What are Volcanoes?
... Often people think of a river of red-hot lava when they think of a volcanic eruption. Lava flow is a river of hot lava. Lava flows are common in nonexplosive eruptions where the lava flows continually. Sometimes they will spray, they are not explosive. ...
... Often people think of a river of red-hot lava when they think of a volcanic eruption. Lava flow is a river of hot lava. Lava flows are common in nonexplosive eruptions where the lava flows continually. Sometimes they will spray, they are not explosive. ...
Volcanoes Day 1 - NVHSEarthScienceOlsen
... – This means that something that has a high viscosity does not flow easily. A substance with a high viscosity would be honey. A substance with a low viscosity would be water. – If the lava of a volcano has _______ _______, the _______ of a volcano will be _______ _______. – There are three factors t ...
... – This means that something that has a high viscosity does not flow easily. A substance with a high viscosity would be honey. A substance with a low viscosity would be water. – If the lava of a volcano has _______ _______, the _______ of a volcano will be _______ _______. – There are three factors t ...
Geological Cycle Rock Formation
... Geological significance of Igneous Rocks The upper 16 kilometers (10 mi) of Earth's crust is composed of approximately 95% igneous rocks with only a thin, widespread covering of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are geologically important because: q Their minerals and global chemistr ...
... Geological significance of Igneous Rocks The upper 16 kilometers (10 mi) of Earth's crust is composed of approximately 95% igneous rocks with only a thin, widespread covering of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are geologically important because: q Their minerals and global chemistr ...
10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions 10.1 The Nature of
... • Types of pyroclastic material - Ash and dust—fine, glassy fragments - Pumice—frothy, air-filled lava - Lapilli—walnut-sized particles - Cinders—pea-sized particles • Particles larger than lapilli - Blocks—hardened lava - Bombs—ejected as hot lava ...
... • Types of pyroclastic material - Ash and dust—fine, glassy fragments - Pumice—frothy, air-filled lava - Lapilli—walnut-sized particles - Cinders—pea-sized particles • Particles larger than lapilli - Blocks—hardened lava - Bombs—ejected as hot lava ...
Stratovolcano and Shield Volcano Morphology
... Stratovolcanoes are typically tall, steep-sided, and nearly symmetrical cones built from alternating layers of lava flows and ash. Most stratovolcanoes have a central crater at the summit that vents gases and lava. The lava is typically thick and resistant to flow, which prevents gases from escaping ...
... Stratovolcanoes are typically tall, steep-sided, and nearly symmetrical cones built from alternating layers of lava flows and ash. Most stratovolcanoes have a central crater at the summit that vents gases and lava. The lava is typically thick and resistant to flow, which prevents gases from escaping ...
Color Luster Streak
... Sediment – rock material that forms where rocks are broken down into smaller pieces or dissolved in water as rocks erode rock cycle – the series of processes that change one type of rock into another type of rock Section 8.2 igneous rock – rock formed from magma or lava that has been cooled and hard ...
... Sediment – rock material that forms where rocks are broken down into smaller pieces or dissolved in water as rocks erode rock cycle – the series of processes that change one type of rock into another type of rock Section 8.2 igneous rock – rock formed from magma or lava that has been cooled and hard ...
File
... Geological significance of Igneous Rocks The upper 16 kilometers (10 mi) of Earth's crust is composed of approximately 95% igneous rocks with only a thin, widespread covering of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are geologically important because: Their minerals and global chemistr ...
... Geological significance of Igneous Rocks The upper 16 kilometers (10 mi) of Earth's crust is composed of approximately 95% igneous rocks with only a thin, widespread covering of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks are geologically important because: Their minerals and global chemistr ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... All volcanoes have a pocket of magma beneath the surface, called a magma chamber, where the magma collects. Magma moves upward through a pipe, a long tube that extends from Earth’s crust up though the top of the volcano, connecting the magma chamber to Earth’s surface. Molten rock and gas leave the ...
... All volcanoes have a pocket of magma beneath the surface, called a magma chamber, where the magma collects. Magma moves upward through a pipe, a long tube that extends from Earth’s crust up though the top of the volcano, connecting the magma chamber to Earth’s surface. Molten rock and gas leave the ...
Volcanoes
... 6. Often the volcano sides will be higher than the vent forming a depression called a crater ...
... 6. Often the volcano sides will be higher than the vent forming a depression called a crater ...
Section 2: Volcanic Activity - SS. Peter and Paul Salesian
... • There are many types of magma. – Some are thick and flows slowly. – Some are fluid and flow very easily. – The temperature of the magma will determine how it flows. ...
... • There are many types of magma. – Some are thick and flows slowly. – Some are fluid and flow very easily. – The temperature of the magma will determine how it flows. ...
SZO - economic geology_Final
... History), John Muntean (University of Nevada, Reno), Adam Simon (University of Michigan) Subduction zones are important tectonic settings for the formation of hydrothermal and other ore deposits, which are the source of most of the world’s copper, gold, silver, molybdenum, and other metals. Here, th ...
... History), John Muntean (University of Nevada, Reno), Adam Simon (University of Michigan) Subduction zones are important tectonic settings for the formation of hydrothermal and other ore deposits, which are the source of most of the world’s copper, gold, silver, molybdenum, and other metals. Here, th ...
Volcanoes-Help of Hindrance
... Severe weather-related events often accompany volcanic activity. These include lightning, thunderstorms, and whirlwinds (including tornadoes). In addition, the heat caused by a volcanic eruption can melt snow and glaciers, which can lead to flooding and landslides. Ash clouds from an erupting volcan ...
... Severe weather-related events often accompany volcanic activity. These include lightning, thunderstorms, and whirlwinds (including tornadoes). In addition, the heat caused by a volcanic eruption can melt snow and glaciers, which can lead to flooding and landslides. Ash clouds from an erupting volcan ...
The rock cycle shows how rocks change.
... 8–3.4 Explain how igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks are interrelated in the rock cycle. 8–3.7 Illustrate the creation and changing of landforms that have occurred through geologic processes (including volcanic eruptions and mountain-building forces). ...
... 8–3.4 Explain how igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks are interrelated in the rock cycle. 8–3.7 Illustrate the creation and changing of landforms that have occurred through geologic processes (including volcanic eruptions and mountain-building forces). ...
Volcanoes - BrainPOP
... 1. Which of the following is an opinion about volcanic activity? a. Volcanoes are made of hardened lava b. A large number of volcanoes can be found along the edge of the Pacific Ocean c. The 1991 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo was the scariest volcanic event in history d. Shield volcanoes can actually cre ...
... 1. Which of the following is an opinion about volcanic activity? a. Volcanoes are made of hardened lava b. A large number of volcanoes can be found along the edge of the Pacific Ocean c. The 1991 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo was the scariest volcanic event in history d. Shield volcanoes can actually cre ...
Unit 5.2 PowerPoint File
... When magma flows between layers of rock and hardens to form a body of rock that is parallel to the layers of rock that surround it, a sill forms. When magma forces its way through rock layers by following existing fractures or by creating new fractures, a dike forms. Dikes cut ...
... When magma flows between layers of rock and hardens to form a body of rock that is parallel to the layers of rock that surround it, a sill forms. When magma forces its way through rock layers by following existing fractures or by creating new fractures, a dike forms. Dikes cut ...
11-Heimaey- Living with Natural Hazards.indd
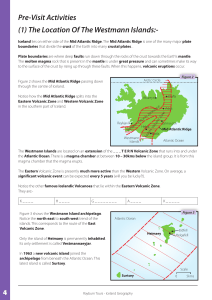
... Pre-Visit Activities (1) The Location Of The Westmann Islands:Iceland lies on either side of the Mid Atlantic Ridge. The Mid Atlantic Ridge is one of the many major plate boundaries that divide the crust of the Earth into many crustal plates. . Plate boundaries are where deep faults run down through ...
... Pre-Visit Activities (1) The Location Of The Westmann Islands:Iceland lies on either side of the Mid Atlantic Ridge. The Mid Atlantic Ridge is one of the many major plate boundaries that divide the crust of the Earth into many crustal plates. . Plate boundaries are where deep faults run down through ...
Volcano Making - Manchester Museum
... and watch the lava as it flows out of your volcano! The lava will only erupt if there is baking powder in the crater. When your volcanic eruption has finished, it is a good idea to take out the crater and give it a quick wash before having another go! ...
... and watch the lava as it flows out of your volcano! The lava will only erupt if there is baking powder in the crater. When your volcanic eruption has finished, it is a good idea to take out the crater and give it a quick wash before having another go! ...
chapter 6 - Geophile.net
... 10. What causes a big bulge to slowly grow on the flank of an active Cascades volcano? * It grows because rising magma is pushing it up 11. If you visit Mount St. Helens, Washington, you will see thousands of trees lying on the ground, all parallel to one another. Explain how they got that way. * Th ...
... 10. What causes a big bulge to slowly grow on the flank of an active Cascades volcano? * It grows because rising magma is pushing it up 11. If you visit Mount St. Helens, Washington, you will see thousands of trees lying on the ground, all parallel to one another. Explain how they got that way. * Th ...
Hazard map for volcanic ballistic impacts at El Chichón volcano
... The 1982 eruption of El Chichón Volcano in southeastern Mexico had a strong social and environmental impact. The eruption resulted in the worst volcanic disaster in the recorded history of Mexico, causing about 2,000 casualties, displacing thousands, and producing severe economic losses. Even when s ...
... The 1982 eruption of El Chichón Volcano in southeastern Mexico had a strong social and environmental impact. The eruption resulted in the worst volcanic disaster in the recorded history of Mexico, causing about 2,000 casualties, displacing thousands, and producing severe economic losses. Even when s ...
Volcano Types (39)
... • Water vapor and carbon dioxide are trapped in magma by the pressure of the surrounding magma and rock. • As magma nears the surface, it is under less pressure, which allows gases to escape, causing non explosive volcanoes. • Gas that builds up to high pressures eventually causes explosive eruption ...
... • Water vapor and carbon dioxide are trapped in magma by the pressure of the surrounding magma and rock. • As magma nears the surface, it is under less pressure, which allows gases to escape, causing non explosive volcanoes. • Gas that builds up to high pressures eventually causes explosive eruption ...
Volcanoes PPT - Van Buren Public Schools
... tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. • The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. • An example is the Hawaiian Islands ...
... tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. • The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. • An example is the Hawaiian Islands ...
Ch3_Igneous
... common at Earth’s surface (Deccan Traps) – The presence of water promotes partial melting of the mantle to create basalt ...
... common at Earth’s surface (Deccan Traps) – The presence of water promotes partial melting of the mantle to create basalt ...
Mount Pleasant Caldera

The Mount Pleasant Caldera is a large eroded Late Devonian volcanic caldera complex, located in the northern Appalachian Mountains of southwestern New Brunswick, Canada. It is one of few noticeable pre-Cenozoic calderas, and its formation is associated to a period of crustal thinning that followed the Acadian orogeny in the northern Appalachian Mountains.It sits relatively near to the coastline.