Fiscal Policies and Rules in the Face of Revenue Volatility Within
... option is to adjust the fiscal stance, either by increasing non-SACU revenue, decreasing spending, or both. The debt pattern remains otherwise fixed.9 Optimal fiscal adjustment strategies are based on multiple instruments, as the composition of the adjustment is of utmost importance.10 Five strategi ...
... option is to adjust the fiscal stance, either by increasing non-SACU revenue, decreasing spending, or both. The debt pattern remains otherwise fixed.9 Optimal fiscal adjustment strategies are based on multiple instruments, as the composition of the adjustment is of utmost importance.10 Five strategi ...
Comprehensive Assessment: Developments in Economic Activity
... F. Effects of the Decline in Real Interest Rates on Economic Activity and Prices As explained at the outset, the main transmission channel of QQE and "QQE with a Negative Interest Rate" is to push down real interest rates and thereby produce a positive impact on economic activity and prices (Chart ...
... F. Effects of the Decline in Real Interest Rates on Economic Activity and Prices As explained at the outset, the main transmission channel of QQE and "QQE with a Negative Interest Rate" is to push down real interest rates and thereby produce a positive impact on economic activity and prices (Chart ...
Thesis description: Name: Taylor Branch Major/Area of Study
... victimization for black women over a ten year period. I found that overall rates of victimization declined from 2005 to 2015. Significant factors that increase the likelihood of being the victim of a violent crime are age, employment status, and if an individual resides in a two parent home. Post-gr ...
... victimization for black women over a ten year period. I found that overall rates of victimization declined from 2005 to 2015. Significant factors that increase the likelihood of being the victim of a violent crime are age, employment status, and if an individual resides in a two parent home. Post-gr ...
Opportunistic Deep-Value Investing: A Multi-Asset Class
... We expect deep-value investments to exhibit higher absolute volatility than broad market indices because of concentration, added business risks, and potentially greater economic sensitivity. How to manage the potentially high volatility of deep-value investments is a question that must be addressed ...
... We expect deep-value investments to exhibit higher absolute volatility than broad market indices because of concentration, added business risks, and potentially greater economic sensitivity. How to manage the potentially high volatility of deep-value investments is a question that must be addressed ...
The Social Consequences of the Global Economic Crisis in South East Europe
... University of Zagreb. His work in 1990s and 2000s deals with different issues of economics and political economy of post-socialism, Croatia in particular, as well as with some issues in economic theory. This includes published papers on institutional theory, privatisation, entrepreneurship, SME poli ...
... University of Zagreb. His work in 1990s and 2000s deals with different issues of economics and political economy of post-socialism, Croatia in particular, as well as with some issues in economic theory. This includes published papers on institutional theory, privatisation, entrepreneurship, SME poli ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INTERNATIONAL RESERVE HOLDINGS WITH Joshua Aizenman
... in international financial markets and faced new challenges. In the aftermath of the 199798 Asian financial crises, some observers have called on emerging markets to reduce short-term external debt relative to international reserve holdings in order to lower their vulnerability to crisis. Countries ...
... in international financial markets and faced new challenges. In the aftermath of the 199798 Asian financial crises, some observers have called on emerging markets to reduce short-term external debt relative to international reserve holdings in order to lower their vulnerability to crisis. Countries ...
Macroeconomic Effects of Fiscal Policy
... new employees receive higher income and are able to increase their consumption, and also changes in e.g. the consumption and savings behaviour of households and firms. Therefore, the aggregate economic effects of fiscal policy can be determined only through an economic model and all models are based ...
... new employees receive higher income and are able to increase their consumption, and also changes in e.g. the consumption and savings behaviour of households and firms. Therefore, the aggregate economic effects of fiscal policy can be determined only through an economic model and all models are based ...
University of Lethbridge — Department of Economics
... 43) If the natural unemployment rate rises A) the long-run Phillips curve shifts leftward and the short-run Phillips curve does not change. B) the short-run Phillips curve shifts rightward and the long-run Phillips curve does not change. C) the short-run and long-run Phillips curves both shift leftw ...
... 43) If the natural unemployment rate rises A) the long-run Phillips curve shifts leftward and the short-run Phillips curve does not change. B) the short-run Phillips curve shifts rightward and the long-run Phillips curve does not change. C) the short-run and long-run Phillips curves both shift leftw ...
Glossary of Mutual Fund and Other Related Financial Terms
... credit quality. A term used in portfolio management to describe the creditworthiness of an issuer of fixed-income securities and to indicate the likelihood that the issuer will be willing and able to repay its debt. credit risk. The possibility that a bond issuer may not be willing and able to pay i ...
... credit quality. A term used in portfolio management to describe the creditworthiness of an issuer of fixed-income securities and to indicate the likelihood that the issuer will be willing and able to repay its debt. credit risk. The possibility that a bond issuer may not be willing and able to pay i ...
Chapter 4
... straight line would depict increases that were the same amount each period (such as, $5,000 per month) but would then be a declining rate of growth (percentage change) each period. In equilibrium, the rate of growth (percentage change) is constant from period to period, which means the amount of gro ...
... straight line would depict increases that were the same amount each period (such as, $5,000 per month) but would then be a declining rate of growth (percentage change) each period. In equilibrium, the rate of growth (percentage change) is constant from period to period, which means the amount of gro ...
12 INFLATION
... got clear what it means from the beginning. It is another case of unfortunate jargon; the issue is that the forecast based on rational expectations makes use of all information available, up to the point where expected improvements in accuracy are no more valuable than their cost. A rational expecta ...
... got clear what it means from the beginning. It is another case of unfortunate jargon; the issue is that the forecast based on rational expectations makes use of all information available, up to the point where expected improvements in accuracy are no more valuable than their cost. A rational expecta ...
Chapter 9 The IS-LM/AD
... (a) increases output, national saving, and investment, but not the real interest rate. (b) increases output, national saving, and the real interest rate, but not investment. (c) increases the real interest rate, investment, and output, but not national saving. (d) increases output, national saving, ...
... (a) increases output, national saving, and investment, but not the real interest rate. (b) increases output, national saving, and the real interest rate, but not investment. (c) increases the real interest rate, investment, and output, but not national saving. (d) increases output, national saving, ...
Chapter 1: Introduction
... Draw another diagram with the nominal interest rate i=r+π on the vertical axis and the level of total income Y on the horizontal axis. For each possible value of Y on the x-axis, plot the point whose y-axis value is equilibrium nominal interest rate. You have just plotted the LM curve. The LM curve ...
... Draw another diagram with the nominal interest rate i=r+π on the vertical axis and the level of total income Y on the horizontal axis. For each possible value of Y on the x-axis, plot the point whose y-axis value is equilibrium nominal interest rate. You have just plotted the LM curve. The LM curve ...
Chapter 6
... or graph of all possible outcomes, such as expected rates of return, with a probability assigned to each outcome. When in graph form, the tighter the probability distribution, the less uncertain the outcome. b. The expected rate of return (^r ) is the expected value of a probability distribution of ...
... or graph of all possible outcomes, such as expected rates of return, with a probability assigned to each outcome. When in graph form, the tighter the probability distribution, the less uncertain the outcome. b. The expected rate of return (^r ) is the expected value of a probability distribution of ...
Inflation Report 1/2003
... seemed to suggest that global growth would pick up again. Equity markets and long-term interest rates moved up (see Chart 1.3). Equity prices declined sharply during the summer of 2002, however. This increased the likelihood of a deeper and more prolonged downturn. Since then, world stock markets ha ...
... seemed to suggest that global growth would pick up again. Equity markets and long-term interest rates moved up (see Chart 1.3). Equity prices declined sharply during the summer of 2002, however. This increased the likelihood of a deeper and more prolonged downturn. Since then, world stock markets ha ...
The Term Structure of Interest Rates
... • John Moody began the modern bond rating business by publishing Moody’s Analyses of Railroad Investments in 1909. • By the 1920s, the work of rating agencies expanded to cover an increasing number of industries. • In the post-World War II period, prosperity diminished the role of rating agencies, b ...
... • John Moody began the modern bond rating business by publishing Moody’s Analyses of Railroad Investments in 1909. • By the 1920s, the work of rating agencies expanded to cover an increasing number of industries. • In the post-World War II period, prosperity diminished the role of rating agencies, b ...
http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-629X.2011.00462.x
... of hurdle rates (WACCs) in five Nordic countries. Combining survey data with a rich set of determinants, including ownership data, CFO characteristics, and financial data, we find that the use of the Net Present Value method and the sophistication of the capital budgeting are related to firm characteris ...
... of hurdle rates (WACCs) in five Nordic countries. Combining survey data with a rich set of determinants, including ownership data, CFO characteristics, and financial data, we find that the use of the Net Present Value method and the sophistication of the capital budgeting are related to firm characteris ...
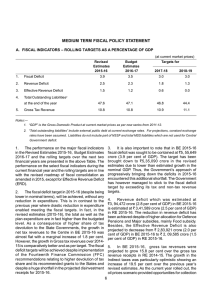
The Fiscal Policy Strategy Statement
... shelf of PSU stakes available for disinvestment as for cash build up required during first quarter of 2016well as the market conditions which were quite 17 for meeting requirements on higher redemptions optimistic and buoyant at the time of budget of existing debt stock. presentation. During the cou ...
... shelf of PSU stakes available for disinvestment as for cash build up required during first quarter of 2016well as the market conditions which were quite 17 for meeting requirements on higher redemptions optimistic and buoyant at the time of budget of existing debt stock. presentation. During the cou ...
Macroeconomic Shocks and Monetary Policy
... such as Sweden and the UK, which started at lower inflation rates when adopting the inflation targeting framework, and which have had more constant inflation targets or inflation targeting ranges during the studied time period. The absence of excessive fluctuations in the macro economy of these two ...
... such as Sweden and the UK, which started at lower inflation rates when adopting the inflation targeting framework, and which have had more constant inflation targets or inflation targeting ranges during the studied time period. The absence of excessive fluctuations in the macro economy of these two ...
A Model of Monetary Policy and Risk Premia
... A low liquidity premium decreases the cost of taking leverage and hence increases risk taking, which reduces risk premia and the cost of capital in the economy. Our model features an economy populated by two types of agents who differ in their risk aversion. We think of the more risk tolerant agents ...
... A low liquidity premium decreases the cost of taking leverage and hence increases risk taking, which reduces risk premia and the cost of capital in the economy. Our model features an economy populated by two types of agents who differ in their risk aversion. We think of the more risk tolerant agents ...
Responding to Seniors` Needs and Improving Medicare Choices
... less than half as large as the shortfall in 2009, which was 10.1 percent of GDP. Because revenues, under current law, are projected to rise more rapidly than spending in the next two years, deficits in CBO’s baseline projections continue to shrink, falling to 2.1 percent of GDP by 2015 (see Table 1 ...
... less than half as large as the shortfall in 2009, which was 10.1 percent of GDP. Because revenues, under current law, are projected to rise more rapidly than spending in the next two years, deficits in CBO’s baseline projections continue to shrink, falling to 2.1 percent of GDP by 2015 (see Table 1 ...
Cyclically Adjusted Fiscal Balance – OECD and ESCB Methods
... tax based on the proportionality assumption of corporate income and output. The proportionality assumption implies that the tax elasticity is equal to the elasticity of the tax base (corporate income, i.e. profits) with respect to output. If output rises, employment changes in the same direction an ...
... tax based on the proportionality assumption of corporate income and output. The proportionality assumption implies that the tax elasticity is equal to the elasticity of the tax base (corporate income, i.e. profits) with respect to output. If output rises, employment changes in the same direction an ...
Fiscal Policy and Monetary Integration in Europe
... The fiscal apparatus of the European Monetary Union – as embedded in the Maastricht Treaty (MT) and the Stability and Growth Pact (SGP)1 – is increasingly regarded by many as an unnecessary and harmful straightjacket on national fiscal policies, or even as downright ‘stupid’.2 The SGP, the argument ...
... The fiscal apparatus of the European Monetary Union – as embedded in the Maastricht Treaty (MT) and the Stability and Growth Pact (SGP)1 – is increasingly regarded by many as an unnecessary and harmful straightjacket on national fiscal policies, or even as downright ‘stupid’.2 The SGP, the argument ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES NEW-KEYNESIAN ECONOMICS: AN AS-AD VIEW Pierpaolo Benigno
... and AS equations are derived from an intertemporal model of optimizing behavior by households and firms respectively. The AD equation is derived from households’ decisions on intertemporal consumption allocation. A standard Euler equation links consumption growth to the real interest rate, implying ...
... and AS equations are derived from an intertemporal model of optimizing behavior by households and firms respectively. The AD equation is derived from households’ decisions on intertemporal consumption allocation. A standard Euler equation links consumption growth to the real interest rate, implying ...
PDF
... There are currently two methods available in the standard GTAP model for allocating global saving across regional investment. The first method allocates global saving across investment so that percentage changes2 in the nominal rates of return expected for the period following the solution period (‘ ...
... There are currently two methods available in the standard GTAP model for allocating global saving across regional investment. The first method allocates global saving across investment so that percentage changes2 in the nominal rates of return expected for the period following the solution period (‘ ...