y - iyang
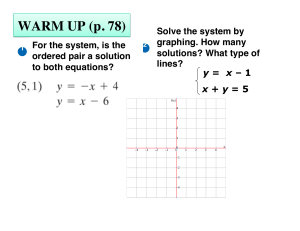
... Since there are only three possible outcomes with two lines in a plane, we can determine how many solutions of the system there will be without graphing the lines. ...
... Since there are only three possible outcomes with two lines in a plane, we can determine how many solutions of the system there will be without graphing the lines. ...
CBrayMath216-4-1
... SPEAKER 1: So we just saw that there's a strong similarity between the structure of solutions to an nth order linear differential equation and the structure of the solutions to a matrix equation. In both cases, the solutions form vector spaces. So in both cases, we're talking about linear algebra pr ...
... SPEAKER 1: So we just saw that there's a strong similarity between the structure of solutions to an nth order linear differential equation and the structure of the solutions to a matrix equation. In both cases, the solutions form vector spaces. So in both cases, we're talking about linear algebra pr ...
Foundations of Logic Programmin:
... Example Vy3x (p(x,y)Ao(x.)) is closed. However. 3x (p(x.y)Aq(x)} is not closed, since there is a free occurrence of the variable y. Definition If F is a formula, then V(F) denotes the universal closure of F, which is the closed formula obtained by adding a universal quantifier for every variable hav ...
... Example Vy3x (p(x,y)Ao(x.)) is closed. However. 3x (p(x.y)Aq(x)} is not closed, since there is a free occurrence of the variable y. Definition If F is a formula, then V(F) denotes the universal closure of F, which is the closed formula obtained by adding a universal quantifier for every variable hav ...
Algebra note sheet test 10
... 1) changing the “b” value shifts the graph up or down. Adding shifts up, subtracting shifts down This is a translation or slide. 2) changing the “m” value or slope, changes the steepness of the graph. Values of “m” that are between 0 & 1 will flatten the line or make it less steep. Values of “m” tha ...
... 1) changing the “b” value shifts the graph up or down. Adding shifts up, subtracting shifts down This is a translation or slide. 2) changing the “m” value or slope, changes the steepness of the graph. Values of “m” that are between 0 & 1 will flatten the line or make it less steep. Values of “m” tha ...
3.0 Chapter 3 Packet
... 2) Apply the linear combination method to eliminate any one of the variables. 3) Choose two of the original equations but not the same two used in Step 2. 4) Apply the linear combination method to eliminate the same variable as in Step 3. 5) Apply the linear combination to the equations from steps 3 ...
... 2) Apply the linear combination method to eliminate any one of the variables. 3) Choose two of the original equations but not the same two used in Step 2. 4) Apply the linear combination method to eliminate the same variable as in Step 3. 5) Apply the linear combination to the equations from steps 3 ...
cs-171-15-FOL-Inference
... • GMP is complete for a KB consisting of definite clauses – Complete: derives all sentences that are entailed – OR…answers every query whose answers are entailed by such a KB – Definite clause: disjunction of literals of which exactly 1 is positive, e.g., King(x) AND Greedy(x) -> Evil(x) ...
... • GMP is complete for a KB consisting of definite clauses – Complete: derives all sentences that are entailed – OR…answers every query whose answers are entailed by such a KB – Definite clause: disjunction of literals of which exactly 1 is positive, e.g., King(x) AND Greedy(x) -> Evil(x) ...
Extraneous solution
... both rational expressions and rational equations • For rational expressions – Simplify by combining over one denominator • Section 6.2 ...
... both rational expressions and rational equations • For rational expressions – Simplify by combining over one denominator • Section 6.2 ...
ch 9 - combining like terms
... Now we combine the like terms on both sides of the equation: 20a = 80 The rest is old hat; divide each side by 20: ...
... Now we combine the like terms on both sides of the equation: 20a = 80 The rest is old hat; divide each side by 20: ...
The Calculus of Variations: An Introduction
... “Calculus of variations seeks to find the path, curve, surface, etc., for which a given function has a stationary value (which, in physical problems, is usually a minimum or ...
... “Calculus of variations seeks to find the path, curve, surface, etc., for which a given function has a stationary value (which, in physical problems, is usually a minimum or ...
Christmas Break Revision
... but the assembly and painting time required for the Traveler is only 1 hour, while it is 3 hours for the Tourister. There are 300 frames and 360 hours of labor available for production. How many bicycles of each model should be produced to maximize revenue? [Answ(270, 30)] ISÄ ...
... but the assembly and painting time required for the Traveler is only 1 hour, while it is 3 hours for the Tourister. There are 300 frames and 360 hours of labor available for production. How many bicycles of each model should be produced to maximize revenue? [Answ(270, 30)] ISÄ ...
6.2ab solve systems by substitution
... Solve one of the equations for one of its variables (if needed).! Substitute expression from Step 1 into other equation and solve for other variable.! Substitute value from Step 2 into (revised) equation from Step 1. Solve. ! ...
... Solve one of the equations for one of its variables (if needed).! Substitute expression from Step 1 into other equation and solve for other variable.! Substitute value from Step 2 into (revised) equation from Step 1. Solve. ! ...
2.6 Solving for Variables ink.notebook
... A.CED.4 Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations. For example, rearrange Ohm’s law V = IR to highlight resistance R. ...
... A.CED.4 Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations. For example, rearrange Ohm’s law V = IR to highlight resistance R. ...
Link - WordPress.com
... If you heat a solid past melting point and then cool it, the structural properties of the solid depend on the rate of cooling. If the liquid is cooled slowly enough, large crystals will be formed. However, if the liquid is cooled quickly (quenched) the crystals will contain imperfections. Metropolis ...
... If you heat a solid past melting point and then cool it, the structural properties of the solid depend on the rate of cooling. If the liquid is cooled slowly enough, large crystals will be formed. However, if the liquid is cooled quickly (quenched) the crystals will contain imperfections. Metropolis ...