Homework for Volcanoes from Geology 1200
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
The Rock cycle: Initially proposed by James Hutton
... 2. Dissolved Gases: Water CO2 Expand as lava rises Large amounts of gas result in explosive eruptions. (pyroclastic) LAVA MATERIALS: Pahoehoe Lava: Ropy lava AA lava: Blocky, sharp and rough lava Columnar Joints: 5- to 7-sided columns of basalt. Produced by slow cooling. Pillow Lava: Surface like pi ...
... 2. Dissolved Gases: Water CO2 Expand as lava rises Large amounts of gas result in explosive eruptions. (pyroclastic) LAVA MATERIALS: Pahoehoe Lava: Ropy lava AA lava: Blocky, sharp and rough lava Columnar Joints: 5- to 7-sided columns of basalt. Produced by slow cooling. Pillow Lava: Surface like pi ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... • The third major earthquake and volcano zone extends through Iceland and to the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. There is under the ocean a long range of volcanic mountains called the Mid-Atlantic Ocean Range. Scientists believe that the volcano and earthquake activity are due to the formation of new ...
... • The third major earthquake and volcano zone extends through Iceland and to the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. There is under the ocean a long range of volcanic mountains called the Mid-Atlantic Ocean Range. Scientists believe that the volcano and earthquake activity are due to the formation of new ...
Earth Science--Ch 9 Volcanoes Review Guide
... like/shape, how they erupt, what types of materials they are primarily made of, where they tend to form.) ...
... like/shape, how they erupt, what types of materials they are primarily made of, where they tend to form.) ...
Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
... Composite Volcanoes • Composite cones or stratovolcanoes – Located around the Ring of Fire ...
... Composite Volcanoes • Composite cones or stratovolcanoes – Located around the Ring of Fire ...
Document
... cool as thin, gently dipping sheets. Lavas also commonly erupt from vents along fractures (rift zones) that develop on the flanks of the cone. ...
... cool as thin, gently dipping sheets. Lavas also commonly erupt from vents along fractures (rift zones) that develop on the flanks of the cone. ...
Developing a Clincher Sentence
... quietly, or it may spew forth in a violent explosion. Clincher sentence: _____ 3. Geologists are not the only scientists who study volcanoes. Biologists and meteorologists are concerned with what happens on the earth’s surface after volcanic events. Biologists may be interested in how life adapts to ...
... quietly, or it may spew forth in a violent explosion. Clincher sentence: _____ 3. Geologists are not the only scientists who study volcanoes. Biologists and meteorologists are concerned with what happens on the earth’s surface after volcanic events. Biologists may be interested in how life adapts to ...
Igneous Environments and Volcanoes - H
... Summarize the main differences between felsic and mafic rocks. Know the order of silicate mineral crystallization (Bowen’s Reaction Series), and be able to relate the series to temperature, mineral content, and kinds of rocks. Be able to explain why the subduction and melting of a mafic plate can re ...
... Summarize the main differences between felsic and mafic rocks. Know the order of silicate mineral crystallization (Bowen’s Reaction Series), and be able to relate the series to temperature, mineral content, and kinds of rocks. Be able to explain why the subduction and melting of a mafic plate can re ...
Volcanoes, Hotspots, and Earthquakes
... Andreas Fault Zone during the past 3 million years is 56 mm/yr (2 in/yr). This is about the same rate at which your fingernails grow. Assuming this rate continues, scientists project that Los Angeles and San Francisco will be adjacent to one another in approximately 15 million years. ...
... Andreas Fault Zone during the past 3 million years is 56 mm/yr (2 in/yr). This is about the same rate at which your fingernails grow. Assuming this rate continues, scientists project that Los Angeles and San Francisco will be adjacent to one another in approximately 15 million years. ...
Chapter 7 Notes: Volcanoes Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcano Magma
... o Lava Flow: an area covered by _______________ as it flows out of a side vent o Crater: a _______________ shaped area that may form at the _______________ of the volcano around the central vent ...
... o Lava Flow: an area covered by _______________ as it flows out of a side vent o Crater: a _______________ shaped area that may form at the _______________ of the volcano around the central vent ...
Igneous
... – 1980’s & 90’s 1.5 billion cubic meters • Geothermal energy- New Zealand; California • Effect on climate- 1816 “year without summer” • Volcanic catastrophies – Mt. St. Helens 1980 – Vesuvius 79 AD – Krakatoa 1883 – Crater Lake 6,600 y.b.p. ...
... – 1980’s & 90’s 1.5 billion cubic meters • Geothermal energy- New Zealand; California • Effect on climate- 1816 “year without summer” • Volcanic catastrophies – Mt. St. Helens 1980 – Vesuvius 79 AD – Krakatoa 1883 – Crater Lake 6,600 y.b.p. ...
Igneous Rocks and Volcanism
... And some rin uphill and down dale, Knapping the chucky stones to pieces wi’ hammers, Like sae mony roadmakers run daft – They say it is to see how the warld was made. - Sir Walter Raleigh ...
... And some rin uphill and down dale, Knapping the chucky stones to pieces wi’ hammers, Like sae mony roadmakers run daft – They say it is to see how the warld was made. - Sir Walter Raleigh ...
6. Volcano PowerPoint
... continued until 1952. The farmer had noticed a fissure (vent) had opened in the field one morning and from it was pouring black ash. In the first year the volcano grew to 336 m (almost 1 metre per day). ...
... continued until 1952. The farmer had noticed a fissure (vent) had opened in the field one morning and from it was pouring black ash. In the first year the volcano grew to 336 m (almost 1 metre per day). ...
volcanoes p p t
... Composite Volcanoes • The magma inside a composite volcano is rich in silica and much thicker than magma from a shield volcano. • Gases get trapped inside this thicker magma. • Eruptions from composite volcanoes can be flowing lava or explosions. The explosive eruptions come from the trapped gases ...
... Composite Volcanoes • The magma inside a composite volcano is rich in silica and much thicker than magma from a shield volcano. • Gases get trapped inside this thicker magma. • Eruptions from composite volcanoes can be flowing lava or explosions. The explosive eruptions come from the trapped gases ...
Lecture11_volcanic_landforms
... A. Cinder Cones: formed by gas-rich lava of any composition (usually basaltic). Built of tephra that is remarkably vesicular (pumice to scoria) Generally short lived eruptions - weeks to a few years until the magma is degassed, then it solidifies in the pipe and flows form from the base ...
... A. Cinder Cones: formed by gas-rich lava of any composition (usually basaltic). Built of tephra that is remarkably vesicular (pumice to scoria) Generally short lived eruptions - weeks to a few years until the magma is degassed, then it solidifies in the pipe and flows form from the base ...
Homework04 n
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions
... • Cinder cones are small volcanoes built primarily of pyroclastic material ejected from a single vent and then cool quickly in the air. These accumulate to make the sides of the volcano. - Steep slope angle - Rather small in height and size - Frequently occur in groups ...
... • Cinder cones are small volcanoes built primarily of pyroclastic material ejected from a single vent and then cool quickly in the air. These accumulate to make the sides of the volcano. - Steep slope angle - Rather small in height and size - Frequently occur in groups ...
Section 1 - kjpederson
... 4. element: a substance in which all the atoms are the same that cannot be broken down into other substances 5. pahoehoe: a hot, fast-moving type of lava that hardens to form smooth, ropelike coils 6. physical property: any characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without chang ...
... 4. element: a substance in which all the atoms are the same that cannot be broken down into other substances 5. pahoehoe: a hot, fast-moving type of lava that hardens to form smooth, ropelike coils 6. physical property: any characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without chang ...
The Origin and Petrogenesis of Mount Hasan (Small Mt. Hasan) and
... Small Mt. Hasan (3069m) and Keçiboyduran (2727m) volcanoes are located within the Cappadocian Volcanic Field in Central Anatolia (Turkey). These Plio-Quaternary volcanoes are major stratovolcanoes of Cappadocian Volcanic Complex (CVC). In this study, we present petrography and major-trace element ge ...
... Small Mt. Hasan (3069m) and Keçiboyduran (2727m) volcanoes are located within the Cappadocian Volcanic Field in Central Anatolia (Turkey). These Plio-Quaternary volcanoes are major stratovolcanoes of Cappadocian Volcanic Complex (CVC). In this study, we present petrography and major-trace element ge ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... from the vent and can flow for many kilometers. Characteristics of an explosive eruption: A volcano erupts explosively if its magma is high in silica. Trapped gases build up pressure until they explode. The erupting gases and steam push the magma out with incredible force. Both kinds of eruptions ca ...
... from the vent and can flow for many kilometers. Characteristics of an explosive eruption: A volcano erupts explosively if its magma is high in silica. Trapped gases build up pressure until they explode. The erupting gases and steam push the magma out with incredible force. Both kinds of eruptions ca ...
Chapter 8
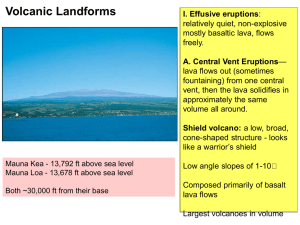
... of layers of lave from repeated non explosive eruptions. Because the lava is very runny, it spreads out over a wide area. Over time the layers of lava create a volcano with gently sloping sides. Although their sides are not very steep, shield volcanoes can be enormous. . ...
... of layers of lave from repeated non explosive eruptions. Because the lava is very runny, it spreads out over a wide area. Over time the layers of lava create a volcano with gently sloping sides. Although their sides are not very steep, shield volcanoes can be enormous. . ...
Devastating landslides related to the 2002 Papandayan eruption
... Papandayan is an A-type active strato volcano located at some 20 km SW of Garut or about 70 km SE of Bandung the capital city of West Java Province. Geographically, the summit of this volcano lies at the intersection between 07º 19’ 42” S and 107º 44” E. The 2002 Papandayan eruption was preceded by ...
... Papandayan is an A-type active strato volcano located at some 20 km SW of Garut or about 70 km SE of Bandung the capital city of West Java Province. Geographically, the summit of this volcano lies at the intersection between 07º 19’ 42” S and 107º 44” E. The 2002 Papandayan eruption was preceded by ...
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano)

Cerro Azul (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈsero aˈsul], blue hill in Spanish), sometimes referred to as Quizapu, is an active stratovolcano in the Maule Region of central Chile, immediately south of Descabezado Grande. Part of the South Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its summit is 3,788 metres (12,428 ft) above sea level, and is capped by a summit crater that is 500 metres (1,600 ft) wide and opens to the north. Beneath the summit, the volcano features numerous scoria cones and flank vents.Cerro Azul is responsible for several of South America's largest recorded eruptions, in 1846 and 1932. In 1846, an effusive eruption formed the vent at the site of present-day Quizapu crater on the northern flank of Cerro Azul and sent lava flowing down the sides of the volcano, creating a lava field 8–9 square kilometres (3–3.5 square miles) in area. Phreatic and Strombolian volcanism between 1907 and 1932 excavated this crater. In 1932, one of the largest explosive eruptions of the 20th century occurred at Quizapu Crater and sent 9.5 cubic kilometres (2.3 cu mi) of ash into the atmosphere. The volcano's most recent eruption was in 1967.The South Volcanic Zone has a long history of eruptions and poses a threat to the surrounding region. Any volcanic hazard—ranging from minor ashfalls to pyroclastic flows—could pose a significant risk to humans and wildlife. Despite its inactivity, Cerro Azul could again produce a major eruption; if this were to happen, relief efforts would probably be quickly organized. Teams such as the Volcano Disaster Assistance Program (VDAP) are prepared to effectively evacuate, assist, and rescue people threatened by volcanic eruptions.