Summary presentation 12.2 alternating currents File
... How do we measure the size of an alternating p.d. (or current) when its value changes from one instant to the next? We could use the peak value, but this occurs only for a moment. What about the average value? This is zero over a complete cycle and so is not very helpful! ...
... How do we measure the size of an alternating p.d. (or current) when its value changes from one instant to the next? We could use the peak value, but this occurs only for a moment. What about the average value? This is zero over a complete cycle and so is not very helpful! ...
2938633 Datasheet
... device continuously supplies the IBOOST output current. The device can supply a nominal output current of IN up to an ambient operating temperature of +60°C. The output power must be decreased by 2.5% per Kelvin temperature increase for ambient operating temperatures over +60°C. At ambient operating ...
... device continuously supplies the IBOOST output current. The device can supply a nominal output current of IN up to an ambient operating temperature of +60°C. The output power must be decreased by 2.5% per Kelvin temperature increase for ambient operating temperatures over +60°C. At ambient operating ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... problem of unregulated ac to regulated dc conversion). This transformation is achieved by the use of semiconductor devices that operate as power switches, turning on and off with a high switching frequency. From the control point of view, power electronic circuits and system constitute excellent exa ...
... problem of unregulated ac to regulated dc conversion). This transformation is achieved by the use of semiconductor devices that operate as power switches, turning on and off with a high switching frequency. From the control point of view, power electronic circuits and system constitute excellent exa ...
EMS_Lecture_32
... If the load is capacitive, current I leads the terminal voltage by . In the new phasor diagram, the voltage Ex across the synchronous reactance is still 90° ahead of the current. Eo is again equal to the phasor sum of E and Ex. The terminal voltage is now greater than the induced voltage Eo ...
... If the load is capacitive, current I leads the terminal voltage by . In the new phasor diagram, the voltage Ex across the synchronous reactance is still 90° ahead of the current. Eo is again equal to the phasor sum of E and Ex. The terminal voltage is now greater than the induced voltage Eo ...
QSX4
... VCB=30V VEB=6V IC=1.5A, IB=75mA VCE=2V, IC=200mA ∗ VCE=2V, IE=−200mA, f=100MHz ∗ VCB=10V, IE=0A, f=1MHz ...
... VCB=30V VEB=6V IC=1.5A, IB=75mA VCE=2V, IC=200mA ∗ VCE=2V, IE=−200mA, f=100MHz ∗ VCB=10V, IE=0A, f=1MHz ...
Luminist Series
... 1). To avoid fire, personal injury, and/or damage to dimmer, turn power OFF at the circuit breaker and test that the power is OFF before wiring. 2). To reduce the risk of overheating and possible damage to other equipment, do not install to control a receptacle, a motor-operated appliance, a fluores ...
... 1). To avoid fire, personal injury, and/or damage to dimmer, turn power OFF at the circuit breaker and test that the power is OFF before wiring. 2). To reduce the risk of overheating and possible damage to other equipment, do not install to control a receptacle, a motor-operated appliance, a fluores ...
POINT OF LOAD CONVERTERS - The Topologies
... and power requirements. Before the point of load converter may be considered, it is necessary to investigate the converter that provides the distributed bus. Historically, the front-end converter has always stepped down to a fixed output to supply the majority of voltages needed by the sub-system. H ...
... and power requirements. Before the point of load converter may be considered, it is necessary to investigate the converter that provides the distributed bus. Historically, the front-end converter has always stepped down to a fixed output to supply the majority of voltages needed by the sub-system. H ...
PhET Electric Circuit Simulator
... 15. Check the “non-contact ammeter” in the tools menu. Place the cross hairs of this meter on different wires at different points in the circuit. Does the current reading change for different points around the circuit? _____________________ ...
... 15. Check the “non-contact ammeter” in the tools menu. Place the cross hairs of this meter on different wires at different points in the circuit. Does the current reading change for different points around the circuit? _____________________ ...
'AND' Away we go!
... Your comfort level with your responses to the following single design challenge should suggest if the presentation that follows will increase you knowledge base on the topic embedded within these questions. ...
... Your comfort level with your responses to the following single design challenge should suggest if the presentation that follows will increase you knowledge base on the topic embedded within these questions. ...
Unit - Current Electricity Worksheet
... 12. If there is a current of 2.0 A through a hair dryer transferring 15 kJ of energy in 55 s, what is the potential difference across the dryer? 13. An electric drill operates at a potential difference of 120V and draws a current of 6.0 mA. If it takes 45 s for the drill to make a hole in a piece of ...
... 12. If there is a current of 2.0 A through a hair dryer transferring 15 kJ of energy in 55 s, what is the potential difference across the dryer? 13. An electric drill operates at a potential difference of 120V and draws a current of 6.0 mA. If it takes 45 s for the drill to make a hole in a piece of ...
Problem
... intention is to update this continuously as mistakes are found. It is important that we have your help in this. If you feel there is a mistake and it does not appear here, then email Chuck at [email protected] and he will check it out as soon as he can. ...
... intention is to update this continuously as mistakes are found. It is important that we have your help in this. If you feel there is a mistake and it does not appear here, then email Chuck at [email protected] and he will check it out as soon as he can. ...
File
... I-V Curve for PV Devices in Parallel The overall I-V characteristics of a system of PV devices in parallel are dependent on the similarity of the current outputs of the individual devices. ...
... I-V Curve for PV Devices in Parallel The overall I-V characteristics of a system of PV devices in parallel are dependent on the similarity of the current outputs of the individual devices. ...
2 LXY28161 Specification
... output current will decrease to 25%. As soon as the temperature is below 110℃, the thermal error flag will return to 0 and the output current will recover from the 25% current. 2.13 LED Supply Voltage LXY28161 are designed to operate with VDS ranging from 0.4V to 0.8V (depending on IOUT=5 ~ 60mA), c ...
... output current will decrease to 25%. As soon as the temperature is below 110℃, the thermal error flag will return to 0 and the output current will recover from the 25% current. 2.13 LED Supply Voltage LXY28161 are designed to operate with VDS ranging from 0.4V to 0.8V (depending on IOUT=5 ~ 60mA), c ...
PPT: Circuits 1
... logic ICs are either TTL (transistor) or CMOS (MOSFET) based. ◊ These are expanded further into numerous families of devices that each have their own electrical and performance characteristics. ...
... logic ICs are either TTL (transistor) or CMOS (MOSFET) based. ◊ These are expanded further into numerous families of devices that each have their own electrical and performance characteristics. ...
180154 - 11050C00 Installation Instructions
... Finally, we measure the output, terminal 1. The output voltage is normally higher than the input voltage. Typical output voltage at 25ºC is 14.2Vdc. Cold readings are typically higher and hot readings are typically lower. If the indicator light is on, that indicates current is now flowing through th ...
... Finally, we measure the output, terminal 1. The output voltage is normally higher than the input voltage. Typical output voltage at 25ºC is 14.2Vdc. Cold readings are typically higher and hot readings are typically lower. If the indicator light is on, that indicates current is now flowing through th ...
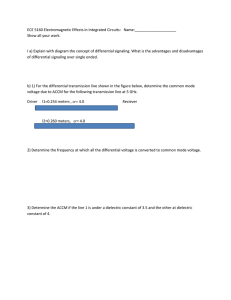
ECE51602012springfinals
... voltage due to ACCM for the following transmission line at 5 GHz. Driver ...
... voltage due to ACCM for the following transmission line at 5 GHz. Driver ...
speed control of dc motor using pulse width modulation
... • The motors become generators and feed the resulting current into an on-board resistance. • When the driver calls for brake, the power circuit connections to the motors are changed from their power configuration to a brake configuration and the resistors inserted into the motor circuit. As the moto ...
... • The motors become generators and feed the resulting current into an on-board resistance. • When the driver calls for brake, the power circuit connections to the motors are changed from their power configuration to a brake configuration and the resistors inserted into the motor circuit. As the moto ...
The Active Front End allows sinusoidal mains current
... represents a "Low Harmonic Drive" for almost all applications. Mains interferences / mains conditions THD(i) less than 4 % No converter transformer required Integrated radio frequency interference filter according to EN 61800-3 category C3 Power factor cos Phi 1 independent of the load situa ...
... represents a "Low Harmonic Drive" for almost all applications. Mains interferences / mains conditions THD(i) less than 4 % No converter transformer required Integrated radio frequency interference filter according to EN 61800-3 category C3 Power factor cos Phi 1 independent of the load situa ...
HM010 OCS072
... outputs when the controller (e.g., OCS100) enters idle/stop mode. The default turns the outputs OFF when the controller enters idle/stop mode. By selecting the Module Setup tab, each output can be set to either turn ON, turn OFF or to hold the last state. Generally, most applications use the default ...
... outputs when the controller (e.g., OCS100) enters idle/stop mode. The default turns the outputs OFF when the controller enters idle/stop mode. By selecting the Module Setup tab, each output can be set to either turn ON, turn OFF or to hold the last state. Generally, most applications use the default ...
Télécharger
... The LM323 are three-terminal positive voltage regulators with a preset 5 V output and a load driving capability of 3 A. New circuit design and processing techniques are used to provide the high output current without sacrificing the regulation characteristics of lower current devices. TO-220 ...
... The LM323 are three-terminal positive voltage regulators with a preset 5 V output and a load driving capability of 3 A. New circuit design and processing techniques are used to provide the high output current without sacrificing the regulation characteristics of lower current devices. TO-220 ...
ComboLight New Construction Recessed w/Trim - 12V AR111 - 2 Light
... De-Rated wattage labels are available. 12V Primary voltage is available. 75W and 100W magnetic transformers are remote and sold separately. ...
... De-Rated wattage labels are available. 12V Primary voltage is available. 75W and 100W magnetic transformers are remote and sold separately. ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.