Chapter 7 Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
... ψ = (ψ1 , ψ2 , ψ3 , ψ4 )T into two 2-component spinors is unavoidable like in the non-relativistic limit (see below). It can be shown that (7.14) is the unique irreducible unitary representation of the Dirac algebra (7.10), up to unitary equivalence αi → U αi U −1 , β → U βU −1 with U U † = 1. Relat ...
... ψ = (ψ1 , ψ2 , ψ3 , ψ4 )T into two 2-component spinors is unavoidable like in the non-relativistic limit (see below). It can be shown that (7.14) is the unique irreducible unitary representation of the Dirac algebra (7.10), up to unitary equivalence αi → U αi U −1 , β → U βU −1 with U U † = 1. Relat ...
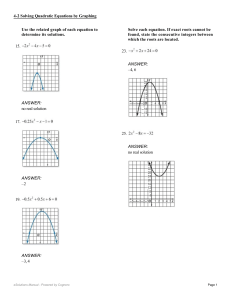
2.2 Equations of Lines Point-Slope Form of a Line ) ( xxmyy
... solve for x. • To find the y-intercept, let x = 0 and solve for y. ...
... solve for x. • To find the y-intercept, let x = 0 and solve for y. ...
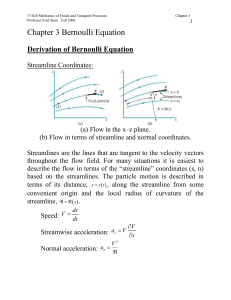
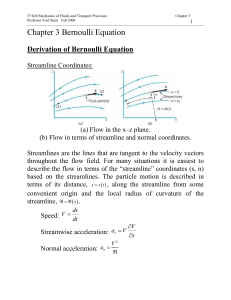
A System of Equations
... • If you plot all of the solutions to a linear equation on a coordinate plane, they form the line. All the points on the line are solutions to the equation- they make the equation true. • A linear equation as an infinite amount of solutions- there are an infinite amount of points on the graph. ...
... • If you plot all of the solutions to a linear equation on a coordinate plane, they form the line. All the points on the line are solutions to the equation- they make the equation true. • A linear equation as an infinite amount of solutions- there are an infinite amount of points on the graph. ...
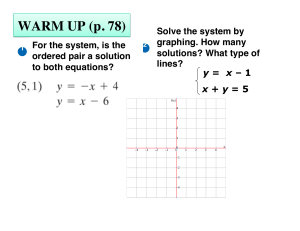
6.2ab solve systems by substitution
... Substitute value from Step 2 into (revised) equation from Step 1. Solve. ! ...
... Substitute value from Step 2 into (revised) equation from Step 1. Solve. ! ...