Volcanism 1
... 10 inches at 10 miles downwind (ash and pumice); 1 inch at 60 miles downwind; ¸ inch at 300 miles downwind Pyroclastic Flows ...
... 10 inches at 10 miles downwind (ash and pumice); 1 inch at 60 miles downwind; ¸ inch at 300 miles downwind Pyroclastic Flows ...
Slide 1
... 4. Dome cone.. Thick lava, bulbous shape… blocks vents & traps gas… erupts destroying itself eg. St Helens USA. 5. Shield… build up of successive slow lava flows … broad base & gentle slope… gentle eruptions flow down the side of volc. Eg. Mauna Lao, Hawaii Hot springs & Geysers…(i) water & material ...
... 4. Dome cone.. Thick lava, bulbous shape… blocks vents & traps gas… erupts destroying itself eg. St Helens USA. 5. Shield… build up of successive slow lava flows … broad base & gentle slope… gentle eruptions flow down the side of volc. Eg. Mauna Lao, Hawaii Hot springs & Geysers…(i) water & material ...
Eruption
... • These volcanoes are typically tens of miles across and 10,000 or more feet in height • they have moderately steep sides • Volcanologists call these "strato-" or composite volcanoes because they consist of layers of solid lava flows mixed with layers of sand- or gravel-like volcanic rock called cin ...
... • These volcanoes are typically tens of miles across and 10,000 or more feet in height • they have moderately steep sides • Volcanologists call these "strato-" or composite volcanoes because they consist of layers of solid lava flows mixed with layers of sand- or gravel-like volcanic rock called cin ...
Volcano Glossary III
... Pumice from basaltic magma, where the walls surrounding the gas bubbles have burst leaving only the stems between each three former bubble walls, and junctions at the intersection of four bubbles. This gives a rock a honeycomb structure. Though it seems light enough to float on water, reticulite doe ...
... Pumice from basaltic magma, where the walls surrounding the gas bubbles have burst leaving only the stems between each three former bubble walls, and junctions at the intersection of four bubbles. This gives a rock a honeycomb structure. Though it seems light enough to float on water, reticulite doe ...
Volcanoes Webquest - Mrs. Gomez`s Class
... Read the following website to answer the following questions. http://volcanoeruptions.wikispaces.com/Igneous+Intrusions 12. List the six types of intrusions and describe their shape and size. a) ...
... Read the following website to answer the following questions. http://volcanoeruptions.wikispaces.com/Igneous+Intrusions 12. List the six types of intrusions and describe their shape and size. a) ...
3-2 Notes: Volcanoes Eruptions • Volcano
... • Molten rock is torn apart as gas ___________________ pop. • Lava ______________ and hardens into rock as it flies through the air. • Rocks rip loose from the volcano’s walls during the eruption. • Tiny rock fragments: volcanic ___________ • __________________ sized rock fragments: volcanic cinders ...
... • Molten rock is torn apart as gas ___________________ pop. • Lava ______________ and hardens into rock as it flies through the air. • Rocks rip loose from the volcano’s walls during the eruption. • Tiny rock fragments: volcanic ___________ • __________________ sized rock fragments: volcanic cinders ...
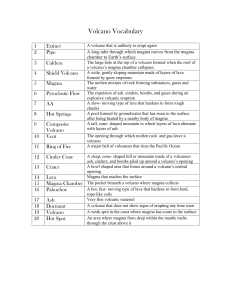
Volcano Vocabulary
... The expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption A slow- moving type of lava that hardens to form rough chunks A pool formed by groundwater that has risen to the surface after being heated by a nearby body of magma A tall, cone- shaped mountain in which layers of ...
... The expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption A slow- moving type of lava that hardens to form rough chunks A pool formed by groundwater that has risen to the surface after being heated by a nearby body of magma A tall, cone- shaped mountain in which layers of ...
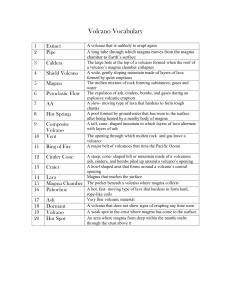
Volcano Vocabulary
... The expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption A slow- moving type of lava that hardens to form rough chunks A pool formed by groundwater that has risen to the surface after being heated by a nearby body of magma A tall, cone- shaped mountain in which layers of ...
... The expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption A slow- moving type of lava that hardens to form rough chunks A pool formed by groundwater that has risen to the surface after being heated by a nearby body of magma A tall, cone- shaped mountain in which layers of ...
Igneous Rocks - Occurrence and Classification
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
Hot Spot
... he people who live near Italy’s Mount Vesuvius (veh-SOO-veeuhs) must be ready to leave the area at any time. Why? Vesuvius, a huge volcano, may soon erupt, or explode. That means big trouble for those people—all 2 million of them! ...
... he people who live near Italy’s Mount Vesuvius (veh-SOO-veeuhs) must be ready to leave the area at any time. Why? Vesuvius, a huge volcano, may soon erupt, or explode. That means big trouble for those people—all 2 million of them! ...
Volcanoes
... that shoot small pieces of magma and ash into the air. O The magma then cools and hardens as it falls back to the Earth, forming a cinder cone. O In many cases, cinder cones form on the sides of a larger volcano. ...
... that shoot small pieces of magma and ash into the air. O The magma then cools and hardens as it falls back to the Earth, forming a cinder cone. O In many cases, cinder cones form on the sides of a larger volcano. ...
Volcanoes Powerpoint
... Pyroclastic Flow - lahars • Hot volcanic activity can melt snow and ice • Melt water picks up rock and debris • Forms fast flowing, high energy torrents • Destroys all in its path ...
... Pyroclastic Flow - lahars • Hot volcanic activity can melt snow and ice • Melt water picks up rock and debris • Forms fast flowing, high energy torrents • Destroys all in its path ...
Volcanoes
... Pyroclastic Flow - lahars • Hot volcanic activity can melt snow and ice • Melt water picks up rock and debris • Forms fast flowing, high energy torrents • Destroys all in its path ...
... Pyroclastic Flow - lahars • Hot volcanic activity can melt snow and ice • Melt water picks up rock and debris • Forms fast flowing, high energy torrents • Destroys all in its path ...
Primary Middle Phase - Volcano Session Notes
... • World map of volcanoes erupted within the past 10,000 years ...
... • World map of volcanoes erupted within the past 10,000 years ...
Lecture 21 Mount St Helens November 29th
... Debris Avalanches Volcanoes are not very stable structures. From time to time, they collapse producing large rock and ash avalanches that travel at high speeds down valleys. Collapse maybe caused by an eruption or an earthquake. They can travel up to 50 miles from their source, burying everythin ...
... Debris Avalanches Volcanoes are not very stable structures. From time to time, they collapse producing large rock and ash avalanches that travel at high speeds down valleys. Collapse maybe caused by an eruption or an earthquake. They can travel up to 50 miles from their source, burying everythin ...
Volcanoes and Earthquakes
... amount of gases 3. Rockfall (RF) – landslides/deformation 4. Volcano Tectonics (VT) – earthquakes in volcano ...
... amount of gases 3. Rockfall (RF) – landslides/deformation 4. Volcano Tectonics (VT) – earthquakes in volcano ...
The Origin and Petrogenesis of Mount Hasan (Small Mt. Hasan) and
... Small Mt. Hasan (3069m) and Keçiboyduran (2727m) volcanoes are located within the Cappadocian Volcanic Field in Central Anatolia (Turkey). These Plio-Quaternary volcanoes are major stratovolcanoes of Cappadocian Volcanic Complex (CVC). In this study, we present petrography and major-trace element ge ...
... Small Mt. Hasan (3069m) and Keçiboyduran (2727m) volcanoes are located within the Cappadocian Volcanic Field in Central Anatolia (Turkey). These Plio-Quaternary volcanoes are major stratovolcanoes of Cappadocian Volcanic Complex (CVC). In this study, we present petrography and major-trace element ge ...
Volcanoes Power Point - Boone County Schools
... Pyroclastic Flow - lahars • Hot volcanic activity can melt snow and ice • Melt water picks up rock and debris • Forms fast flowing, high energy torrents • Destroys all in its path ...
... Pyroclastic Flow - lahars • Hot volcanic activity can melt snow and ice • Melt water picks up rock and debris • Forms fast flowing, high energy torrents • Destroys all in its path ...
Types of Volcanoes
... fine-grained rock. However, andesite is usually light to medium gray in color. Andesite is one of the most common volcanic rocks and can contain olivine, a green mineral. There are different stages of volcanic activity as well as a variety of rocks manufactured through volcanic eruptions. Most peopl ...
... fine-grained rock. However, andesite is usually light to medium gray in color. Andesite is one of the most common volcanic rocks and can contain olivine, a green mineral. There are different stages of volcanic activity as well as a variety of rocks manufactured through volcanic eruptions. Most peopl ...
PDF file of Chapter 5 lecture - Volcanoes
... Alternating lava flows and layers of pyroclastic debris Most violent type of activity (e.g., Mt. Vesuvius) ...
... Alternating lava flows and layers of pyroclastic debris Most violent type of activity (e.g., Mt. Vesuvius) ...
Lecture 12
... 1. Define the term volcano and explain why geologists study volcanoes! 2. Compare and contrast 3 common types of magma! 3. Describe volcanic gases and the role they play in explosive vs effusive eruptions! 4. Identify what gives a shield volcano its distinctive shape! ...
... 1. Define the term volcano and explain why geologists study volcanoes! 2. Compare and contrast 3 common types of magma! 3. Describe volcanic gases and the role they play in explosive vs effusive eruptions! 4. Identify what gives a shield volcano its distinctive shape! ...
Debris Avalanches
... Debris Avalanches Volcanoes are not very stable structures. From time to time, they collapse producing large rock and ash avalanches that travel at high speeds down valleys. Collapse maybe caused by an eruption or an earthquake. They can travel up to 50 miles from their source, burying everythin ...
... Debris Avalanches Volcanoes are not very stable structures. From time to time, they collapse producing large rock and ash avalanches that travel at high speeds down valleys. Collapse maybe caused by an eruption or an earthquake. They can travel up to 50 miles from their source, burying everythin ...