MAX6969 16-Port, 5.5V Constant-Current LED Driver General Description Features
... For applications requiring LED fault detection, refer to the MAX6984*, which automatically detects open-circuit LEDs. For safety-related applications requiring a watchdog timer, refer to the MAX6979, which includes a fail-safe feature that blanks the display if the serial interface becomes inactive ...
... For applications requiring LED fault detection, refer to the MAX6984*, which automatically detects open-circuit LEDs. For safety-related applications requiring a watchdog timer, refer to the MAX6979, which includes a fail-safe feature that blanks the display if the serial interface becomes inactive ...
CY36602610
... farms into the electrical network, Flexible AC transmission Systems, FACTS, are widely used. The FACTS STATCOM system is one of them. ST ATCOM has some advantages, such as better performance, quick response, smaller in size, less cost, and capable of satisfying both active and reactive power require ...
... farms into the electrical network, Flexible AC transmission Systems, FACTS, are widely used. The FACTS STATCOM system is one of them. ST ATCOM has some advantages, such as better performance, quick response, smaller in size, less cost, and capable of satisfying both active and reactive power require ...
low-pass filter
... Let‘s apply a voltage Vin of a very low frequency and of an amplitude of 10V to the input of the circuit in the figure. If we let the frequency become lower and lower, the input voltage will become a DC voltage. This input voltage Vin of 10V will charge the capacitor and in a moment the output volta ...
... Let‘s apply a voltage Vin of a very low frequency and of an amplitude of 10V to the input of the circuit in the figure. If we let the frequency become lower and lower, the input voltage will become a DC voltage. This input voltage Vin of 10V will charge the capacitor and in a moment the output volta ...
electrical power system
... and so the output is able to tail off as the battery charges. This tail off doesn't occur at major orienteering events, where the power requirements are continuous and the charger needs to keep supplying it. What is important is the current the charger can deliver at 100% duty cycle. Many cheap car ...
... and so the output is able to tail off as the battery charges. This tail off doesn't occur at major orienteering events, where the power requirements are continuous and the charger needs to keep supplying it. What is important is the current the charger can deliver at 100% duty cycle. Many cheap car ...
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
... For a resistor of 100 kΩ the value for C is ≈ 33 nF. Values from 47 nF to 100 nF were tried in the lab with good success. The schematics of a 4-channel example are shown in Figure 5. There are only few requirements for the resistor and capacitor, e.g., temperature coefficient or tolerance can be neg ...
... For a resistor of 100 kΩ the value for C is ≈ 33 nF. Values from 47 nF to 100 nF were tried in the lab with good success. The schematics of a 4-channel example are shown in Figure 5. There are only few requirements for the resistor and capacitor, e.g., temperature coefficient or tolerance can be neg ...
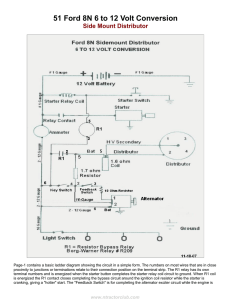
51 Ford 8N 6 to 12 Volt Conversion
... If I were doing this conversion again I would move the terminal strip to the left edge of the fire wall because there is more space between the metal and the steering gear box behind that location. The wiring from the starter relay through the ammeter and to the terminal strip and alternator is two ...
... If I were doing this conversion again I would move the terminal strip to the left edge of the fire wall because there is more space between the metal and the steering gear box behind that location. The wiring from the starter relay through the ammeter and to the terminal strip and alternator is two ...
AP358 LOW POWER DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS Description
... voltage may be larger than V+ without damaging the device. Protection should be provided to prevent the input voltages from going negative more than -0.3 VDC (at 25°C). An input clamp diode with a resistor to the IC input terminal can be used. To reduce the power supply current drain, the amplifiers ...
... voltage may be larger than V+ without damaging the device. Protection should be provided to prevent the input voltages from going negative more than -0.3 VDC (at 25°C). An input clamp diode with a resistor to the IC input terminal can be used. To reduce the power supply current drain, the amplifiers ...
ac circuits
... mH. The generator supplies an rms voltage of 115 V at a frequency of 60.0 Hz. (b) What is the phase angle between the voltage and the current in the circuit? ...
... mH. The generator supplies an rms voltage of 115 V at a frequency of 60.0 Hz. (b) What is the phase angle between the voltage and the current in the circuit? ...
T.W. Barton and D.J. Perreault, “An RF-input Outphasing Power Amplifier with RF Signal Decomposition Network,” 2015 International Microwave Symposium , May 2015.
... the inputs to the four branch PAs. Conceptually, the phase relationship between the four combiner inputs that results in nearly-resistive load modulation (over e.g. a 10:1 range) can be synthesized by varying the RCN terminating resistances over the same resistive range. In practice, the varying RCN ...
... the inputs to the four branch PAs. Conceptually, the phase relationship between the four combiner inputs that results in nearly-resistive load modulation (over e.g. a 10:1 range) can be synthesized by varying the RCN terminating resistances over the same resistive range. In practice, the varying RCN ...
CN-0161
... (Continued from first page) Circuits from the Lab circuits are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the Circuits from the Lab circuits in the design of your product, no other license is granted by i ...
... (Continued from first page) Circuits from the Lab circuits are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the Circuits from the Lab circuits in the design of your product, no other license is granted by i ...
Electricity - is the flow of electrons
... d. the pipes through which water flows e. the distance that water flows through the circuit 4) Which of the following is true about the electrical circuit in your flashlight? a. Charge moves around the circuit very fast - nearly as fast as the speed of light. b. The battery supplies the charge (elec ...
... d. the pipes through which water flows e. the distance that water flows through the circuit 4) Which of the following is true about the electrical circuit in your flashlight? a. Charge moves around the circuit very fast - nearly as fast as the speed of light. b. The battery supplies the charge (elec ...
Professional Literacy Development, Electrical Measurements
... real world solutions. In Electrical Engineering, voltage, current and resistance are three important quantities that need to be measured accurately. Wrong measurements are often the cause of technical faults in electrical and electronic systems. ...
... real world solutions. In Electrical Engineering, voltage, current and resistance are three important quantities that need to be measured accurately. Wrong measurements are often the cause of technical faults in electrical and electronic systems. ...
Redalyc.Distributed maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic
... power extracted from PV panels at a module granularity level [3], [5]. The proposed AB structure uses a parallel-like connection instead of the cascade, series-like, connection of typical DMPPT solutions [3], therefore the AB circuit requires one inductor less than DMPPT based on Boost, Buck or Buck ...
... power extracted from PV panels at a module granularity level [3], [5]. The proposed AB structure uses a parallel-like connection instead of the cascade, series-like, connection of typical DMPPT solutions [3], therefore the AB circuit requires one inductor less than DMPPT based on Boost, Buck or Buck ...
Alternating Current (AC) Circuits
... source of 35.36 V rms at 1591.5 Hz. (a) Calculate the peak voltage. (b) Find the reactances XL and XC and the impedance Z. (c) Find the peak current in the circuit. (d) Determine the phase angle α. (e) Calculate the peak voltage across each element in the circuit. ...
... source of 35.36 V rms at 1591.5 Hz. (a) Calculate the peak voltage. (b) Find the reactances XL and XC and the impedance Z. (c) Find the peak current in the circuit. (d) Determine the phase angle α. (e) Calculate the peak voltage across each element in the circuit. ...
Low Power DC/DC Boost Converter in SOT-23
... 7.3.5 Thermal Shutdown An internal thermal shutdown is implemented and turns off the internal MOSFETs when the typical junction temperature of 168°C is exceeded. The thermal shutdown has a hysteresis of typically 25°C. This data is based on statistical means and is not tested during the regular mass ...
... 7.3.5 Thermal Shutdown An internal thermal shutdown is implemented and turns off the internal MOSFETs when the typical junction temperature of 168°C is exceeded. The thermal shutdown has a hysteresis of typically 25°C. This data is based on statistical means and is not tested during the regular mass ...
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING EA3220: ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT & MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
... three phase system, errors & remedies in wattmeter and energy meter. UNIT II: Instrument transformers: Instrument Transformer and their applications in the extension of instrument range, Introduction to measurement of speed, frequency and power factor. UNIT III: Measurement of Parameters: Different ...
... three phase system, errors & remedies in wattmeter and energy meter. UNIT II: Instrument transformers: Instrument Transformer and their applications in the extension of instrument range, Introduction to measurement of speed, frequency and power factor. UNIT III: Measurement of Parameters: Different ...
Designing the Reliable Driver for the Latest 450A/1.2kV IGBT
... can meet the insulation requirement what is defined by the section 4.2.3.2 of IEC61800-51:2003. The section 5.2.3.2.2 of value and type of test voltage specifies test voltage, and insulation voltage can be calculated according to the following equation: Eq.1 (In TN and TT systems, U0 is the r.m.s va ...
... can meet the insulation requirement what is defined by the section 4.2.3.2 of IEC61800-51:2003. The section 5.2.3.2.2 of value and type of test voltage specifies test voltage, and insulation voltage can be calculated according to the following equation: Eq.1 (In TN and TT systems, U0 is the r.m.s va ...
Elements of Power
... What is Work and Power? • Work is the energy transferred when a force displaces a mass • Power is the rate at which work is done • Typically mechanical, electrical, or fluid ...
... What is Work and Power? • Work is the energy transferred when a force displaces a mass • Power is the rate at which work is done • Typically mechanical, electrical, or fluid ...
DC Circuits - UCF Physics
... The rod in the figure is made of two materials. The figure is not drawn to scale. Each conductor has a square cross section 3.00 mm on a side. The first material has a resistivity of 4.00 × 10–3 Ω · m and is 25.0 cm long, while the second material has a resistivity of 6.00 × 10–3 Ω · m and is 40.0 ...
... The rod in the figure is made of two materials. The figure is not drawn to scale. Each conductor has a square cross section 3.00 mm on a side. The first material has a resistivity of 4.00 × 10–3 Ω · m and is 25.0 cm long, while the second material has a resistivity of 6.00 × 10–3 Ω · m and is 40.0 ...
LP339 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Input voltage range, VI (either input) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . −0.3 V to 36 V Input current, VI ≤ −0.3 V (see Note 3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . −5 ...
... Input voltage range, VI (either input) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . −0.3 V to 36 V Input current, VI ≤ −0.3 V (see Note 3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . −5 ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.