MSA Ticket 2 key
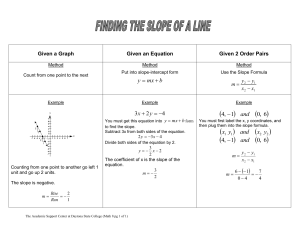
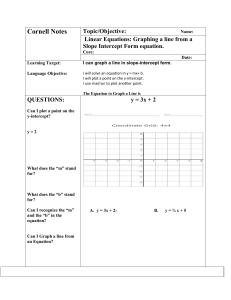
... Remember...... how can tell a relationship is linear from the equation, the table, the graph? Can you give an example of a non-linear relationship? X has an exponent other than 1, like x2 If you notice, all of the equations given in the examples are in the form y = mx + b. For each equation, find th ...
... Remember...... how can tell a relationship is linear from the equation, the table, the graph? Can you give an example of a non-linear relationship? X has an exponent other than 1, like x2 If you notice, all of the equations given in the examples are in the form y = mx + b. For each equation, find th ...
MAT 090 Basic Algebra Quiz 4 Solutions DIRECTIONS. Partial credit
... DIRECTIONS. Partial credit will only be given where there is a clear explanation offered for an answer (i.e., work shown). 1. Is the pair (6, −8) a solution to the following system of equations? Explain. ...
... DIRECTIONS. Partial credit will only be given where there is a clear explanation offered for an answer (i.e., work shown). 1. Is the pair (6, −8) a solution to the following system of equations? Explain. ...