solving for a variable
... solve for in the equation. Step 2 Identify the operations on this variable and the order in which they are applied. Step 3 Use inverse operations to undo operations and isolate the variable. ...
... solve for in the equation. Step 2 Identify the operations on this variable and the order in which they are applied. Step 3 Use inverse operations to undo operations and isolate the variable. ...
2-1 Solving One-Step Equations
... the solutions of an equation is also called solving the equation. ...
... the solutions of an equation is also called solving the equation. ...
Finding the Standard Equation of an Ellipse
... The center of the ellipse is (0, 0). Because the denominator of the y2-term is larger than the denominator of the x2-term, you can conclude that the major axis is vertical. Moreover, because a = 6 the vertices are (0, –6) and (0, 6). Finally, because b = 3, the endpoints of the minor axis are (–3, 0 ...
... The center of the ellipse is (0, 0). Because the denominator of the y2-term is larger than the denominator of the x2-term, you can conclude that the major axis is vertical. Moreover, because a = 6 the vertices are (0, –6) and (0, 6). Finally, because b = 3, the endpoints of the minor axis are (–3, 0 ...
MATH 1 - jridges
... Prior to this unit, students need to have worked extensively with operations on integers, rational numbers, and square roots of nonnegative integers as indicated in the grade 6 – 8 standards for Number and Operations. In the unit students will apply and extend all of standards for algebra listed as ...
... Prior to this unit, students need to have worked extensively with operations on integers, rational numbers, and square roots of nonnegative integers as indicated in the grade 6 – 8 standards for Number and Operations. In the unit students will apply and extend all of standards for algebra listed as ...
5.7 Slope-Intercept Form
... What To Do, What To Do… Graph the equation. 2x + y = 4 Step 1: Find m and b. 2x + y = 4 – 2x = – 2x y = 4 – 2x y = –2x + 4 ...
... What To Do, What To Do… Graph the equation. 2x + y = 4 Step 1: Find m and b. 2x + y = 4 – 2x = – 2x y = 4 – 2x y = –2x + 4 ...
Answers
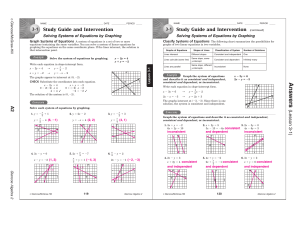
... To solve a system of linear equations by elimination, add or subtract the equations to eliminate one of the variables. You may first need to multiply one or both of the equations by a constant so that one of the variables has the same (or opposite) coefficient in one equation as it has in the other. ...
... To solve a system of linear equations by elimination, add or subtract the equations to eliminate one of the variables. You may first need to multiply one or both of the equations by a constant so that one of the variables has the same (or opposite) coefficient in one equation as it has in the other. ...
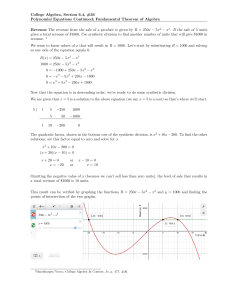
Section 6.6 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Polynomial
... Notice that the degree of the function in Example 1 is the same as the number of zeros. This is true for all polynomial functions. However, all of the zeros are not necessarily real zeros. Polynomials functions, like quadratic functions, may have complex zeros that are not real numbers. ...
... Notice that the degree of the function in Example 1 is the same as the number of zeros. This is true for all polynomial functions. However, all of the zeros are not necessarily real zeros. Polynomials functions, like quadratic functions, may have complex zeros that are not real numbers. ...