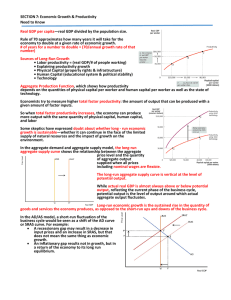
SECTION 7: Economic Growth & Productivity Need to Know —real GDP divided by the population size.
... In the AD/AS model, a short‐run fluctuation of the business cycle would be seen as a shift of the AD curve or SRAS curve. For example: A recessionary gap may result in a decrease in input prices and an increase in SRAS, but that does not mean the same thing as economic growth. An inflati ...
... In the AD/AS model, a short‐run fluctuation of the business cycle would be seen as a shift of the AD curve or SRAS curve. For example: A recessionary gap may result in a decrease in input prices and an increase in SRAS, but that does not mean the same thing as economic growth. An inflati ...
Business Cycle/ Economic Indicators Chart
... 6. If real GDP were increasing where would the economy be on the business cycle? _________________________________________________________________ 7. If real GDP was on the decline where would the economy be on the business cycle? ____________________________________________________________ 8. What ...
... 6. If real GDP were increasing where would the economy be on the business cycle? _________________________________________________________________ 7. If real GDP was on the decline where would the economy be on the business cycle? ____________________________________________________________ 8. What ...
View Additional Attachment
... Role of data in macroeconomic analysis Tracking the U.S. economy Defining and calculating Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Defining and calculating unemployment Defining and calculating inflation The role of productivity in economic growth and standards of living ...
... Role of data in macroeconomic analysis Tracking the U.S. economy Defining and calculating Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Defining and calculating unemployment Defining and calculating inflation The role of productivity in economic growth and standards of living ...
A Brief Economic History of the United States
... The “New Economy” of the Nineties (Continued) • The last two decades our economy has become increasingly integrated with the global economy • This has resulted in – An exodus of jobs making shoes, electronics, toys and clothing to developing countries – Service work like writing software code and p ...
... The “New Economy” of the Nineties (Continued) • The last two decades our economy has become increasingly integrated with the global economy • This has resulted in – An exodus of jobs making shoes, electronics, toys and clothing to developing countries – Service work like writing software code and p ...
Ch. 12 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice
... 5. During the 1930s, the United States experienced A. prosperity before the crash. C. post-War boom. B. depression. D. very high rate of inflation. 6. An economy that experiences decreasing real GDP and increasing prices is said to suffer from A. a recession. C. a business cycle. B. a depression. D. ...
... 5. During the 1930s, the United States experienced A. prosperity before the crash. C. post-War boom. B. depression. D. very high rate of inflation. 6. An economy that experiences decreasing real GDP and increasing prices is said to suffer from A. a recession. C. a business cycle. B. a depression. D. ...
Chapter 10: Economic Performance
... C. Output Produced Within National Borders Explain the four sectors of the product market used to make up the GDP (Output-Expenditure Model): A. Personal Consumption Expenditures B. Gross Investment C. Government Purchases D. Net Exports What is the difference between the Nominal GDP and the Real GD ...
... C. Output Produced Within National Borders Explain the four sectors of the product market used to make up the GDP (Output-Expenditure Model): A. Personal Consumption Expenditures B. Gross Investment C. Government Purchases D. Net Exports What is the difference between the Nominal GDP and the Real GD ...
Romer, Christina D., (2008), Business Cycles, The concise
... System. The series before 1919 is an adjusted and smoothed version of the Miron-Romer index of industrial production. This series is described in the appendix to “Remeasuring Business Cycles” by Christina D. Romer. Note: The peak-to-trough decline is calculated using the actual peaks and troughs in ...
... System. The series before 1919 is an adjusted and smoothed version of the Miron-Romer index of industrial production. This series is described in the appendix to “Remeasuring Business Cycles” by Christina D. Romer. Note: The peak-to-trough decline is calculated using the actual peaks and troughs in ...
International Insolvency Law Organisational matters
... real estate prices. Risk on loans granted by banks increased significantly, as they were not anymore covered by the value of real estate used as collateral. Resulting doubts over long-term solvency of banks caused interbank lending to freeze. Inflation level was 4% and growing before the fall of rea ...
... real estate prices. Risk on loans granted by banks increased significantly, as they were not anymore covered by the value of real estate used as collateral. Resulting doubts over long-term solvency of banks caused interbank lending to freeze. Inflation level was 4% and growing before the fall of rea ...
Economic Issues of the Great Depression
... spending measures may have been critical to avoiding a much larger crisis, but our national debt is rising rapidly. It is now over $12 Trillion (more than $40,000 per citizen) Current deficits are adding to this number at record rates ...
... spending measures may have been critical to avoiding a much larger crisis, but our national debt is rising rapidly. It is now over $12 Trillion (more than $40,000 per citizen) Current deficits are adding to this number at record rates ...
Modeling Dynamics Of Dividend Policy, Capital Structure And
... Classical economic theory has always claimed that the economy is always at full-employment. Guarantee that, all output produced by firms will be taken up by consumers on the principles that, supply creates its own demand. In the short-run there will be temporary disequilibrium in the capital, ...
... Classical economic theory has always claimed that the economy is always at full-employment. Guarantee that, all output produced by firms will be taken up by consumers on the principles that, supply creates its own demand. In the short-run there will be temporary disequilibrium in the capital, ...
ECON 201-100 Principles of Macroeconomics
... Econanics 201 is an introduction to rnacroeconanic theory. As such, it will not undertake to survey all the topics included in the discipline nor will be pursue any one topic in great detail . The aim of the course is t o provide the student with an overview of the econany examining the flow of inco ...
... Econanics 201 is an introduction to rnacroeconanic theory. As such, it will not undertake to survey all the topics included in the discipline nor will be pursue any one topic in great detail . The aim of the course is t o provide the student with an overview of the econany examining the flow of inco ...
STUDY UNIT 1 CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS ECONOMICS ALL ABOUT 1
... - seeks to describe, explain, analyse and predict phenomena like economic growth, unemployment, inflation, trade between individuals, and countries, prices of goods and services, poverty, wealth, money, interest rates, exchange rates, business cycles. 1.1 Scarcity, choice and opportunity Scarcity ...
... - seeks to describe, explain, analyse and predict phenomena like economic growth, unemployment, inflation, trade between individuals, and countries, prices of goods and services, poverty, wealth, money, interest rates, exchange rates, business cycles. 1.1 Scarcity, choice and opportunity Scarcity ...
Guide 3
... Traditional Economic System- An economics system that is based on customs and traditions. The focus is to produce and sell products in the same manner generation after generation. (Example would include the Amish society) Command Economic System- A system where the Government has control over the al ...
... Traditional Economic System- An economics system that is based on customs and traditions. The focus is to produce and sell products in the same manner generation after generation. (Example would include the Amish society) Command Economic System- A system where the Government has control over the al ...
Ch16-- Macroeconomic Viewpoints
... Supply creates its own demand – The classical view prevailed before the Great Depression. ...
... Supply creates its own demand – The classical view prevailed before the Great Depression. ...