* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Eruption of Mount Pinatubo
Survey
Document related concepts
Types of volcanic eruptions wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
David A. Johnston wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Volcanic ash wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Air travel disruption after the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
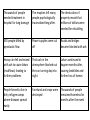
The Eruption of Mount Pinatubo Lesson Objective: To be able to explain the cause, impacts and response of a volcanic eruption in an LIC Characteristics of volcanoes lava flow ash cloud gas emissions pyroclastic flow lahars Wind can blow ash a long way, which causes it to affect a large area by covering crops and roads; collapsing roofs because of the weight and suffocating animals and humans. The main killer during an eruption is this deadly cloud of hot steam and ash that travels at over 200 km/h. Ash in the air often triggers torrential rainfall, which washes the ash and mud down the volcano like a river. This flow of molten rock does not travel quickly, so does not cause many deaths, however it does destroy farmland, property and roads. Sulphur, carbon dioxide and cyanide can all be released during an eruption, causing death to animals and humans. Causes – Mt. Pinatubo in the Philippines Mt Pinatubo erupted in June 1991. It is located on a destructive plate boundary between the Eurasian and Philippine plate. Convection currents cause the Oceanic Philippine plate to subduct below the Eurasian continental plate which causes pressure to build up. As the plate subducts it melts into magma, and forms a magma chamber. Over time, pressure continues to build up in the magma chamber forcing magma to rise up through cracks in the continental crust and eventually erupting as a volcano. Impacts of the eruption: Short term Long term https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=u2vvKFkuPbk KEY WORDS: Make sure you are able to define Pyroclastic flow Lahars https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5x5t ZAHEoRU Thousands of people needed treatment in hospital for lung damage The eruption left many people psychologically traumatized long after. The destruction of property meant that millions of dollars were needed for rebuilding 350 people killed by pyroclastic flow Power supplies were cut off Roads and bridges became blocked with ash Heavy rain fell and mixed with ash to cause lahars (mudflows) leading to further problems Thick ash in the atmosphere blocked out the sun turning day into night Lahars continued to happen months after, causing landslides and further loss of homes People forced to live in dirty refugee camps where diseases spread easily Farmland and crops were destroyed Thousands of people remained homeless for months after the event Response: The Philippines is an LIC LIC (low income country) therefore; • Took longer for rebuilding to take place • People remained homeless for a long time • Diseases spread in refugee camps due to poor sanitary conditions • The country is more dependent on foreign aid • New towns and villages were built further away from disaster areas lava flow Wind can blow ash a long way, which causes it to affect a large area by covering crops and roads; collapsing roofs because of the weight and suffocating animals and humans. lava flow Wind can blow ash a long way, which causes it to affect a large area by covering crops and roads; collapsing roofs because of the weight and suffocating animals and humans. ash cloud The main killer during an eruption is this deadly cloud of hot steam and ash that travels at over 200 km/h. ash cloud The main killer during an eruption is this deadly cloud of hot steam and ash that travels at over 200 km/h. gas emissions Ash in the air often triggers torrential rainfall, which washes the ash and mud down the volcano like a river. gas emissions Ash in the air often triggers torrential rainfall, which washes the ash and mud down the volcano like a river. pyroclastic flow This flow of molten rock does not travel quickly, so does not cause many deaths, however it does destroy farmland, property and roads. pyroclastic flow This flow of molten rock does not travel quickly, so does not cause many deaths, however it does destroy farmland, property and roads. lahars Sulphur, carbon dioxide and cyanide can all be released during an eruption, causing death to animals and humans. lahars Sulphur, carbon dioxide and cyanide can all be released during an eruption, causing death to animals and humans.