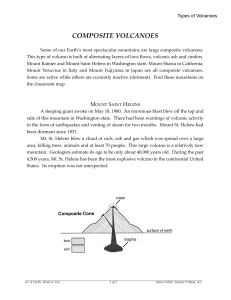
composite volcanoes - Mesa Public Schools
... Now Paricutín is just another small, inactive volcano. Geologists were able to learn a great deal about volcanoes from studying Paricutín while it was active. ...
... Now Paricutín is just another small, inactive volcano. Geologists were able to learn a great deal about volcanoes from studying Paricutín while it was active. ...
magma and lava
... 12.The depression that results when a volcanic cone collapses over an emptying magma chamber is called a caldera. 13.Why does magma rise to the surface? Magma rises because it is less dense than the surrounding material 14.What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is molten rock undergrou ...
... 12.The depression that results when a volcanic cone collapses over an emptying magma chamber is called a caldera. 13.Why does magma rise to the surface? Magma rises because it is less dense than the surrounding material 14.What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is molten rock undergrou ...
Virtual Volcano
... Now go to the left hand side of the screen. Find the menu. Click on “volcano types.” How many common categories of volcanoes are there? ___________ Italy is home to what mountain that destroyed Pompeii in 79 ad? _____________ Now click on “cinder cone” in the bottom right hand side. Name two famous ...
... Now go to the left hand side of the screen. Find the menu. Click on “volcano types.” How many common categories of volcanoes are there? ___________ Italy is home to what mountain that destroyed Pompeii in 79 ad? _____________ Now click on “cinder cone” in the bottom right hand side. Name two famous ...
Volcano - Greenwich Central School
... volcanoes along a deep ocean trench. An area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust above it. ...
... volcanoes along a deep ocean trench. An area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust above it. ...
Volcanoes - Jefferson Township Public Schools
... Evidence of Volcano Volcanic neck: the core of a volcano’s vent that remains after the outer layers of lava and tephra have been eroded away from an extinct volcano Caldera: the large opening formed at the top of a volcano when the crater collapses into the vent following an eruption ...
... Evidence of Volcano Volcanic neck: the core of a volcano’s vent that remains after the outer layers of lava and tephra have been eroded away from an extinct volcano Caldera: the large opening formed at the top of a volcano when the crater collapses into the vent following an eruption ...
Cornell Notes Template
... 3) Composite volcano (also called Stratovolcano) Large base and tall (often has snow on the peaks) Steep slopes Medium-high viscosity lava Explosive eruptions that occur suddenly after years of being inactive Made of alternate layers of pyroclastic material and lava o Examples- Mount St. He ...
... 3) Composite volcano (also called Stratovolcano) Large base and tall (often has snow on the peaks) Steep slopes Medium-high viscosity lava Explosive eruptions that occur suddenly after years of being inactive Made of alternate layers of pyroclastic material and lava o Examples- Mount St. He ...
iss__st4_files/Comenius Volcanoes
... Not only can satellites be used for forecasting eruptions by analyzing the movements of the surface, but they can also be used to observe gas and ash clouds and lava flows that are created during an eruption. ...
... Not only can satellites be used for forecasting eruptions by analyzing the movements of the surface, but they can also be used to observe gas and ash clouds and lava flows that are created during an eruption. ...
Volcanoes Powerpoint
... population. These are designed to monitor and potentially to predict the eruptive behaviour of the volcano in question. ...
... population. These are designed to monitor and potentially to predict the eruptive behaviour of the volcano in question. ...
Volcanoes
... population. These are designed to monitor and potentially to predict the eruptive behaviour of the volcano in question. ...
... population. These are designed to monitor and potentially to predict the eruptive behaviour of the volcano in question. ...
Unit 4 Chapter
... form steep sided volcanoes with a lot of activity Most famous volcanoes Mt St Helen's & Mt Vesuvius The Aleutian Islands, island arcs, by the North Pacific Ocean, ...
... form steep sided volcanoes with a lot of activity Most famous volcanoes Mt St Helen's & Mt Vesuvius The Aleutian Islands, island arcs, by the North Pacific Ocean, ...
The 1996 Surtseyan Type Eruption in Karymskoye Intracaldera Lake
... Belousova (Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia ; e - ma il: [email protected]) On January 2-3, 1996 a surtseyan type eruption with a discharge rate of basaltic magma of ~10 millions kg/s occurred in Karymskoe caldera lake. Initial water depth above ...
... Belousova (Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia ; e - ma il: [email protected]) On January 2-3, 1996 a surtseyan type eruption with a discharge rate of basaltic magma of ~10 millions kg/s occurred in Karymskoe caldera lake. Initial water depth above ...
Study Guide: Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... 1. Different types of dangers associated with earthquakes and how the earthquake causes those dangers ...
... 1. Different types of dangers associated with earthquakes and how the earthquake causes those dangers ...
DR 9.1a- Volcanic Eruptions
... 5. Which of the following can happen during nonexplosive eruptions? a. violent explosions c. huge lava flows b. tons of rock blast into air d. fire shooting into the air 6. The most common type of volcanic eruption is ...
... 5. Which of the following can happen during nonexplosive eruptions? a. violent explosions c. huge lava flows b. tons of rock blast into air d. fire shooting into the air 6. The most common type of volcanic eruption is ...
Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity - sir
... volcanic pipes are short conduits that connect a magma chamber to the surface. ...
... volcanic pipes are short conduits that connect a magma chamber to the surface. ...
Volcano-Glacier Interactions during Historical Eruptions of Aleutian
... drainages and produced deposits with more classic morphology, including blocky, lobate margins and levees. Lahars and mixed avalanches of snow, water, and pyroclastic debris formed beyond the pyroclastic flows that swept across snow. Flow morphologies, lithologies, and depositional contacts indicate ...
... drainages and produced deposits with more classic morphology, including blocky, lobate margins and levees. Lahars and mixed avalanches of snow, water, and pyroclastic debris formed beyond the pyroclastic flows that swept across snow. Flow morphologies, lithologies, and depositional contacts indicate ...
Volcanoes - Helena High School
... • An extinct volcano is one that has not erupted for a very long time and is considered unlikely to do so in the future. ...
... • An extinct volcano is one that has not erupted for a very long time and is considered unlikely to do so in the future. ...
Earth Science - Mr.E Science
... As magma rises toward the surface, the dissolved gas begins to expand as pressure decreases and this exerts an enormous upward force on the magma. When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the magma chamber through the pipe until it flows or explodes out of the vent. ...
... As magma rises toward the surface, the dissolved gas begins to expand as pressure decreases and this exerts an enormous upward force on the magma. When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the magma chamber through the pipe until it flows or explodes out of the vent. ...
Earth Science--Ch 9 Volcanoes Review Guide
... like/shape, how they erupt, what types of materials they are primarily made of, where they tend to form.) ...
... like/shape, how they erupt, what types of materials they are primarily made of, where they tend to form.) ...
Volcanism 3
... Helicopter view, NW coast (btw, this cliff tends to collapse quite often on the road) ...
... Helicopter view, NW coast (btw, this cliff tends to collapse quite often on the road) ...
Take a `Chance` on the volcano erupting
... other gases at fumaroles (minor vents on the volcano’s surface); • Shallow seismic swarms (groups of small earthquake shocks), indicating very near surface movement of magma and gases; • Harmonic seismic tremors (shocks produced by magma movement), indicating magma rising from a magma reservoir belo ...
... other gases at fumaroles (minor vents on the volcano’s surface); • Shallow seismic swarms (groups of small earthquake shocks), indicating very near surface movement of magma and gases; • Harmonic seismic tremors (shocks produced by magma movement), indicating magma rising from a magma reservoir belo ...
Axial Seamount

Axial Seamount (also Coaxial Seamount or Axial Volcano) is a seamount and submarine volcano located on the Juan de Fuca Ridge, approximately 480 km (298 mi) west of Cannon Beach, Oregon. Standing 1,100 m (3,609 ft) high, Axial Seamount is the youngest volcano and current eruptive center of the Cobb-Eickelberg Seamount chain. Located at the center of both a geological hotspot and a mid-ocean ridge, the seamount is geologically complex, and its origins are still poorly understood. Axial Seamount is set on a long, low-lying plateau, with two large rift zones trending 50 km (31 mi) to the northeast and southwest of its center. The volcano features an unusual rectangular caldera, and its flanks are pockmarked by fissures, vents, sheet flows, and pit craters up to 100 m (328 ft) deep; its geology is further complicated by its intersection with several smaller seamounts surrounding it.Axial Seamount was first detected in the 1970s by satellite altimetry, and mapped and explored by Pisces IV, DSV Alvin, and others through the 1980s. A large package of sensors was dropped on the seamount through 1992, and the New Millennium Observatory was established on its flanks in 1996. Axial Seamount received significant scientific attention following the seismic detection of a submarine eruption at the volcano in January 1998, the first time a submarine eruption had been detected and followed in situ. Subsequent cruises and analysis showed that the volcano had generated lava flows up to 13 m (43 ft) thick, and the total eruptive volume was found to be 18,000–76,000 km3 (4,300–18,200 cu mi). Axial Seamount erupted again in April 2011, producing a mile-wide lava flow and fulfilling a 16-year cycle that had been predicted in 2006.