Courtney Kearney, Jon Dehn, Ken Dean
... eruptive episodes. The algorithm MAP_SO2 provides a means to create SO2 concentration maps based on modelled radiance values. These maps provide a total SO2 tonnage emitted along with a further understanding of the internal plume structure. Since MAP_SO2 was initially developed to detect passive deg ...
... eruptive episodes. The algorithm MAP_SO2 provides a means to create SO2 concentration maps based on modelled radiance values. These maps provide a total SO2 tonnage emitted along with a further understanding of the internal plume structure. Since MAP_SO2 was initially developed to detect passive deg ...
Volcanoes - LambertEarth
... through which magma and volcanic gases pass. Explosion of a volcanic eruption can turn an entire ...
... through which magma and volcanic gases pass. Explosion of a volcanic eruption can turn an entire ...
Volcanoes, Hotspots, and Earthquakes
... 9. What are the 3 types of plate boundaries? 10. What are the 3 types of faults? 11. What causes a fault? ...
... 9. What are the 3 types of plate boundaries? 10. What are the 3 types of faults? 11. What causes a fault? ...
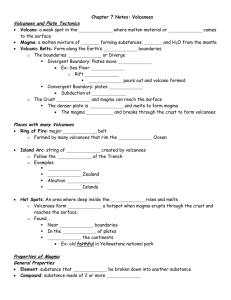
Chapter 7 Notes: Volcanoes Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcano Magma
... o This is a _______________ hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain ...
... o This is a _______________ hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain ...
Volcanoes - OpenStax CNX
... 1. The occurrence and causes of volcanoes Molten rock below the earth's crust is called magma. When it ows to the surface it is called lava. Why lava ows to the surface is not clear enough for people to agree on the reasons for eruptions and no one has been able to investigate the heart of the ear ...
... 1. The occurrence and causes of volcanoes Molten rock below the earth's crust is called magma. When it ows to the surface it is called lava. Why lava ows to the surface is not clear enough for people to agree on the reasons for eruptions and no one has been able to investigate the heart of the ear ...
Volcanic Landforms
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
Volcanobackground
... evacuation of the area around it? If so, what kind of evidence do the scientists need to make such a prediction? 4. Describe the hazards that volcanoes present for humans who live near them. ...
... evacuation of the area around it? If so, what kind of evidence do the scientists need to make such a prediction? 4. Describe the hazards that volcanoes present for humans who live near them. ...
File
... Lava Plateaus Sometimes, instead of forming mountains, thin runny lava flows out of several cracks and flows for many miles before cooling and solidifying. These flows pile up to form large flat areas called plateaus. ...
... Lava Plateaus Sometimes, instead of forming mountains, thin runny lava flows out of several cracks and flows for many miles before cooling and solidifying. These flows pile up to form large flat areas called plateaus. ...
Mudflow Slumps and Creep
... people. When a volcano erupted there, the heat caused ice and snow near the top of the volcano to melt, releasing a large amount of water that mixed with ash from the volcano. The mixture of ash and water rushed down the volcano and picked up debris. It formed gigantic mudflows that poured into all ...
... people. When a volcano erupted there, the heat caused ice and snow near the top of the volcano to melt, releasing a large amount of water that mixed with ash from the volcano. The mixture of ash and water rushed down the volcano and picked up debris. It formed gigantic mudflows that poured into all ...
Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
... pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions. The pyroclastic material forms steep slopes. ...
... pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions. The pyroclastic material forms steep slopes. ...
File
... rock, spills from a vent, or opening in the earth, and spreads widely. The lava gradually builds up a low, broad, dome-shaped mountain. (Example: Mauna Loa in Hawaii.) 2. A cinder cone builds up when mostly ash erupts from a vent and falls to the earth around the vent. The accumulated ash forms a co ...
... rock, spills from a vent, or opening in the earth, and spreads widely. The lava gradually builds up a low, broad, dome-shaped mountain. (Example: Mauna Loa in Hawaii.) 2. A cinder cone builds up when mostly ash erupts from a vent and falls to the earth around the vent. The accumulated ash forms a co ...
Volcanoes
... Pre-eruption activities: Increase in earthquake activity under the cone increase in temperature of cone, melting of ice/snow in the crater swelling of the cone steam eruptions minor ash eruptions ...
... Pre-eruption activities: Increase in earthquake activity under the cone increase in temperature of cone, melting of ice/snow in the crater swelling of the cone steam eruptions minor ash eruptions ...
Cause(s) - elearningadulted
... many cause-and-effect relationships. When the temperature rises deep under the Earth’s crust, it becomes hot enough to melt rock and turn it into magma. Sometimes this melted rock blasts through the Earth’s surface, which causes rock, ash, and deadly gases to fly into the air. The lava that flows ou ...
... many cause-and-effect relationships. When the temperature rises deep under the Earth’s crust, it becomes hot enough to melt rock and turn it into magma. Sometimes this melted rock blasts through the Earth’s surface, which causes rock, ash, and deadly gases to fly into the air. The lava that flows ou ...
http://kids - wikifuller
... 33. Scroll Back up to the GAS AND VISCOSITY SETTINGS. Now, set the both levels of viscosity and gas to high. Be careful!! DO NOT click on “set conditions”. Look at the magma, is flowing faster or slower???? Does it have more or less gas bubbles???? 34. Scroll down to Eruption 2: Strato Cone Eruption ...
... 33. Scroll Back up to the GAS AND VISCOSITY SETTINGS. Now, set the both levels of viscosity and gas to high. Be careful!! DO NOT click on “set conditions”. Look at the magma, is flowing faster or slower???? Does it have more or less gas bubbles???? 34. Scroll down to Eruption 2: Strato Cone Eruption ...
Volcano
... Composite or Strato Volcano - A steep-coned volcano that explosively emits gases, ash, pumice, and a small amount of stiff, silica lava (called rhyolite). This type of volcano can have eruptions accompanied by lahars -- deadly mudflows. Most volcanoes on Earth are of this type. Stratovolcanoes kill ...
... Composite or Strato Volcano - A steep-coned volcano that explosively emits gases, ash, pumice, and a small amount of stiff, silica lava (called rhyolite). This type of volcano can have eruptions accompanied by lahars -- deadly mudflows. Most volcanoes on Earth are of this type. Stratovolcanoes kill ...
VOLCANOES MR.OCHOA CHAPTER 6
... many layers of lava. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt. They result from quiet eruptions. The Hawaiian Islands are shield volcanoes. It is a gently sloping mountain formed by repeated lava flows (e) ...
... many layers of lava. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt. They result from quiet eruptions. The Hawaiian Islands are shield volcanoes. It is a gently sloping mountain formed by repeated lava flows (e) ...
Types of Volcano
... Strombolian – More viscous. Gas released regularly in small explosions. Vulcanian – Larger explosions, with large clouds of tephra and gas being produced. Andesitic magma. Vesuvian – More explosive still, with huge clouds spreading tephra over large areas. Plinian – Extremely violent Vesuvian erupti ...
... Strombolian – More viscous. Gas released regularly in small explosions. Vulcanian – Larger explosions, with large clouds of tephra and gas being produced. Andesitic magma. Vesuvian – More explosive still, with huge clouds spreading tephra over large areas. Plinian – Extremely violent Vesuvian erupti ...
Basalt has a high melting point and is very runny (like honey) – in
... silica content of only 50%. Basalt is also very dense and has a high specific gravity. Examples of shield volcanoes include the Dunedin and Lyttleton volcanoes, and Rangitoto Island. The ‘Organ Pipes’ on Mt Cargill are an example of a basalt formation. Andesite is an intermediate type of magma, and ...
... silica content of only 50%. Basalt is also very dense and has a high specific gravity. Examples of shield volcanoes include the Dunedin and Lyttleton volcanoes, and Rangitoto Island. The ‘Organ Pipes’ on Mt Cargill are an example of a basalt formation. Andesite is an intermediate type of magma, and ...
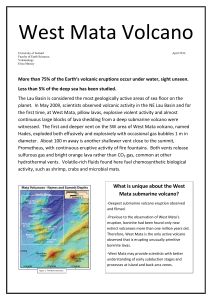
What is unique about the West Mata submarine volcano?
... The West Mata volcano produces pillow lavas and both pyroclastic and phreatic events occuring at its two vents, named Prometheus and Hades. Boninite is a primitive andesite composed of mafic extrusive rock that is derived from metasomatised mantle melting and likely fractional crystallization. It co ...
... The West Mata volcano produces pillow lavas and both pyroclastic and phreatic events occuring at its two vents, named Prometheus and Hades. Boninite is a primitive andesite composed of mafic extrusive rock that is derived from metasomatised mantle melting and likely fractional crystallization. It co ...
Magma Composition at Volcanoes Quiz
... *6) If magma is high in silica and more viscous, what type of eruption will form? a) Effusive b) Explosive c) Alternative ...
... *6) If magma is high in silica and more viscous, what type of eruption will form? a) Effusive b) Explosive c) Alternative ...
AP Physics SBHS Petyak
... Discuss the relationships between tsunamis and earthquakes. (9b) Describe two possible effects of a major earthquake on buildings.(9b) List three safety techniques to prevent injury caused by earthquake activity. (IE, 1m) Identify four methods scientists use to forecast earthquake risks. (9b ...
... Discuss the relationships between tsunamis and earthquakes. (9b) Describe two possible effects of a major earthquake on buildings.(9b) List three safety techniques to prevent injury caused by earthquake activity. (IE, 1m) Identify four methods scientists use to forecast earthquake risks. (9b ...
CASCADES OF LAVA. 441 through these numerous craters into the
... Of the mountain, Mouna Loa, itself, a fearful ertiption took place in 1840, and it has since given repeated evidences of its activity. An eruption also occurred in 1843 from a crater about 2000 feet below the summit. A river of lava pouring down the mountain-side, rolled over the elevated plain betw ...
... Of the mountain, Mouna Loa, itself, a fearful ertiption took place in 1840, and it has since given repeated evidences of its activity. An eruption also occurred in 1843 from a crater about 2000 feet below the summit. A river of lava pouring down the mountain-side, rolled over the elevated plain betw ...
Shield volcanoes
... Earth that erupts gases, ash, and lava. • Volcanic mountains form when layers of lava, ash, and other material build up around these openings. ...
... Earth that erupts gases, ash, and lava. • Volcanic mountains form when layers of lava, ash, and other material build up around these openings. ...
Warm up question
... ash – materials less than 2mm; worldwide Volcanic dust – materials less than 0.25mm; same Lapilli – materials less than 64mm – fall near vent Volcanic bombs – red hot lava that cools in the air Volcanic blocks – solid rock blasted from the fissure, can be as big as a house ...
... ash – materials less than 2mm; worldwide Volcanic dust – materials less than 0.25mm; same Lapilli – materials less than 64mm – fall near vent Volcanic bombs – red hot lava that cools in the air Volcanic blocks – solid rock blasted from the fissure, can be as big as a house ...
Mount Pinatubo

Mount Pinatubo (Filipino: Bundok Pinatubo) is an active stratovolcano in the Cabusilan Mountains on the island of Luzon, near the tripoint of the Philippine provinces of Zambales, Tarlac, and Pampanga. Before the volcanic activities of 1991, its eruptive history was unknown to most people. It was heavily eroded, inconspicuous and obscured from view. It was covered with dense forest which supported a population of several thousand indigenous people, the Aetas, who fled to the mountains during the Spanish conquest of the Philippines.The volcano's Plinian / Ultra-Plinian eruption on 15 June 1991 produced the second largest terrestrial eruption of the 20th century after the 1912 eruption of Novarupta in the Alaska Peninsula.Complicating the eruption was the arrival of Typhoon Yunya (Diding), bringing a lethal mix of ash and rain to areas surrounding the volcano. Successful predictions at the onset of the climactic eruption led to the evacuation of tens of thousands of people from the surrounding areas, saving many lives, but the surrounding areas were severely damaged by pyroclastic flows, ash deposits, and subsequently, by the lahars caused by rainwaters re-mobilizing earlier volcanic deposits causing extensive destruction to infrastructure and changing the river systems months to years after the eruption.The effects of the eruption were felt worldwide. It ejected roughly 10,000,000,000 tonnes (1.1×1010 short tons) or 10 km3 (2.4 cu mi) of magma, and 20,000,000 tonnes (22,000,000 short tons) SO2, bringing vast quantities of minerals and metals to the surface environment. It injected more particulate into the stratosphere than any eruption since Krakatoa in 1883. Over the following months, the aerosols formed a global layer of sulfuric acid haze. Global temperatures dropped by about 0.5 °C (0.9 °F) in the years 1991-93, and ozone depletion temporarily increased substantially.