NH_4e_Lecture_Ch05
... – One of the most lethal aspects of volcanic eruptions • Hot and race down side of volcano at speeds exceeding 400 km/hr (~250 mph) • Hot expanding gases carry low-density ash upward • Base of flow contains larger debris ...
... – One of the most lethal aspects of volcanic eruptions • Hot and race down side of volcano at speeds exceeding 400 km/hr (~250 mph) • Hot expanding gases carry low-density ash upward • Base of flow contains larger debris ...
LAB 4 - W.W. Norton
... Scroll down again until you locate the Volcanoes of the World file. Click the down arrow next to the name of the file to open the subfolders Scroll down the file until you locate the file named: Hawaii and Pacific Ocean. Click on the down arrow to open the subfolders. Scroll down until you locate Ha ...
... Scroll down again until you locate the Volcanoes of the World file. Click the down arrow next to the name of the file to open the subfolders Scroll down the file until you locate the file named: Hawaii and Pacific Ocean. Click on the down arrow to open the subfolders. Scroll down until you locate Ha ...
Focused melt supply at the Cobb hot spot / Juan de Fuca ridge
... Lamont-Doherty Earth Obervatory of Columbia University, Palisades, NY 10964 1Now at New Mexico State University, Physics Department, Las Cruces, NM 88005 ...
... Lamont-Doherty Earth Obervatory of Columbia University, Palisades, NY 10964 1Now at New Mexico State University, Physics Department, Las Cruces, NM 88005 ...
Molten rock material generated within Earth. Magma that
... Molten rock material generated within Earth. ...
... Molten rock material generated within Earth. ...
PDF version
... Volcano Seismicity.” http://volcanoes.usgs.gov/activity/ methods/seismic/signatures.php. Seismograms from Brantley and Topinka, 1984, “Volcanic Studies at the David A. Johnston Cascade Volcano Observatory”. Earthquake Information Bulletin, March-April 1984, v.16, n.2 http:// vulcan.wr.usgs.gov/Volca ...
... Volcano Seismicity.” http://volcanoes.usgs.gov/activity/ methods/seismic/signatures.php. Seismograms from Brantley and Topinka, 1984, “Volcanic Studies at the David A. Johnston Cascade Volcano Observatory”. Earthquake Information Bulletin, March-April 1984, v.16, n.2 http:// vulcan.wr.usgs.gov/Volca ...
MAUNA LOA Mauna Loa is one of five volcanoes that form the
... Mauna Loa, the volcano becomes unstable, setting the stage for large earthquakes." These earthquakes can also trigger landslides and tsunamis. An erupting Mauna Loa triggered a massive earthquake on April 2, 1868, with an estimated magnitude of 8.0, causing a landslide and a tidal wave that took man ...
... Mauna Loa, the volcano becomes unstable, setting the stage for large earthquakes." These earthquakes can also trigger landslides and tsunamis. An erupting Mauna Loa triggered a massive earthquake on April 2, 1868, with an estimated magnitude of 8.0, causing a landslide and a tidal wave that took man ...
Magma Viscosity Quiz
... 4. Magma viscosity is primarily dependent upon which combination of factors? a) Water content and temperature of magma. b) Water content and pressure of magma. c) Depth of magma source and gas content of magma. d) Composition and temperature of magma. e) Basalt content and gas content of magma. 5. W ...
... 4. Magma viscosity is primarily dependent upon which combination of factors? a) Water content and temperature of magma. b) Water content and pressure of magma. c) Depth of magma source and gas content of magma. d) Composition and temperature of magma. e) Basalt content and gas content of magma. 5. W ...
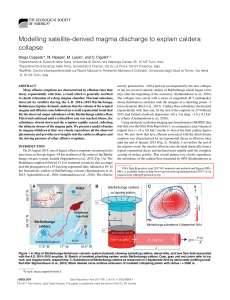
Modelling satellite-derived magma discharge to explain
... The best-fit of the exponential decay (Equation 1) to the effusion rates derived by MODIS during the Holuhraun eruption gives, in its logarithmic form (Fig. 2), an initial flow rate, Q0, of ~242 (± 121) m3 s–1 and allows us to calculate the characteristic relaxation time, τ, of 9.6 × 106 s (~111 d). ...
... The best-fit of the exponential decay (Equation 1) to the effusion rates derived by MODIS during the Holuhraun eruption gives, in its logarithmic form (Fig. 2), an initial flow rate, Q0, of ~242 (± 121) m3 s–1 and allows us to calculate the characteristic relaxation time, τ, of 9.6 × 106 s (~111 d). ...
Hotspots – Tutorial Script - FOG
... Hotspots are deep-seated sources of heat and magma that extend from depths as deep as the core-mantle boundary and generally stay fixed relative to plate motion – the plate move across the hotspots, but the hotspot doesn’t move. Volcanoes are left behind in tracks that show us the direction and spee ...
... Hotspots are deep-seated sources of heat and magma that extend from depths as deep as the core-mantle boundary and generally stay fixed relative to plate motion – the plate move across the hotspots, but the hotspot doesn’t move. Volcanoes are left behind in tracks that show us the direction and spee ...
LAVA FLOWS ON VENUS - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... Practical Applications. Using the models for flow motion and cooling discussed above to analyze real flows is difficult. Laboratory data for basalt viscosity and yield strength are very limited, and in all cases use remelted material. Field measurements have been used to estimate magma rheology, but ...
... Practical Applications. Using the models for flow motion and cooling discussed above to analyze real flows is difficult. Laboratory data for basalt viscosity and yield strength are very limited, and in all cases use remelted material. Field measurements have been used to estimate magma rheology, but ...
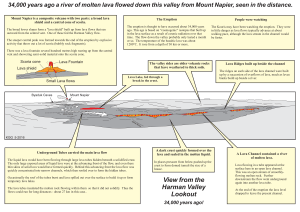
34,000 years ago a river of molten lava flowed down this valley from
... shield and a central cone of scoria. The broad lower slopes form a "lava shield" built up from lava flows that ran outward from the central vent. One of these fed the Harman Valley flow. The steeper central peak was formed towards the end of the eruption by explosive activity that threw out a lot of ...
... shield and a central cone of scoria. The broad lower slopes form a "lava shield" built up from lava flows that ran outward from the central vent. One of these fed the Harman Valley flow. The steeper central peak was formed towards the end of the eruption by explosive activity that threw out a lot of ...
Devastating landslides related to the 2002 Papandayan eruption
... volcano lies at the intersection between 07º 19’ 42” S and 107º 44” E. The 2002 Papandayan eruption was preceded by two felt earthquakes, 8 times of A-type volcanic earthquakes and 150 times of Btype volcanic earthquake. These events were followed by a phreatic eruption that took place on 11 Novembe ...
... volcano lies at the intersection between 07º 19’ 42” S and 107º 44” E. The 2002 Papandayan eruption was preceded by two felt earthquakes, 8 times of A-type volcanic earthquakes and 150 times of Btype volcanic earthquake. These events were followed by a phreatic eruption that took place on 11 Novembe ...
Super Volcanoes
... 1. super volcanoes, more specifically caldera forming volcanoes, form when magma pools in country rock. 2. After a small pool is created, the mafic magma assimilates the country rock, which is felsic, this assimilation of country rock forms rhyolitic magma. 3. Rhyolitic magma is more viscous and so ...
... 1. super volcanoes, more specifically caldera forming volcanoes, form when magma pools in country rock. 2. After a small pool is created, the mafic magma assimilates the country rock, which is felsic, this assimilation of country rock forms rhyolitic magma. 3. Rhyolitic magma is more viscous and so ...
INA PIT CRATER ON THE MOON: EXTRUSION OF WANING
... About 50% of the interior terrain is made up of the unusual bleb-like mounds with the remainder composed of two floor units: 1) a hummocky unit (44%), composed of relatively optically immature terrain with ridged and pitted textures, and 2) an optically immature blocky unit (6%) with a rougher textu ...
... About 50% of the interior terrain is made up of the unusual bleb-like mounds with the remainder composed of two floor units: 1) a hummocky unit (44%), composed of relatively optically immature terrain with ridged and pitted textures, and 2) an optically immature blocky unit (6%) with a rougher textu ...
The Big Island
... • produced by current eruptive activity • covers the surface of most of the volcano ...
... • produced by current eruptive activity • covers the surface of most of the volcano ...
Combining historical and 14C data to assess pyroclastic density
... show that the 1640, 1773, and 1886 PDC-forming eruptions are recorded in the valley, while products of the 1918 and 2006 events were likely removed. Through considering recorded/unrecorded bias in the reconstruction of past PDC emplacement in Vazcún, we calculate a minimal average return rate of 18 ...
... show that the 1640, 1773, and 1886 PDC-forming eruptions are recorded in the valley, while products of the 1918 and 2006 events were likely removed. Through considering recorded/unrecorded bias in the reconstruction of past PDC emplacement in Vazcún, we calculate a minimal average return rate of 18 ...
Unit 3: Volcanic Activity: Ranking Hazardous Volcanoes
... Unit 3: Volcanic Activity: Ranking Hazardous Volcanoes Some volcanoes can be explosively dangerous. Along with clouds of ash and other volcanic debris that can linger in the air for years after an eruption, pyroclastic flows, landslides, and mudflows are common volcanic hazards. An explosive volcano ...
... Unit 3: Volcanic Activity: Ranking Hazardous Volcanoes Some volcanoes can be explosively dangerous. Along with clouds of ash and other volcanic debris that can linger in the air for years after an eruption, pyroclastic flows, landslides, and mudflows are common volcanic hazards. An explosive volcano ...
Hot Spot
... If Vesuvius erupts, it will release hot gases, thick ashes, and lava, or red-hot liquid rock. It will be very dangerous for anyone to be nearby. “We expect that a large area could be destroyed in a few minutes,” says Edoardo Del Pezzo, a volcano expert. This is what ...
... If Vesuvius erupts, it will release hot gases, thick ashes, and lava, or red-hot liquid rock. It will be very dangerous for anyone to be nearby. “We expect that a large area could be destroyed in a few minutes,” says Edoardo Del Pezzo, a volcano expert. This is what ...
Viscosity Activity
... Background: Viscosity is a liquid’s “resistance to flow”. All Lava is made out of rock, but flows differently depending on silica content, amount of water, gas content and temperature. When lava erupts from a vent in the Earth’s crust it spreads out in all directions and eventually cools and becomes ...
... Background: Viscosity is a liquid’s “resistance to flow”. All Lava is made out of rock, but flows differently depending on silica content, amount of water, gas content and temperature. When lava erupts from a vent in the Earth’s crust it spreads out in all directions and eventually cools and becomes ...
Types of volcanic eruptions

Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has been observed. Some volcanoes may exhibit only one characteristic type of eruption during a period of activity, while others may display an entire sequence of types all in one eruptive series.There are three different types of eruptions. The most well-observed are magmatic eruptions, which involve the decompression of gas within magma that propels it forward. Phreatomagmatic eruptions are another type of volcanic eruption, driven by the compression of gas within magma, the direct opposite of the process powering magmatic activity. The third eruptive type is the phreatic eruption, which is driven by the superheating of steam via contact with magma; these eruptive types often exhibit no magmatic release, instead causing the granulation of existing rock.Within these wide-defining eruptive types are several subtypes. The weakest are Hawaiian and submarine, then Strombolian, followed by Vulcanian and Surtseyan. The stronger eruptive types are Pelean eruptions, followed by Plinian eruptions; the strongest eruptions are called ""Ultra Plinian."" Subglacial and phreatic eruptions are defined by their eruptive mechanism, and vary in strength. An important measure of eruptive strength is Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI), an order of magnitude scale ranging from 0 to 8 that often correlates to eruptive types.