Management`s primary goal is to maximize stockholder
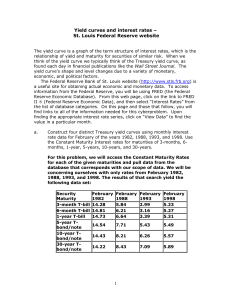
... Treasury maturities five years and beyond were much higher. In February 1998 long-term rates had declined 120 basis points (1.20%) but short-term rates had risen by over 200 basis points (despite low inflation). A "flat" yield curve, where short-term rates are similar to long-term rates, is often as ...
... Treasury maturities five years and beyond were much higher. In February 1998 long-term rates had declined 120 basis points (1.20%) but short-term rates had risen by over 200 basis points (despite low inflation). A "flat" yield curve, where short-term rates are similar to long-term rates, is often as ...
Beyond the liquidity trap: ineffectiveness of monetary policy as an
... However, more sophisticated consumption (and savings) function would make the natural interest rate depend on real wages. Then flexible wages could – formally – constitute a factor which allows for macro-equilibrium for any given level of interest rate set by the central bank. Even so, elastic wages ...
... However, more sophisticated consumption (and savings) function would make the natural interest rate depend on real wages. Then flexible wages could – formally – constitute a factor which allows for macro-equilibrium for any given level of interest rate set by the central bank. Even so, elastic wages ...
Economic Policy Vignettes - Georgetown Center for Business and
... political reasons, is a source of macroeconomic volatility. How can we ensure that fiscal policy will not be subject to political interference while it remains a powerful tool for controlling business cycles? How can fiscal policy maintain the balance between the need for short-term action and long- ...
... political reasons, is a source of macroeconomic volatility. How can we ensure that fiscal policy will not be subject to political interference while it remains a powerful tool for controlling business cycles? How can fiscal policy maintain the balance between the need for short-term action and long- ...
Monetary Policy - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... – The banking system must be willing to increase lending activity. – Banks may pile up excess reserves instead of making loans. – They might have concerns about their financial well-being and about making loans to those who might not pay back the money. – They might be uncertain about how new bank r ...
... – The banking system must be willing to increase lending activity. – Banks may pile up excess reserves instead of making loans. – They might have concerns about their financial well-being and about making loans to those who might not pay back the money. – They might be uncertain about how new bank r ...
Macroeconomics
... there is a lag in recognizing the phase of the business cycle to determine when the government might want to provide help. Second, there is an administrative lag in decision-making that involves deciding which specific policies should be adopted. Third, there is an operational lag because the adopti ...
... there is a lag in recognizing the phase of the business cycle to determine when the government might want to provide help. Second, there is an administrative lag in decision-making that involves deciding which specific policies should be adopted. Third, there is an operational lag because the adopti ...
The art of distinguishing between cause and effect in the macroeconomy
... of the economy. A number of parameters, which determine the relationships among different variables, are introduced into the model. For instance, if we know that consumers’ aggregate demand for goods and services is affected by the expected real interest rate, this relationship should be incorporate ...
... of the economy. A number of parameters, which determine the relationships among different variables, are introduced into the model. For instance, if we know that consumers’ aggregate demand for goods and services is affected by the expected real interest rate, this relationship should be incorporate ...
Money
... 1. Open market operations: CB purchases and sells government bonds. Increases / decreases M through change of B 2. Reserve requirements: CB sets minimum. Affects creation of money by banks (rr) 3. Discount rate: charged on loans by CB for banks (if do not have enough R, or want more loans ) Affects ...
... 1. Open market operations: CB purchases and sells government bonds. Increases / decreases M through change of B 2. Reserve requirements: CB sets minimum. Affects creation of money by banks (rr) 3. Discount rate: charged on loans by CB for banks (if do not have enough R, or want more loans ) Affects ...
Reflections on Monetary and Fiscal Policies and Economic
... era. For achieving stability, it is generally considered necessary to keep the growth of money supply in step with the demand for it, which is assumed to be uniquely related to national income, at any rate over the medium-term and when due allowance is made for secular changes such as those arising ...
... era. For achieving stability, it is generally considered necessary to keep the growth of money supply in step with the demand for it, which is assumed to be uniquely related to national income, at any rate over the medium-term and when due allowance is made for secular changes such as those arising ...
View/Open
... where the notation xz means ∂x / ∂z. Under the assumption that the system is stable (see Appendix), then 1 – kR e(Li + LYYi) would be positive and consequently expansive monetary policies would lower reserves, increase domestic rates of interest and lower the level of economic activity. Therefore, w ...
... where the notation xz means ∂x / ∂z. Under the assumption that the system is stable (see Appendix), then 1 – kR e(Li + LYYi) would be positive and consequently expansive monetary policies would lower reserves, increase domestic rates of interest and lower the level of economic activity. Therefore, w ...
monetary policy
... 2. Consumer Price Index (CPI)= measures how much money people spend on consumer goods - Measures changes in inflation (increase in the price of goods) - Too much money in circulation can lead to HIGH levels of inflation look at Zimbabwe 3. Unemployment Rate: measures the percentage of people who w ...
... 2. Consumer Price Index (CPI)= measures how much money people spend on consumer goods - Measures changes in inflation (increase in the price of goods) - Too much money in circulation can lead to HIGH levels of inflation look at Zimbabwe 3. Unemployment Rate: measures the percentage of people who w ...
CHAPTER 16: Monetary Policy
... Why Did Homebuilder Toll Brothers, Inc. Prosper during the 2001 Recession? ...
... Why Did Homebuilder Toll Brothers, Inc. Prosper during the 2001 Recession? ...
Economics Study Guide
... enterprise zone area where companies can locate free of certain local, state, and federal taxes and restrictions (p. 350) fixed income income that does not increase even when prices go up (p. 343) food stamps government-issued coupons that recipients exchange for food (p. 348) frictional unemploymen ...
... enterprise zone area where companies can locate free of certain local, state, and federal taxes and restrictions (p. 350) fixed income income that does not increase even when prices go up (p. 343) food stamps government-issued coupons that recipients exchange for food (p. 348) frictional unemploymen ...
A rise in the price of oil imports has resulted in a decrease of short
... in the treasury from tax revenue. c. How the fed can not increase the money supply further when interest rates have hit zero percent. 10. What is the real rate of interest? a. the nominal interest rate plus the inflation rate. b. the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate. c. the nominal int ...
... in the treasury from tax revenue. c. How the fed can not increase the money supply further when interest rates have hit zero percent. 10. What is the real rate of interest? a. the nominal interest rate plus the inflation rate. b. the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate. c. the nominal int ...
Answers to Test Your Understanding Questions
... minus increased target reserves of 10% x 100 = 10). Loaning out these excess reserves will result in an increase in demand deposits, which is part of the money supply. 6. Economic growth and full-employment are compatible goals but both can come into conflict with the goals of stable prices and a fa ...
... minus increased target reserves of 10% x 100 = 10). Loaning out these excess reserves will result in an increase in demand deposits, which is part of the money supply. 6. Economic growth and full-employment are compatible goals but both can come into conflict with the goals of stable prices and a fa ...
Economic Stability - New Zealand Treasury
... adjust the overall fiscal stance. In particular, the Treasury considers that any loosening in fiscal policy settings by more than 2% of GDP in any one year is likely to impose excessive pressure on monetary management. Since recent changes already imply movement of around that extent in 1996/97 and ...
... adjust the overall fiscal stance. In particular, the Treasury considers that any loosening in fiscal policy settings by more than 2% of GDP in any one year is likely to impose excessive pressure on monetary management. Since recent changes already imply movement of around that extent in 1996/97 and ...
Monetary Policy, Part 2
... firms is more sensitive to monetary policy than the spending of large firms. – Consumers and small firms are financially riskier than large firms, so when monetary policy tightens they’re more likely to be disqualified from loans. ...
... firms is more sensitive to monetary policy than the spending of large firms. – Consumers and small firms are financially riskier than large firms, so when monetary policy tightens they’re more likely to be disqualified from loans. ...
History of European Monetary Integration
... During a period of intensifying efforts to create a single market (from the adoption of the Single European Act (SEA) in 1986 to its completion in 1992, the costs created by the existence of several currencies and unstable exchange rates became more evident. In this context, France and Italy led ini ...
... During a period of intensifying efforts to create a single market (from the adoption of the Single European Act (SEA) in 1986 to its completion in 1992, the costs created by the existence of several currencies and unstable exchange rates became more evident. In this context, France and Italy led ini ...
Inflation, Disinflation, and Deflation
... negotiate a contract for your pay, what would you demand? Why might it be in the interest of the business to pay you the higher wage? Hiring workers might be more expensive later Output is selling for higher prices ...
... negotiate a contract for your pay, what would you demand? Why might it be in the interest of the business to pay you the higher wage? Hiring workers might be more expensive later Output is selling for higher prices ...
chapter # 6 - how the markets work - supply
... government spending . This strategy will cause crowding – out when government borrowing to cover the budget deficit raises the demand for loanable funds and , hence , interest rates rise . When interest rates rise , investment falls and reduces long run economic growth . ...
... government spending . This strategy will cause crowding – out when government borrowing to cover the budget deficit raises the demand for loanable funds and , hence , interest rates rise . When interest rates rise , investment falls and reduces long run economic growth . ...
FIXED INCOME UPDATE – FEB `17
... • Short- end of the curve is strongly recommended (play on liquidity) • Investor should look to invest in short to medium term funds as a core portfolio allocation • Investors looking to take duration exposure can look to do it through funds having dynamic duration management ...
... • Short- end of the curve is strongly recommended (play on liquidity) • Investor should look to invest in short to medium term funds as a core portfolio allocation • Investors looking to take duration exposure can look to do it through funds having dynamic duration management ...
background
... capital from overseas. As it became apparent that the economic impact of the Asian Crisis was deeper than had been expected, fiscal targets in Asian countries were relaxed to take account of falling government tax revenues. Monetary policy A high interest rate policy has the twin effects of reducing ...
... capital from overseas. As it became apparent that the economic impact of the Asian Crisis was deeper than had been expected, fiscal targets in Asian countries were relaxed to take account of falling government tax revenues. Monetary policy A high interest rate policy has the twin effects of reducing ...
AP review wk 2
... – Results from a poor match of workers’ abilities and skills with current requirements of employers ...
... – Results from a poor match of workers’ abilities and skills with current requirements of employers ...
slides - Harvard University
... On the one hand, the private sector dislikes risk as much as the government does & will take steps to mitigate it. On the other hand the government cannot entirely ignore the issue of volatility; ...
... On the one hand, the private sector dislikes risk as much as the government does & will take steps to mitigate it. On the other hand the government cannot entirely ignore the issue of volatility; ...
Homework for Chapter 8
... price of bonds. Therefore, the retired executive would suffer a capital loss if he or she decided to cash in some of the bonds at this time and the fixed interest received on these existing bonds is worth less in terms of purchasing power. In other words, the executive, although wealthier than the r ...
... price of bonds. Therefore, the retired executive would suffer a capital loss if he or she decided to cash in some of the bonds at this time and the fixed interest received on these existing bonds is worth less in terms of purchasing power. In other words, the executive, although wealthier than the r ...
Monetary policy

Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting an inflation rate or interest rate to ensure price stability and general trust in the currency.Further goals of a monetary policy are usually to contribute to economic growth and stability, to lower unemployment, and to maintain predictable exchange rates with other currencies.Monetary economics provides insight into how to craft optimal monetary policy.Monetary policy is referred to as either being expansionary or contractionary, where an expansionary policy increases the total supply of money in the economy more rapidly than usual, and contractionary policy expands the money supply more slowly than usual or even shrinks it. Expansionary policy is traditionally used to try to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering interest rates in the hope that easy credit will entice businesses into expanding. Contractionary policy is intended to slow inflation in order to avoid the resulting distortions and deterioration of asset values.Monetary policy differs from fiscal policy, which refers to taxation, government spending, and associated borrowing.























