MA 114: Calculus II Exam 3 Review (New Material) §8.1 Arc Length
... set up and solve the differential equation corresponding to Newton’s Law of Cooling and free-fall with air resistance; focus on word problems §9.3 Graphical and Numerical Methods how to construct/identify the slope field corresponding to a given differential equation; how to plot integral curves §9. ...
... set up and solve the differential equation corresponding to Newton’s Law of Cooling and free-fall with air resistance; focus on word problems §9.3 Graphical and Numerical Methods how to construct/identify the slope field corresponding to a given differential equation; how to plot integral curves §9. ...
Week 1 - Student Classroom Worksheet
... A linear equation in one variable is an equation that can be written in the form ax + b = 0 where a and b are real numbers and a ≠ 0. Determine whether the equation is linear or non-linear. 1. 4x2 + 11x = 1 ...
... A linear equation in one variable is an equation that can be written in the form ax + b = 0 where a and b are real numbers and a ≠ 0. Determine whether the equation is linear or non-linear. 1. 4x2 + 11x = 1 ...
Lecture: Boundary Value Problem Boundary Value Problem 1 The
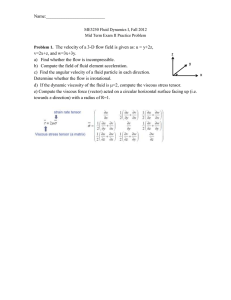
... This example is also a fluid flow problem. The original problem definition is available in Schlichting [Boundary Layer Theory]. Figure below illustrates the features of the problem. A disk of radius R is rotating with the angular speed ω in still fluid. The flow is steady, incompressible, has consta ...
... This example is also a fluid flow problem. The original problem definition is available in Schlichting [Boundary Layer Theory]. Figure below illustrates the features of the problem. A disk of radius R is rotating with the angular speed ω in still fluid. The flow is steady, incompressible, has consta ...
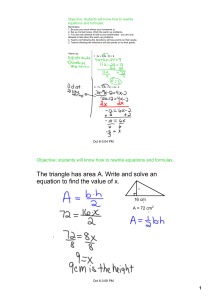
The triangle has area A. Write and solve an equation to
... walking rate of each student. Formula: distance = (rate)(time) d = rt to save time the teacher solves the formula for 'r' and programs the computer to determine the rate for each hiker. the computer asks each student how many minutes did they take. When the student enters the number, it ev ...
... walking rate of each student. Formula: distance = (rate)(time) d = rt to save time the teacher solves the formula for 'r' and programs the computer to determine the rate for each hiker. the computer asks each student how many minutes did they take. When the student enters the number, it ev ...
1.1 - ASU
... be used to come up with two equations which only involve the variables y and z. These equations in turn can be solved for y and z, which in turn will give us the value of x. The bad news is that it takes a lot more work and a lot more care, but it can be done. ...
... be used to come up with two equations which only involve the variables y and z. These equations in turn can be solved for y and z, which in turn will give us the value of x. The bad news is that it takes a lot more work and a lot more care, but it can be done. ...
... Suppose that A and do not satisfy the Coulomb gauge condition. Show that the Coulomb gauge can be reached by selecting a suitable , which is ...
... Suppose that A and do not satisfy the Coulomb gauge condition. Show that the Coulomb gauge can be reached by selecting a suitable , which is ...
Simplify Expressions to Solve Equations.
... Isolate the variable term on one side: Add (or subtract) to get the variable term on one side of the equation and a number on the other using the addition (or subtraction) property of equality. ...
... Isolate the variable term on one side: Add (or subtract) to get the variable term on one side of the equation and a number on the other using the addition (or subtraction) property of equality. ...