ee301 - series circuits, kirchhoff`s voltage law
... f. Apply concept of voltage potential between two points to the use of subscripts and the location of the reference voltage g. Analyze a series resistive circuit with the ground placed at various points h. Explain and compute how voltage divides between elements in a series circuit Series Circuits T ...
... f. Apply concept of voltage potential between two points to the use of subscripts and the location of the reference voltage g. Analyze a series resistive circuit with the ground placed at various points h. Explain and compute how voltage divides between elements in a series circuit Series Circuits T ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-ISSN: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331,
... for storing and supplying energy. For charging and discharging of the batteries a converter which can operate in both directions is required. Bidirectional converters are the main part of a system where it is necessary to interface an energy storage device to a renewable energy sources like fuel cel ...
... for storing and supplying energy. For charging and discharging of the batteries a converter which can operate in both directions is required. Bidirectional converters are the main part of a system where it is necessary to interface an energy storage device to a renewable energy sources like fuel cel ...
Interrelationships among the network code, the evolution
... In this case, the WF is interconnected with a systems whose topology includes a line with serial compensation. There is a potential risk that, for some reason, the WF will remain connected radially through the compensated line. Connected in this manner, the serial capacitors would be able to resonat ...
... In this case, the WF is interconnected with a systems whose topology includes a line with serial compensation. There is a potential risk that, for some reason, the WF will remain connected radially through the compensated line. Connected in this manner, the serial capacitors would be able to resonat ...
Temperature sensor solutions for low-voltage
... a nominal voltage and the regulator tolerance can cause a voltage output of 1.6V or lower. Therefore, to monitor a location by using an analog temperature sensor from -50°C to +150°C with a supply voltage of 1.8V nominal, the maximum gain that analog sensor can have is 6 mV/°C. To handle this gain a ...
... a nominal voltage and the regulator tolerance can cause a voltage output of 1.6V or lower. Therefore, to monitor a location by using an analog temperature sensor from -50°C to +150°C with a supply voltage of 1.8V nominal, the maximum gain that analog sensor can have is 6 mV/°C. To handle this gain a ...
LXM1623-12-4x
... lamp degradation occurs, while allowing significant power savings at lower dim levels. The modules convert DC voltage from the system battery or AC adapter directly to high frequency, high-voltage waves required to ignite and operate CCFL lamps. A 5V input inverter also is available (LXM1623-05-4x), ...
... lamp degradation occurs, while allowing significant power savings at lower dim levels. The modules convert DC voltage from the system battery or AC adapter directly to high frequency, high-voltage waves required to ignite and operate CCFL lamps. A 5V input inverter also is available (LXM1623-05-4x), ...
MAX8536EVKIT
... that sets the charge-pump frequency or functions as a logic enabler. The EV kit circuit provides a 3-pin jumper (JU1) to configure the TIMER pin. Place a shunt across pins 2-3 of JU1 to shut down the IC. Place a shunt across pins 1-2 of JU1 to connect the TIMER pin to ground through R7 to set the ch ...
... that sets the charge-pump frequency or functions as a logic enabler. The EV kit circuit provides a 3-pin jumper (JU1) to configure the TIMER pin. Place a shunt across pins 2-3 of JU1 to shut down the IC. Place a shunt across pins 1-2 of JU1 to connect the TIMER pin to ground through R7 to set the ch ...
AN-912 Common Data Transmission Parameters and their Definitions
... IIL—Low-Level Input Current. The current into (out of) an input when a low-level voltage is applied to that input. Note that current out of a device pin is given as a negative value. II—Maximum Input Current. The current into (out of) an input when the maximum specified input voltage is applied to t ...
... IIL—Low-Level Input Current. The current into (out of) an input when a low-level voltage is applied to that input. Note that current out of a device pin is given as a negative value. II—Maximum Input Current. The current into (out of) an input when the maximum specified input voltage is applied to t ...
1. device purpose 2. delivery set 10. enclosures
... (1) through a terminal board for connecting network cable (4). Stabilized output voltage (12 V DC, Channel 1) is supplied to a terminal board for connecting outer mains (9) through a photocell control circuit (2). Voltage is supplied at the illumination level of a photocell (5) less than 10±5 lx. Wh ...
... (1) through a terminal board for connecting network cable (4). Stabilized output voltage (12 V DC, Channel 1) is supplied to a terminal board for connecting outer mains (9) through a photocell control circuit (2). Voltage is supplied at the illumination level of a photocell (5) less than 10±5 lx. Wh ...
Difet OPA627 OPA637 Precision High-Speed
... gain greater than five. Noise gain refers to the closed-loop gain of a circuit as if the non-inverting op amp input were being driven. For example, the OPA637 may be used in a non-inverting amplifier with gain greater than five, or an inverting amplifier of gain greater than four. ...
... gain greater than five. Noise gain refers to the closed-loop gain of a circuit as if the non-inverting op amp input were being driven. For example, the OPA637 may be used in a non-inverting amplifier with gain greater than five, or an inverting amplifier of gain greater than four. ...
How to Calculate/Find the Rating of Transformer in kVA (Single
... P = 11000V x 5.25A = 57,750 VA = 57.75kVA Or P = V x I (Secondary voltages x Secondary Current) P= 415V x 139.1A = 57,726 VA = 57.72kVA Once again, we noticed that the rating of Transformer (on Nameplate) is 100kVA but according to calculation…it comes about 57kVA… The difference comes due to ignora ...
... P = 11000V x 5.25A = 57,750 VA = 57.75kVA Or P = V x I (Secondary voltages x Secondary Current) P= 415V x 139.1A = 57,726 VA = 57.72kVA Once again, we noticed that the rating of Transformer (on Nameplate) is 100kVA but according to calculation…it comes about 57kVA… The difference comes due to ignora ...
Evaluates: MAX15023 MAX15023 Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... MAX15023 dual, synchronous step-down controller. The MAX15023 EV kit is designed to operate from a single DC power supply that provides 9V to 16V and 5A of current. The MAX15023 controller can also be operated using a separate 4.5V to 5.5V power source applied at the VCC and SGND PCB pads. When oper ...
... MAX15023 dual, synchronous step-down controller. The MAX15023 EV kit is designed to operate from a single DC power supply that provides 9V to 16V and 5A of current. The MAX15023 controller can also be operated using a separate 4.5V to 5.5V power source applied at the VCC and SGND PCB pads. When oper ...
Evaluates: MAX8662 MAX8662 Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... 1) Enable outputs OUT1–OUT7 by placing a shunt across pins 1-2 of EN1–EN7 (Table 1). 2) Set the OUT4–OUT7 outputs voltages by setting shunts SL1 and SL2, as shown in Table 3. Note that the SL1 and SL2 jumper settings are read-only on power-up. Changes to these jumpers after powerup are ignored. 3) P ...
... 1) Enable outputs OUT1–OUT7 by placing a shunt across pins 1-2 of EN1–EN7 (Table 1). 2) Set the OUT4–OUT7 outputs voltages by setting shunts SL1 and SL2, as shown in Table 3. Note that the SL1 and SL2 jumper settings are read-only on power-up. Changes to these jumpers after powerup are ignored. 3) P ...
25V, 2A, PNP Bipolar Transistor, SOT-89
... Any and all SANYO Semiconductor Co.,Ltd. products described or contained herein are, with regard to "standard application", intended for the use as general electronics equipment (home appliances, AV equipment, communication device, office equipment, industrial equipment etc.). The products mentioned ...
... Any and all SANYO Semiconductor Co.,Ltd. products described or contained herein are, with regard to "standard application", intended for the use as general electronics equipment (home appliances, AV equipment, communication device, office equipment, industrial equipment etc.). The products mentioned ...
How To Measure Voltage - MIT Technology Review
... There are many issues to consider when measuring higher voltages. When specifying a data acquisition system, the first question you should ask is whether the system will be safe. Making high-voltage measurements can be hazardous to your equipment, to the unit under test, and even to you and your co ...
... There are many issues to consider when measuring higher voltages. When specifying a data acquisition system, the first question you should ask is whether the system will be safe. Making high-voltage measurements can be hazardous to your equipment, to the unit under test, and even to you and your co ...
Advance electroncis Assignment Question
... What is Digital to Analog Convertor ? Draw and Explain R-2R DAC ? Also give the advantages and disadvantages of R-2R Digital to Analog convertor. Mention the types of ADC and describe successive approximation type of ...
... What is Digital to Analog Convertor ? Draw and Explain R-2R DAC ? Also give the advantages and disadvantages of R-2R Digital to Analog convertor. Mention the types of ADC and describe successive approximation type of ...
DS1813 - Maxim Integrated
... The DS1813 provides the functions of detecting out-of-tolerance power-supply conditions and warning a processor-based system of impending power failure. When VCC is detected as out-of-tolerance, the RST signal is asserted. On power-up, RST is kept active for approximately 150ms after the power suppl ...
... The DS1813 provides the functions of detecting out-of-tolerance power-supply conditions and warning a processor-based system of impending power failure. When VCC is detected as out-of-tolerance, the RST signal is asserted. On power-up, RST is kept active for approximately 150ms after the power suppl ...
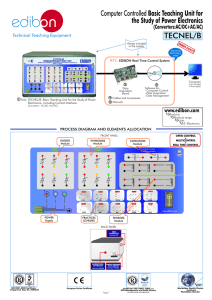
TECNEL/B Basic Teaching Unit for the Study of Power Electronics (Converters:AC/DC+AC/AC)
... - TECNEL/B. Computer Controlled Basic Teaching Unit for the Study of Power Electronics. (Converters: AC/DC + AC/AC). Offered in other catalogue: - TECNEL. Computer Controlled Teaching Unit for the Study of Power Electronics.(Converters: DC/AC + AC/DC + DC/DC + ...
... - TECNEL/B. Computer Controlled Basic Teaching Unit for the Study of Power Electronics. (Converters: AC/DC + AC/AC). Offered in other catalogue: - TECNEL. Computer Controlled Teaching Unit for the Study of Power Electronics.(Converters: DC/AC + AC/DC + DC/DC + ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.