From Short Run to Long Run
... • Nominal wages eventually rise to maintain real wages (purchasing power). • Other input prices rise • Short run aggregate supply shifts left because costs are higher. • Return to potential output at a higher price level. LO1 ...
... • Nominal wages eventually rise to maintain real wages (purchasing power). • Other input prices rise • Short run aggregate supply shifts left because costs are higher. • Return to potential output at a higher price level. LO1 ...
Social Studies 30 - Sundre High School
... to fail. In a panic, people tried to sell their shares which drove the price of shares far below what people had paid for them. Companies failed, creating unemployment and further reducing consumer demand. Governments of market economies were largely unresponsive to the crisis, believing that the do ...
... to fail. In a panic, people tried to sell their shares which drove the price of shares far below what people had paid for them. Companies failed, creating unemployment and further reducing consumer demand. Governments of market economies were largely unresponsive to the crisis, believing that the do ...
ch23
... The economy is operating efficiently when workers are assigned to jobs based upon comparative advantage – Inflexible labor markets lead to inefficient allocations of workers to jobs and thus to an economy operating below potential output ...
... The economy is operating efficiently when workers are assigned to jobs based upon comparative advantage – Inflexible labor markets lead to inefficient allocations of workers to jobs and thus to an economy operating below potential output ...
Economic Activity in a Changing World
... The USA has a very high GDP compared to other countries Higher Standard of Living – is the ...
... The USA has a very high GDP compared to other countries Higher Standard of Living – is the ...
CHAPTER 4: GLOBAL ECONOMICS
... 4. STABLE PRICES- PRICES THAT DO NOT INCREASE IN A SHORT PERIOD OF TIME. ...
... 4. STABLE PRICES- PRICES THAT DO NOT INCREASE IN A SHORT PERIOD OF TIME. ...
Lecture 2 PPT - Kleykamp in Taiwan
... Some Criticisms of This Policy (1)It is not “people” but commercial banks that want to sit on trillions of dollars of money (reserves held at the Fed). They do this because of simple Keynesian liquidity preference – they expect higher rates will prevail in the future and do not want to lend now at ...
... Some Criticisms of This Policy (1)It is not “people” but commercial banks that want to sit on trillions of dollars of money (reserves held at the Fed). They do this because of simple Keynesian liquidity preference – they expect higher rates will prevail in the future and do not want to lend now at ...
Notes 1. that`s a Fedspeak for - что на языке ФРС означает 2
... How does the author define NAIRU? What Russian term corresponds to it? What does the term "tight labor market" mean? What does the "Federal Reserve" stand for? What's its function? What's the name of the Fed policy? What is its Russian equivalent? Why may 2006 be different from the late 90s? Expand ...
... How does the author define NAIRU? What Russian term corresponds to it? What does the term "tight labor market" mean? What does the "Federal Reserve" stand for? What's its function? What's the name of the Fed policy? What is its Russian equivalent? Why may 2006 be different from the late 90s? Expand ...
Course contents - East West University
... function and national income distribution among factors, implication of factor’s share. o Business Cycle: relationship between GDP growth, inflation and unemployment, sources of the economic growth, convergence in the economy: East Asian Miracle. o Real Sector Economy: consumption function, consumpt ...
... function and national income distribution among factors, implication of factor’s share. o Business Cycle: relationship between GDP growth, inflation and unemployment, sources of the economic growth, convergence in the economy: East Asian Miracle. o Real Sector Economy: consumption function, consumpt ...
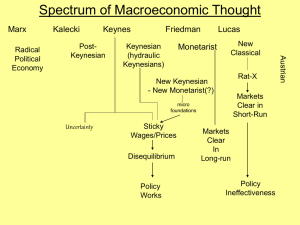
Macro Spectrum
... • A New Classical Story: Because they do not have all the information that would enable them to compute perfectly the relative prices they care about, agents make errors…[A]gents temporarily mistake a general increase in all absolute prices as an increase in the relative price of the good they are s ...
... • A New Classical Story: Because they do not have all the information that would enable them to compute perfectly the relative prices they care about, agents make errors…[A]gents temporarily mistake a general increase in all absolute prices as an increase in the relative price of the good they are s ...
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
... Expansionary Fiscal Policy (Fiscal – of/or relating to govt.) Tools: Decrease Taxes / Increase Govt. spending {Goal?} Federal Reserve – Expansionary Monetary Policy Tools: Decrease Interest rates (increase money supply) {Goal?} ...
... Expansionary Fiscal Policy (Fiscal – of/or relating to govt.) Tools: Decrease Taxes / Increase Govt. spending {Goal?} Federal Reserve – Expansionary Monetary Policy Tools: Decrease Interest rates (increase money supply) {Goal?} ...
Zero Unemployment in a Plural Economy
... necessity of having markets for its products. The public sector normally has insufficient resources to satisfy social needs, even ...
... necessity of having markets for its products. The public sector normally has insufficient resources to satisfy social needs, even ...
Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation
... Bank, http://www.minneapolisfed.org/ Output data are in 2000 dollars LO1 ...
... Bank, http://www.minneapolisfed.org/ Output data are in 2000 dollars LO1 ...
Getting Back to Full Employment - The Center for Economic and
... middle-wage workers relative to those at the top of the pay scale. In other words, it pushes back against the long-term trend of wage and income inequality. Moving towards full employment is clearly associated with higher tax revenues, due to more people working and thus paying taxes, and at the sam ...
... middle-wage workers relative to those at the top of the pay scale. In other words, it pushes back against the long-term trend of wage and income inequality. Moving towards full employment is clearly associated with higher tax revenues, due to more people working and thus paying taxes, and at the sam ...
Short run - TerpConnect
... Consumption and investment fluctuate with GDP, but consumption tends to be less volatile and investment more volatile than GDP. ...
... Consumption and investment fluctuate with GDP, but consumption tends to be less volatile and investment more volatile than GDP. ...
The Art and Science of Economics
... For example, suppose the government increases unemployment benefits and finances these transfer payments with higher taxes on current workers. If the marginal propensity to consume is the same for both groups, the reduction in spending by those whose taxes increase should just offset the increase in ...
... For example, suppose the government increases unemployment benefits and finances these transfer payments with higher taxes on current workers. If the marginal propensity to consume is the same for both groups, the reduction in spending by those whose taxes increase should just offset the increase in ...
Unemployment and Inflation
... labor force U-2 Job losers and persons who completed temporary jobs, as a percent of the civilian labor force U-3 Total unemployed, as a percent of the civilian labor force (official unemployment rate) U-4 Total unemployed plus discouraged workers, as a percent of the civilian labor force plus disco ...
... labor force U-2 Job losers and persons who completed temporary jobs, as a percent of the civilian labor force U-3 Total unemployed, as a percent of the civilian labor force (official unemployment rate) U-4 Total unemployed plus discouraged workers, as a percent of the civilian labor force plus disco ...
20140416 Budgeting and Macro Policy
... – If PY too large relative to trend, Federal Reserve pushes M down— and so Y (production and employment) falls and P (inflation) decelerates. – If the rest of the government does something that disturbs this relationship, the Federal Reserve can and does neutralize it • Hence fiscal policy should be ...
... – If PY too large relative to trend, Federal Reserve pushes M down— and so Y (production and employment) falls and P (inflation) decelerates. – If the rest of the government does something that disturbs this relationship, the Federal Reserve can and does neutralize it • Hence fiscal policy should be ...
THE GREAT DEPRESSION
... unemployment never fell below 14.3% Since 1941 it has never risen above 10% ...
... unemployment never fell below 14.3% Since 1941 it has never risen above 10% ...
ppt
... Rule of thumb: in the U.S. today, boost the (risky) real interest rate r by 1%-point: reduces exports by $50 billion/year; reduces household consumption spending by $50 billion/year; and reduces business investment spending by $200 billion/year ...
... Rule of thumb: in the U.S. today, boost the (risky) real interest rate r by 1%-point: reduces exports by $50 billion/year; reduces household consumption spending by $50 billion/year; and reduces business investment spending by $200 billion/year ...
PPT 1 Economic Indicators
... A nation’s rate of economic growth is the percentage change in its real GDP from one year to another ...
... A nation’s rate of economic growth is the percentage change in its real GDP from one year to another ...
Fall 1996 Midterm #2
... b) (2 pts.) Mark anticipates the price level will rise by 20% during the year. What real interest rate does he expect to pay? ...
... b) (2 pts.) Mark anticipates the price level will rise by 20% during the year. What real interest rate does he expect to pay? ...
Full employment
Full employment, in macroeconomics, is the level of employment rates where there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment. It is defined by the majority of mainstream economists as being an acceptable level of unemployment somewhere above 0%. The discrepancy from 0% arises due to non-cyclical types of unemployment, such as frictional unemployment (there will always be people who have quit or have lost a seasonal job and are in the process of getting a new job) and structural unemployment (mismatch between worker skills and job requirements). Unemployment above 0% is seen as necessary to control inflation in capitalist economies, to keep inflation from accelerating, i.e., from rising from year to year. This view is based on a theory centering on the concept of the Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (NAIRU); in the current era, the majority of mainstream economists mean NAIRU when speaking of ""full"" employment. The NAIRU has also been described by Milton Friedman, among others, as the ""natural"" rate of unemployment. Having many names, it has also been called the structural unemployment rate.The 20th century British economist William Beveridge stated that an unemployment rate of 3% was full employment. Other economists have provided estimates between 2% and 13%, depending on the country, time period, and their political biases. For the United States, economist William T. Dickens found that full-employment unemployment rate varied a lot over time but equaled about 5.5 percent of the civilian labor force during the 2000s. Recently, economists have emphasized the idea that full employment represents a ""range"" of possible unemployment rates. For example, in 1999, in the United States, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) gives an estimate of the ""full-employment unemployment rate"" of 4 to 6.4%. This is the estimated unemployment rate at full employment, plus & minus the standard error of the estimate.The concept of full employment of labor corresponds to the concept of potential output or potential real GDP and the long run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve. In neoclassical macroeconomics, the highest sustainable level of aggregate real GDP or ""potential"" is seen as corresponding to a vertical LRAS curve: any increase in the demand for real GDP can only lead to rising prices in the long run, while any increase in output is temporary.