Answers to the 13-2 two column notes
... Viscosity – is the resistance to flow and affects the force behind a volcanoes eruption. Pahoehoe- Mafic lava that cools rapidly to form a crust on surface of the flow. If the lava continues to flow after crust forms, it wrinkles the crust to form this type of rock called pahoehoe. It is smooth with ...
... Viscosity – is the resistance to flow and affects the force behind a volcanoes eruption. Pahoehoe- Mafic lava that cools rapidly to form a crust on surface of the flow. If the lava continues to flow after crust forms, it wrinkles the crust to form this type of rock called pahoehoe. It is smooth with ...
Volcanoes
... have not recently erupted nor do they give indications of erupting in the future. > Thousands of these types of volcanoes exist. ...
... have not recently erupted nor do they give indications of erupting in the future. > Thousands of these types of volcanoes exist. ...
Volcano Report
... through landmasses, but also break through the sea floor and form islands. The Hawaiian Islands formed from volcanoes. Volcano Facts Stages of Volcanic Activity Volcanic activity can range from permanently active to inactive. During the active state, volcanoes can erupt. The inactive stage is when v ...
... through landmasses, but also break through the sea floor and form islands. The Hawaiian Islands formed from volcanoes. Volcano Facts Stages of Volcanic Activity Volcanic activity can range from permanently active to inactive. During the active state, volcanoes can erupt. The inactive stage is when v ...
powerpoint_Volcanoes Lava and Types of Eruptions
... become trapped underground in a narrow crack. – Builds up pressure until it sprays out of the ground. ...
... become trapped underground in a narrow crack. – Builds up pressure until it sprays out of the ground. ...
Volcano activity
... become trapped underground in a narrow crack. – Builds up pressure until it sprays out of the ground. ...
... become trapped underground in a narrow crack. – Builds up pressure until it sprays out of the ground. ...
Virtual Volcano Lab - www .alexandria .k12 .mn .us
... --Using the topic menu in the lower right corner, read about: 1) Tectonic Plates: Where are most of the active volcanoes found? __________________ 2) The Ring of Fire: Where is the Ring of Fire located? ___________________________ 3) The Layers Within: How do volcanoes form? ________________________ ...
... --Using the topic menu in the lower right corner, read about: 1) Tectonic Plates: Where are most of the active volcanoes found? __________________ 2) The Ring of Fire: Where is the Ring of Fire located? ___________________________ 3) The Layers Within: How do volcanoes form? ________________________ ...
Hot Spot
... he people who live near Italy’s Mount Vesuvius (veh-SOO-veeuhs) must be ready to leave the area at any time. Why? Vesuvius, a huge volcano, may soon erupt, or explode. That means big trouble for those people—all 2 million of them! ...
... he people who live near Italy’s Mount Vesuvius (veh-SOO-veeuhs) must be ready to leave the area at any time. Why? Vesuvius, a huge volcano, may soon erupt, or explode. That means big trouble for those people—all 2 million of them! ...
Volcanoes - davis.k12.ut.us
... scientists learn more about the inside of the earth. But they have many downsides too. If you want to know more about volcanoes, read on! ...
... scientists learn more about the inside of the earth. But they have many downsides too. If you want to know more about volcanoes, read on! ...
Do All VolCAnoES ERupT In THE SAmE WAy?
... The force of an eruption and its effects depend on the type The violent eruption of Mt Lamington, Papua of volcano. There are four main types New Guinea, on 21 January 1951 took local people of volcano and they each erupt in by surprise. Many people had not even realised different ways: the mountain ...
... The force of an eruption and its effects depend on the type The violent eruption of Mt Lamington, Papua of volcano. There are four main types New Guinea, on 21 January 1951 took local people of volcano and they each erupt in by surprise. Many people had not even realised different ways: the mountain ...
Introduction to volcanoes, volcanic eruptions, and volcanic
... ex: CRBs 17–15 Ma; Deccan Traps--India 65 Ma; Siberian Traps ~250 Ma) ...
... ex: CRBs 17–15 Ma; Deccan Traps--India 65 Ma; Siberian Traps ~250 Ma) ...
Mt. Vesuvius - Central Square School District
... Minerals from lava: Plagioclase, Augate, Nephaline… ...
... Minerals from lava: Plagioclase, Augate, Nephaline… ...
Chapter 10.1
... OTHER VOLCANIC LANDFORMS • Calderas - a large depression in a volcano. This is cause by the collapse of the top of a composite volcano or from the collapse of the top of a shield volcano. • Necks and Pipes – most volcanoes get magma through conduits called pipes that connect a magma chamber to the ...
... OTHER VOLCANIC LANDFORMS • Calderas - a large depression in a volcano. This is cause by the collapse of the top of a composite volcano or from the collapse of the top of a shield volcano. • Necks and Pipes – most volcanoes get magma through conduits called pipes that connect a magma chamber to the ...
notable events and disasters of 2014. highlights of volcanic eruptions
... • The leading edge of the molten rock stalled at the edge of town on Oct. 30, but lava began to break away at several other upslope spots.. • Between October 30 and November 10, the flow smothered part of a cemetery, and burned down a garden shed, tires, some metal materials, and vegetation. ...
... • The leading edge of the molten rock stalled at the edge of town on Oct. 30, but lava began to break away at several other upslope spots.. • Between October 30 and November 10, the flow smothered part of a cemetery, and burned down a garden shed, tires, some metal materials, and vegetation. ...
VOLCANIC HAZARDS: INTRODUCTION
... Controlled by plate tectonics 80% at subduction zones - stratovolcanoes (composite cones) - explosive calderas Fujiyama - Japan, Vesuvius - Italy, Mayon - Philippines, Mount Hood - Oregon USA Constructive margins - rift volcanoes - less explosive + more effusive - Iceland Hot spot volcanoes - Hawaii ...
... Controlled by plate tectonics 80% at subduction zones - stratovolcanoes (composite cones) - explosive calderas Fujiyama - Japan, Vesuvius - Italy, Mayon - Philippines, Mount Hood - Oregon USA Constructive margins - rift volcanoes - less explosive + more effusive - Iceland Hot spot volcanoes - Hawaii ...
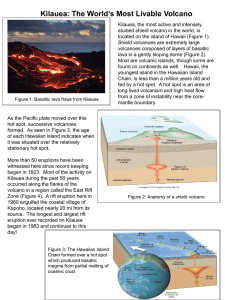
Kilauea: The World`s Most Livable Volcano
... located on the island of Hawaii (Figure 1). Shield volcanoes are extremely large volcanoes composed of layers of basaltic lava in a gently sloping dome (Figure 2). Most are volcanic islands, though some are found on continents as well. Hawaii, the youngest island in the Hawaiian Island Chain, is les ...
... located on the island of Hawaii (Figure 1). Shield volcanoes are extremely large volcanoes composed of layers of basaltic lava in a gently sloping dome (Figure 2). Most are volcanic islands, though some are found on continents as well. Hawaii, the youngest island in the Hawaiian Island Chain, is les ...
Volcano Lecture ppt
... • Kills plants • Contaminates water supplies • Respiratory hazard for humans and animals ...
... • Kills plants • Contaminates water supplies • Respiratory hazard for humans and animals ...
Chapter 5 lesson 2
... a long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface the opening through which molten rock and gas leave a volcano the area covered by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent a bowl shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening a material found in magma that i ...
... a long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface the opening through which molten rock and gas leave a volcano the area covered by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent a bowl shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening a material found in magma that i ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... (also the largest volcano on earth) ...
... (also the largest volcano on earth) ...
Parts of a Volcano
... The more silica the greater the viscosity. Flow is slowed due to the long chains of silica molecules ...
... The more silica the greater the viscosity. Flow is slowed due to the long chains of silica molecules ...
Volcanoes Day 1 - NVHSEarthScienceOlsen
... • The particles produced in volcanic eruptions are called pyroclastic material. • Pyroclastic materials include ash, cinders and lapili. • The most abundant gas associated with volcanic activity is water vapor. • A cinder cone is a type of volcano that is built almost entirely from ejected lava frag ...
... • The particles produced in volcanic eruptions are called pyroclastic material. • Pyroclastic materials include ash, cinders and lapili. • The most abundant gas associated with volcanic activity is water vapor. • A cinder cone is a type of volcano that is built almost entirely from ejected lava frag ...
Chapter 9 Section 1 Notes
... is forced to the Earth’s surface. Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called _________________. Non explosive Eruptions 1. _________________________eruptions are the most common type of eruption. 2. These eruptions produce relatively calm flows of ______________. Explosive Eruptions 1. ____ ...
... is forced to the Earth’s surface. Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called _________________. Non explosive Eruptions 1. _________________________eruptions are the most common type of eruption. 2. These eruptions produce relatively calm flows of ______________. Explosive Eruptions 1. ____ ...
Shapes of igneous bodies
... Pyroclastic Fall Deposits – material falls from vertical eruption, well sorted, blankets everything, very extensive distribution, voluminous eruptions Pyroclastic Flow Deposits – 400-800°C, 50 to 200km/hr, unsorted deposits, dense flows that fill valleys, often welded (fiamme), contains trapped gase ...
... Pyroclastic Fall Deposits – material falls from vertical eruption, well sorted, blankets everything, very extensive distribution, voluminous eruptions Pyroclastic Flow Deposits – 400-800°C, 50 to 200km/hr, unsorted deposits, dense flows that fill valleys, often welded (fiamme), contains trapped gase ...
Typical shield volcano Mauna Loa, Hawaii
... Types of volcanoes – Composite volcano (Stratovolcano) – Large, classic-shaped volcano – Most located adjacent to the Pacific Ocean – Interbedded lava flows and layers of pyroclastic debris ...
... Types of volcanoes – Composite volcano (Stratovolcano) – Large, classic-shaped volcano – Most located adjacent to the Pacific Ocean – Interbedded lava flows and layers of pyroclastic debris ...
Axial Seamount

Axial Seamount (also Coaxial Seamount or Axial Volcano) is a seamount and submarine volcano located on the Juan de Fuca Ridge, approximately 480 km (298 mi) west of Cannon Beach, Oregon. Standing 1,100 m (3,609 ft) high, Axial Seamount is the youngest volcano and current eruptive center of the Cobb-Eickelberg Seamount chain. Located at the center of both a geological hotspot and a mid-ocean ridge, the seamount is geologically complex, and its origins are still poorly understood. Axial Seamount is set on a long, low-lying plateau, with two large rift zones trending 50 km (31 mi) to the northeast and southwest of its center. The volcano features an unusual rectangular caldera, and its flanks are pockmarked by fissures, vents, sheet flows, and pit craters up to 100 m (328 ft) deep; its geology is further complicated by its intersection with several smaller seamounts surrounding it.Axial Seamount was first detected in the 1970s by satellite altimetry, and mapped and explored by Pisces IV, DSV Alvin, and others through the 1980s. A large package of sensors was dropped on the seamount through 1992, and the New Millennium Observatory was established on its flanks in 1996. Axial Seamount received significant scientific attention following the seismic detection of a submarine eruption at the volcano in January 1998, the first time a submarine eruption had been detected and followed in situ. Subsequent cruises and analysis showed that the volcano had generated lava flows up to 13 m (43 ft) thick, and the total eruptive volume was found to be 18,000–76,000 km3 (4,300–18,200 cu mi). Axial Seamount erupted again in April 2011, producing a mile-wide lava flow and fulfilling a 16-year cycle that had been predicted in 2006.