The mathematics of PDEs and the wave equation
... This is a powerful technique that is applicable to many areas of mathematics. The idea is to look first for solutions of a particularly simple form, then combine to obtain the most general solution. In the PDE case, we look for solutions of the form u(x, y, z, t) = A(x)B(y)C(z)D(t). For instance, co ...
... This is a powerful technique that is applicable to many areas of mathematics. The idea is to look first for solutions of a particularly simple form, then combine to obtain the most general solution. In the PDE case, we look for solutions of the form u(x, y, z, t) = A(x)B(y)C(z)D(t). For instance, co ...
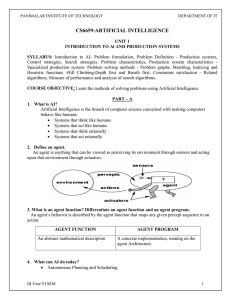
CS6659-ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
... the agent needs some sort of goal information that describes situations that are desirable-for example, being at the passenger's destination. 10. What are utility based agents? Goals alone are not really enough to generate high-quality behavior in most environments. For example, there are many actio ...
... the agent needs some sort of goal information that describes situations that are desirable-for example, being at the passenger's destination. 10. What are utility based agents? Goals alone are not really enough to generate high-quality behavior in most environments. For example, there are many actio ...
solving equations and inequalities
... Solution: Let x represent the number of minutes of use. Peg’s phone costs 25 + 0.25x. Larry’s phone costs 35 + 0.20x. We want Peg’s cost to exceed Larry’s: P > L or P – L > 0. If we subtract 35 + 0.20x from 25 + 0.25x, the result is –10 + 0.05x. Replacing P – L with –10 + 0.05x, we have –10 + 0.05x ...
... Solution: Let x represent the number of minutes of use. Peg’s phone costs 25 + 0.25x. Larry’s phone costs 35 + 0.20x. We want Peg’s cost to exceed Larry’s: P > L or P – L > 0. If we subtract 35 + 0.20x from 25 + 0.25x, the result is –10 + 0.05x. Replacing P – L with –10 + 0.05x, we have –10 + 0.05x ...
Anytime A* Algorithm – An Extension to A* Algorithm
... A* is probably one of the most well known Artificial Intelligence Algorithms[1, 20]. Its objective is to find the shortest path in a graph from a node x-start to a node x-goal[13]. It combines the features of uniform-cost search and pure heuristic search to efficiently compute optimal solutions. As ...
... A* is probably one of the most well known Artificial Intelligence Algorithms[1, 20]. Its objective is to find the shortest path in a graph from a node x-start to a node x-goal[13]. It combines the features of uniform-cost search and pure heuristic search to efficiently compute optimal solutions. As ...
1-3_Solving_Equations Evens - MOC-FV
... • Your new number is twice your original. SOLUTION: This number trick is a series of steps that can be represented by an equation with x representing the number chosen. ...
... • Your new number is twice your original. SOLUTION: This number trick is a series of steps that can be represented by an equation with x representing the number chosen. ...
AIRS: Anytime Iterative Refinement of a Solution
... Figure 1 provides a Greedy Solution in which we observe three such plateaus: one from steps 50-80, another from 90-130, and the third from 150-250. Greedy plateaus often result from greedy searches where h, while admissible, badly underestimates the actual remaining distance to the goal. After most ...
... Figure 1 provides a Greedy Solution in which we observe three such plateaus: one from steps 50-80, another from 90-130, and the third from 150-250. Greedy plateaus often result from greedy searches where h, while admissible, badly underestimates the actual remaining distance to the goal. After most ...
Winner determination in combinatorial auctions using hybrid ant
... Auctions play a significant role in multi-agent systems, where the auction mechanisms are used for task distribution and resource allocation. The items that are auctioned range from network bandwidth to radio frequencies, and pollution rights. Combinatorial Auction (CA) is a sort of auctions in whic ...
... Auctions play a significant role in multi-agent systems, where the auction mechanisms are used for task distribution and resource allocation. The items that are auctioned range from network bandwidth to radio frequencies, and pollution rights. Combinatorial Auction (CA) is a sort of auctions in whic ...
A Proof Theory for Generic Judgments
... Γ0 , ∀xB −→ C is proved using the introduction of ∀ on the left from the premise Γ0 , B[t/x] −→ C, where t is some term. To reduce the rank of the cut formula ∀x.B between the sequents Γ −→ ∀x.B and Γ0 , ∀xB −→ C, the eigenvariable c in the sequent calculus proof Π(c) must be substituted by t to yie ...
... Γ0 , ∀xB −→ C is proved using the introduction of ∀ on the left from the premise Γ0 , B[t/x] −→ C, where t is some term. To reduce the rank of the cut formula ∀x.B between the sequents Γ −→ ∀x.B and Γ0 , ∀xB −→ C, the eigenvariable c in the sequent calculus proof Π(c) must be substituted by t to yie ...
Full Text
... Abstract: The MAXimum propositional SATisfiability problem (MAXSAT) is a well known NP-hard optimization problem with many theoretical and practical applications in artificial intelligence and mathematical logic. Heuristic local search algorithms are widely recognized as the most effective approache ...
... Abstract: The MAXimum propositional SATisfiability problem (MAXSAT) is a well known NP-hard optimization problem with many theoretical and practical applications in artificial intelligence and mathematical logic. Heuristic local search algorithms are widely recognized as the most effective approache ...
Solve equations with variables on both sides of the equal sign.
... Subtract 24y from both sides. Subtract 18 from both sides. Divide both sides by 2. ...
... Subtract 24y from both sides. Subtract 18 from both sides. Divide both sides by 2. ...