS ...
Lecture - 12
... » In practice, the address space will not be used efficiently. In the most pessimistic scenario, there will still be well over 1000 IP addresses per square meter of the earth’s surface » In any likely scenario, there will be trillions of them per square meter » Only 28% of the address space has been ...
... » In practice, the address space will not be used efficiently. In the most pessimistic scenario, there will still be well over 1000 IP addresses per square meter of the earth’s surface » In any likely scenario, there will be trillions of them per square meter » Only 28% of the address space has been ...
Network Design
... Installation of LAN switching at MDF and IDFs affects size of collision domains and data speed in each of horizontal cable and vertical cable. Vertical cable must handle all data traffic between MDF and ...
... Installation of LAN switching at MDF and IDFs affects size of collision domains and data speed in each of horizontal cable and vertical cable. Vertical cable must handle all data traffic between MDF and ...
Data transfer using the UDP protocol in the Gigabit Ethernet environment
... Computer networks have come a long way since their initial introduction in the middle of the 20th century. While still developing rapidly even today, we can already say that a computer network has become a highly effective technology for data transfer, especially over long distances. As the complexi ...
... Computer networks have come a long way since their initial introduction in the middle of the 20th century. While still developing rapidly even today, we can already say that a computer network has become a highly effective technology for data transfer, especially over long distances. As the complexi ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 3
... segments may be: lost delivered out of order to app connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
... segments may be: lost delivered out of order to app connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...























