Forecasting Interest Rates
... Predominant suppliers of loanable funds are households at about 35% Main determinants of household savings are Some funds are supplied by governments and businesses Foreign funds suppliers examine the same factors as U.S. funds suppliers ...
... Predominant suppliers of loanable funds are households at about 35% Main determinants of household savings are Some funds are supplied by governments and businesses Foreign funds suppliers examine the same factors as U.S. funds suppliers ...
Business cycles
... The monetary policy tools available to achieve these ends: increasing interest rates by fiat; reducing the monetary base; and increasing reserve requirements. Wages and prices will begin to rise at faster rates if monetary policy stimulates aggregate demand enough to push labor and capital markets b ...
... The monetary policy tools available to achieve these ends: increasing interest rates by fiat; reducing the monetary base; and increasing reserve requirements. Wages and prices will begin to rise at faster rates if monetary policy stimulates aggregate demand enough to push labor and capital markets b ...
Fiscal policy
... argue that such policies may destabilize the economy rather than help it: By the time the policies affect agg demand, the economy’s condition may have changed. These critics contend that policymakers should focus on long-run goals like economic growth and low inflation. ...
... argue that such policies may destabilize the economy rather than help it: By the time the policies affect agg demand, the economy’s condition may have changed. These critics contend that policymakers should focus on long-run goals like economic growth and low inflation. ...
Monetary policy and forward guidance in the UK
... that the significant positive news on the economic outlook means that the 7% unemployment level might be reached within around eighteen months. This is rather sooner than I think is likely. It is plausible that the level of productivity – which has fallen enormously relative to the trend we have bee ...
... that the significant positive news on the economic outlook means that the 7% unemployment level might be reached within around eighteen months. This is rather sooner than I think is likely. It is plausible that the level of productivity – which has fallen enormously relative to the trend we have bee ...
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from... of Economic Research Volume Title: NBER Macroeconomics Annual 2012, Volume 27
... Estimate of the effects of fiscal policy on the economy have struggled with the problem of how to identify “exogenous” shifts in a country’s fiscal stance for over twenty years. A first set of estimates (e.g., Giavazzi and Pagano 1996; Alesina and Perotti 1997; Alesina, Perotti, and Tavares 1998) re ...
... Estimate of the effects of fiscal policy on the economy have struggled with the problem of how to identify “exogenous” shifts in a country’s fiscal stance for over twenty years. A first set of estimates (e.g., Giavazzi and Pagano 1996; Alesina and Perotti 1997; Alesina, Perotti, and Tavares 1998) re ...
course objectives - University of Belize
... Riddell, Tom; Shackelford, Jean; & Stamos, Steve. 1998. “Economics: A Tool for Critically Understanding Society.” 5th Edition, Addison Wesley Longman Inc. ...
... Riddell, Tom; Shackelford, Jean; & Stamos, Steve. 1998. “Economics: A Tool for Critically Understanding Society.” 5th Edition, Addison Wesley Longman Inc. ...
Homework 1
... Long-run Now assume that the factory managers can vary the number of die presses. Calculate the average total cost function for each level of production for each # of die presses. For each quantity of die-presses, calculate the minimum average cost. For each level of production, calculate the minimu ...
... Long-run Now assume that the factory managers can vary the number of die presses. Calculate the average total cost function for each level of production for each # of die presses. For each quantity of die-presses, calculate the minimum average cost. For each level of production, calculate the minimu ...
Macro_online_chapter_09_14e
... the short-run and long-run. Investigate how aggregate demand and supply determine the price level, output, and employment. Recognize how the resource market is connected to the goods and services market. Recognize how the loanable funds market is connected to the goods and services market. Recognize ...
... the short-run and long-run. Investigate how aggregate demand and supply determine the price level, output, and employment. Recognize how the resource market is connected to the goods and services market. Recognize how the loanable funds market is connected to the goods and services market. Recognize ...
3 - GCC
... what sense do banks borrow on a short term basis and lend on a long term basis. Why did this cause problems for Savings & Loans during the 1970s? (Explain thoroughly). b. When calculating the profit of a bank, what is the source of the revenue of the bank? c. Show the four most important items which ...
... what sense do banks borrow on a short term basis and lend on a long term basis. Why did this cause problems for Savings & Loans during the 1970s? (Explain thoroughly). b. When calculating the profit of a bank, what is the source of the revenue of the bank? c. Show the four most important items which ...
Eduardo Cavallo
... This scenario could trigger a liquidity crisis in quite a few countries. If a country does not have sufficient international reserves to cover the debt service, it could generate a stampede by everyone who believes that the reserves are not going to be there when needed. ...
... This scenario could trigger a liquidity crisis in quite a few countries. If a country does not have sufficient international reserves to cover the debt service, it could generate a stampede by everyone who believes that the reserves are not going to be there when needed. ...
14.02 Principles of Macroeconomics Spring 03 Quiz 3 Thursday, May 8, 2003
... 7. The Bush tax cut has been criticized for the following reasons: I. The tax cut would cause the budget deficit to increase rapidly, putting pressure on long term interest rates to rise. II. Even though the tax cut is large relative to GDP, the average household does not profit much from it, and th ...
... 7. The Bush tax cut has been criticized for the following reasons: I. The tax cut would cause the budget deficit to increase rapidly, putting pressure on long term interest rates to rise. II. Even though the tax cut is large relative to GDP, the average household does not profit much from it, and th ...
British economic performance
... relative prices in different countries: exchange rates fluctuate, sometimes by large amounts, without there being any corresponding change in living standards (prices do not fluctuate by the same amount). To get round this problem it is better to use purchasing power parities. The purchasing power p ...
... relative prices in different countries: exchange rates fluctuate, sometimes by large amounts, without there being any corresponding change in living standards (prices do not fluctuate by the same amount). To get round this problem it is better to use purchasing power parities. The purchasing power p ...
Bank of England Inflation Report February 2015 Money and asset
... Constant-maturity unweighted average of secondary market spreads to swaps for the major UK lenders’ five-year euro senior unsecured bonds or a suitable proxy. Sterling average of two and three-year spreads on retail bonds, over relevant swap rates. Unweighted average of the five-year senior CDS prem ...
... Constant-maturity unweighted average of secondary market spreads to swaps for the major UK lenders’ five-year euro senior unsecured bonds or a suitable proxy. Sterling average of two and three-year spreads on retail bonds, over relevant swap rates. Unweighted average of the five-year senior CDS prem ...
Macro_3.7-_Problems_with_Fiscal_Policy
... • Now but consumer spend less on books (AD decreases) Another Example: • The government increases spending but must borrow the money (AD increases) • This increases the price for money (the interest rate). • Interest rates rise so Investment to fall. (AD decrease) ...
... • Now but consumer spend less on books (AD decreases) Another Example: • The government increases spending but must borrow the money (AD increases) • This increases the price for money (the interest rate). • Interest rates rise so Investment to fall. (AD decrease) ...
Monetary Policy Tools 16.3
... (a) deposits to reserves required of banks by the Federal Reserve. (b) accounts to customers required of banks by the Federal Reserve. (c) reserves to deposits required of banks by the Federal Reserve. (d) paper currency to coins required of banks by the Federal Reserve. 2. All of the following will ...
... (a) deposits to reserves required of banks by the Federal Reserve. (b) accounts to customers required of banks by the Federal Reserve. (c) reserves to deposits required of banks by the Federal Reserve. (d) paper currency to coins required of banks by the Federal Reserve. 2. All of the following will ...
the short-run policy trade-off
... 1. The Phillips curve “harbors a fundamental defect, namely, that the supply of labor is a function of the nominal wage.” This violates a basic axiom of microeconomic theory. 2. “There is no long run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.” Suggests there may be a short-run tradeoff. 3. The lo ...
... 1. The Phillips curve “harbors a fundamental defect, namely, that the supply of labor is a function of the nominal wage.” This violates a basic axiom of microeconomic theory. 2. “There is no long run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.” Suggests there may be a short-run tradeoff. 3. The lo ...
Final Exam Cram Assignment
... the bank’s use of money creation 59. What does the Consumer Price Index measure? a. the willingness and ability of consumers to purchase goods and services b. the economy’s total output (GDP) c. the price of money, or the interest rate d. the rate of inflation ...
... the bank’s use of money creation 59. What does the Consumer Price Index measure? a. the willingness and ability of consumers to purchase goods and services b. the economy’s total output (GDP) c. the price of money, or the interest rate d. the rate of inflation ...
aggregate supply aggregate demand krugman 2nd ed
... Why is the Aggregate Demand Curve downward sloping? What factors shift the Aggregate Demand Curve? What factors shift the Aggregate Supply Curve? Why is there a long run and short run supply curve? What stabilizing policies does the government have at its disposal, when are they used? How does fisca ...
... Why is the Aggregate Demand Curve downward sloping? What factors shift the Aggregate Demand Curve? What factors shift the Aggregate Supply Curve? Why is there a long run and short run supply curve? What stabilizing policies does the government have at its disposal, when are they used? How does fisca ...
Management`s primary goal is to maximize stockholder
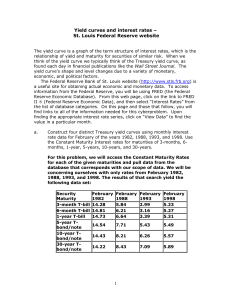
... Treasury maturities five years and beyond were much higher. In February 1998 long-term rates had declined 120 basis points (1.20%) but short-term rates had risen by over 200 basis points (despite low inflation). A "flat" yield curve, where short-term rates are similar to long-term rates, is often as ...
... Treasury maturities five years and beyond were much higher. In February 1998 long-term rates had declined 120 basis points (1.20%) but short-term rates had risen by over 200 basis points (despite low inflation). A "flat" yield curve, where short-term rates are similar to long-term rates, is often as ...
Monetary policy

Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting an inflation rate or interest rate to ensure price stability and general trust in the currency.Further goals of a monetary policy are usually to contribute to economic growth and stability, to lower unemployment, and to maintain predictable exchange rates with other currencies.Monetary economics provides insight into how to craft optimal monetary policy.Monetary policy is referred to as either being expansionary or contractionary, where an expansionary policy increases the total supply of money in the economy more rapidly than usual, and contractionary policy expands the money supply more slowly than usual or even shrinks it. Expansionary policy is traditionally used to try to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering interest rates in the hope that easy credit will entice businesses into expanding. Contractionary policy is intended to slow inflation in order to avoid the resulting distortions and deterioration of asset values.Monetary policy differs from fiscal policy, which refers to taxation, government spending, and associated borrowing.