Volcano Research Project
... What type of lava forms your volcano? What type of eruption does it produce: Violent, quiet, or both? What types of volcanic rock fragments or lava come out of your volcano? ________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________ ...
... What type of lava forms your volcano? What type of eruption does it produce: Violent, quiet, or both? What types of volcanic rock fragments or lava come out of your volcano? ________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________ ...
PowerPoint explanation of volcanic impact on climate
... air, it carries on rising – unstable. • If the air is colder than the surrounding air, it sinks back to where is came from – stable. • The stratosphere is always very stable – but explosive volcanic eruptions can blast material up into the stratosphere. • Once in the stratosphere, the stability mean ...
... air, it carries on rising – unstable. • If the air is colder than the surrounding air, it sinks back to where is came from – stable. • The stratosphere is always very stable – but explosive volcanic eruptions can blast material up into the stratosphere. • Once in the stratosphere, the stability mean ...
Geysers: Types: cone (has a cone of “geyserite” around a small vent
... many short explosions. Eruptive columns are typically larger than Stromb. columns, and they are mostly made up of ashy pyrocl. material. The explosions are initiated by hi-viscosity, hi-gas-content magma in which small amounts of gas pressure build up and thrust material into the air. In addition to ...
... many short explosions. Eruptive columns are typically larger than Stromb. columns, and they are mostly made up of ashy pyrocl. material. The explosions are initiated by hi-viscosity, hi-gas-content magma in which small amounts of gas pressure build up and thrust material into the air. In addition to ...
Volcano - Greenwich Central School
... The opening through which molten rock and gas leave the volcano. ...
... The opening through which molten rock and gas leave the volcano. ...
What do we expect in a volcanic eruption?
... • Solids lofted into atm • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
... • Solids lofted into atm • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
Climate and Volcanism - Natural Climate Change
... Volcanoes are active, meaning they show some level of activity and are likely to explode again, dormant, showing no current signs of exploding but are likely to become active at some point in the future, or extinct meaning they won’t be active again. About 1,900 volcanoes on Earth are considered act ...
... Volcanoes are active, meaning they show some level of activity and are likely to explode again, dormant, showing no current signs of exploding but are likely to become active at some point in the future, or extinct meaning they won’t be active again. About 1,900 volcanoes on Earth are considered act ...
Volcanic
... Small Eruptions: Rhyolite Domes, Mt Elden Rhyolite so viscous has trouble flowing, so piles up in dome shape ...
... Small Eruptions: Rhyolite Domes, Mt Elden Rhyolite so viscous has trouble flowing, so piles up in dome shape ...
Volcanoes Booklet Info Basic Info
... Make a list of things you think might happen and what might be damaged by them ...
... Make a list of things you think might happen and what might be damaged by them ...
Volcanoes - davis.k12.ut.us
... All the magma is held in the magma chamber. The pressure grows and soon the magma chamber bursts open and zips up the central vent, taking some buddies with it. It picks up A diagram of a land volcano. some ash from the ash deposit layer and some loose rocks from the hardened lava layer. They do not ...
... All the magma is held in the magma chamber. The pressure grows and soon the magma chamber bursts open and zips up the central vent, taking some buddies with it. It picks up A diagram of a land volcano. some ash from the ash deposit layer and some loose rocks from the hardened lava layer. They do not ...
a geological-petrological model of the karymsky volcanic center
... Research on deep structure, the geological-structural location of volcanoes in the central part of the Karymsky circular structure (KCS), and study of the eruptive products of Karymsky volcano and a new eruptive center (NEC, Tokarev’s crater) from 1996-2000 provides the basis for the following petro ...
... Research on deep structure, the geological-structural location of volcanoes in the central part of the Karymsky circular structure (KCS), and study of the eruptive products of Karymsky volcano and a new eruptive center (NEC, Tokarev’s crater) from 1996-2000 provides the basis for the following petro ...
Click here for the "Dynamic Earth Vocabulary"
... molten or liquid. While it's still below the surface, it's called magma. Once the magma erupts to the surface through a volcano, it's called lava. The hotter and thinner the lava is, the farther it will flow. Lava can be very hot, sometimes as hot as 1000 degrees C. A major unfavorable event from na ...
... molten or liquid. While it's still below the surface, it's called magma. Once the magma erupts to the surface through a volcano, it's called lava. The hotter and thinner the lava is, the farther it will flow. Lava can be very hot, sometimes as hot as 1000 degrees C. A major unfavorable event from na ...
Volcanoes13 - PAMS-Doyle
... Pompeii (79AD) The cities remained buried and undiscovered for almost 1700 years until excavation began in 1748. These excavations continue today and provide insight into life during the Roman Empire. ...
... Pompeii (79AD) The cities remained buried and undiscovered for almost 1700 years until excavation began in 1748. These excavations continue today and provide insight into life during the Roman Empire. ...
Debris Avalanches
... of Hawaii left by a debris avalanche that occurred less than 200 thousand years ago. ...
... of Hawaii left by a debris avalanche that occurred less than 200 thousand years ago. ...
Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity - sir
... spreading centers the greatest volume of volcanic rock is produced along the oceanic ridge system mechanism of spreading lithosphere pulls apart ...
... spreading centers the greatest volume of volcanic rock is produced along the oceanic ridge system mechanism of spreading lithosphere pulls apart ...
ICELAND`S VOLCANO HEKLA ABOUT TO ERUPT
... boundary between the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates that is marked by earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. ...
... boundary between the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates that is marked by earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. ...
Volcanoes Day 1 - NVHSEarthScienceOlsen
... • A lava flow with a surface of rough, jagged blocks and sharp, angular projections is called aa flow. • As the temperature of lava increases, the viscocity decreases. • Highly explosive volcanoes tend to have magma with high silica, high viscosity, and higher gas content. • The particles produced i ...
... • A lava flow with a surface of rough, jagged blocks and sharp, angular projections is called aa flow. • As the temperature of lava increases, the viscocity decreases. • Highly explosive volcanoes tend to have magma with high silica, high viscosity, and higher gas content. • The particles produced i ...
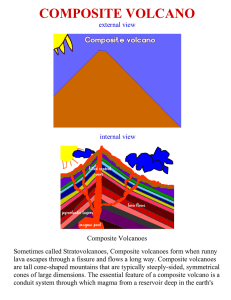
composite volcano
... material erupted through the conduit and increases in size as lava, cinders, ash etc. are added to its slopes. Composite volcanoes erupt in different ways at different times. These volcanoes are built in layers by multiple eruptions, sometimes recurring over hundreds of thousands of years, sometimes ...
... material erupted through the conduit and increases in size as lava, cinders, ash etc. are added to its slopes. Composite volcanoes erupt in different ways at different times. These volcanoes are built in layers by multiple eruptions, sometimes recurring over hundreds of thousands of years, sometimes ...
Chapter 9 Section 1 Notes
... Shape is caused by the magma spinning through the air as it cools Lapilli Means “little stones” in Italian Pebblelike bits of magma that hardened before they hit the ground ...
... Shape is caused by the magma spinning through the air as it cools Lapilli Means “little stones” in Italian Pebblelike bits of magma that hardened before they hit the ground ...
Topic 8 Volcanoes
... The photograph above shows a dike composed of a dark band of basaltic rock which cuts across the lighter layers of gneiss. This dike is located on the west side of the Palisades Interstate Parkway in New Jersey. ...
... The photograph above shows a dike composed of a dark band of basaltic rock which cuts across the lighter layers of gneiss. This dike is located on the west side of the Palisades Interstate Parkway in New Jersey. ...
Volcanoes
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kilauea on the big island of Hawa ...
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kilauea on the big island of Hawa ...
Учитель: Размахнина О
... 2. You might think that the peak of Mount Everest is the most distant point from the center of the Earth, but that's not true. Instead, it's the volcano Chimborazo in Ecuador. That's because the Earth's is spinning in space and is flattened out. Points at the equator are further from the center of t ...
... 2. You might think that the peak of Mount Everest is the most distant point from the center of the Earth, but that's not true. Instead, it's the volcano Chimborazo in Ecuador. That's because the Earth's is spinning in space and is flattened out. Points at the equator are further from the center of t ...
magma chamber - Madison County Schools
... • A pyroclastic flow is a fast-moving current of superheated gas (which can reach temperatures of about 1,000 °C) and rock, which reaches speeds moving away from a volcano of up to 700 km/h. The flows normally hug the ground and travel downhill. They are a common and devastating result of certain ex ...
... • A pyroclastic flow is a fast-moving current of superheated gas (which can reach temperatures of about 1,000 °C) and rock, which reaches speeds moving away from a volcano of up to 700 km/h. The flows normally hug the ground and travel downhill. They are a common and devastating result of certain ex ...
Nevado del Ruiz

The Nevado del Ruiz (Spanish pronunciation: [neβaðo ðel ˈrwis]), also known as La Mesa de Herveo (English: Mesa of Herveo (the nearby town)), or Kumanday in the language of the local pre-Columbian indigenous people, is a volcano located on the border of the departments of Caldas and Tolima in Colombia, about 129 kilometers (80 mi) west of the capital city Bogotá. It is a stratovolcano, composed of many layers of lava alternating with hardened volcanic ash and other pyroclastic rocks. Nevado del Ruiz has been active for about two million years, since the early Pleistocene or late Pliocene epoch, with three major eruptive periods. The current volcanic cone formed during the present eruptive period, which began 150 thousand years ago.The volcano usually generates Plinian eruptions, which produce swift-moving currents of hot gas and rock called pyroclastic flows. These eruptions often cause massive lahars (mud and debris flows), which pose a threat to human life and the environment. The impact of such an eruption is increased as the hot gas and lava melts the mountain's snowcap, adding large quantities of water to the flow. On November 13, 1985, a small eruption produced an enormous lahar that buried and destroyed the town of Armero in Tolima, causing an estimated 25,000 deaths. This event later became known as the Armero tragedy—the deadliest lahar in recorded history. Similar but less deadly incidents occurred in 1595 and 1845, consisting of a small explosive eruption followed by a large lahar.The volcano is part of Los Nevados National Natural Park, which also contains several other volcanoes. The summit of Nevado del Ruiz is covered by large glaciers, although these have retreated significantly since 1985 because of global warming. The volcano continues to pose a threat to the nearby towns and villages, and it is estimated that up to 500,000 people could be at risk from lahars from future eruptions.