What is String Theory?
... Perturbation expansion and UV finiteness Supersymmetry? Space-time dimension, and compactification Geometrization of interactions, moduli, landscape of vacua ...
... Perturbation expansion and UV finiteness Supersymmetry? Space-time dimension, and compactification Geometrization of interactions, moduli, landscape of vacua ...
Intro to particle physics 1. Particles, Fields
... Read off strength of interaction from term. Here, e=coupling constant In QED, this is a coupling ...
... Read off strength of interaction from term. Here, e=coupling constant In QED, this is a coupling ...
General Relativity as an Effective Field Theory
... Recall the need for gauge fixing and ghosts Gauge invariance causes problems - no propagator in pert. theory - infinite gauge copies in path integral We proceed by fixing gauge But some gauges include non-physical DOF Removed by Feynman-DeWitt-Fadeev-Popov trick - exponentiating gauge constraint as ...
... Recall the need for gauge fixing and ghosts Gauge invariance causes problems - no propagator in pert. theory - infinite gauge copies in path integral We proceed by fixing gauge But some gauges include non-physical DOF Removed by Feynman-DeWitt-Fadeev-Popov trick - exponentiating gauge constraint as ...
Hamiltonian Mechanics and Symplectic Geometry
... there are a lot more ways to choose the complex structure on phase space. This will be discussed in detail when we come to the quantum harmonic oscillator. Another important example corresponds physically to the behavior of a particle with magnetic moment proportional to its “spin”, moving in a magn ...
... there are a lot more ways to choose the complex structure on phase space. This will be discussed in detail when we come to the quantum harmonic oscillator. Another important example corresponds physically to the behavior of a particle with magnetic moment proportional to its “spin”, moving in a magn ...
The effective field theory of general relativity and running couplings
... -Background field method ‘t Hooft Veltman -retains symmetries of GR -path integral Background field: Expand around this background: ...
... -Background field method ‘t Hooft Veltman -retains symmetries of GR -path integral Background field: Expand around this background: ...
slides
... In this model the best discretization would be the Abelian one we presented. One could then construct H and show that zero is an eigenvalue. Since the method coincides with the Dirac method for Abelian constraints, there is no need to do this. In order to illustrate what is expected to happen in mor ...
... In this model the best discretization would be the Abelian one we presented. One could then construct H and show that zero is an eigenvalue. Since the method coincides with the Dirac method for Abelian constraints, there is no need to do this. In order to illustrate what is expected to happen in mor ...
Two-dimensional SYM theory with fundamental mass and Chern
... • Supersymmetric Discretized Light-Cone Quantization (SDLCQ) is a practical tool to calculate bound state masses, structure functions and more • Generated mass term for fundamentals from VEV of perpendicular gauge boson in higher dimensional theory • Studied masses and bound-state properties as a fu ...
... • Supersymmetric Discretized Light-Cone Quantization (SDLCQ) is a practical tool to calculate bound state masses, structure functions and more • Generated mass term for fundamentals from VEV of perpendicular gauge boson in higher dimensional theory • Studied masses and bound-state properties as a fu ...
RENORMALIZATION AND GAUGE INVARIANCE∗
... When the dynamical laws of continuous systems, such as the equations for fields in a multi-dimensional world, are subject to the rules of Quantum Mechanics, one encounters divergent expressions that, at first sight, seem to invalidate the entire theory. Quantum corrections are never small, because t ...
... When the dynamical laws of continuous systems, such as the equations for fields in a multi-dimensional world, are subject to the rules of Quantum Mechanics, one encounters divergent expressions that, at first sight, seem to invalidate the entire theory. Quantum corrections are never small, because t ...
Path integral approach to the heat kernel 1 Introduction
... V to contain it). In the path integral approach similar ambiguities appear. They take the form of ambiguous Feynman diagrams. As we have seen, Feynman diagrams correspond to integrations of various propagators joined at vertices with some factors and/or derivatives. The propagators correspond in gen ...
... V to contain it). In the path integral approach similar ambiguities appear. They take the form of ambiguous Feynman diagrams. As we have seen, Feynman diagrams correspond to integrations of various propagators joined at vertices with some factors and/or derivatives. The propagators correspond in gen ...
Gauges - ETH Zürich
... entirely on the electric and magnetic fields that are present. • These fields can be represented as derivatives of scalar and vector potential functions that are often mathematically convenient, but are actually only auxiliary quantities. (Each such set is called a gauge.) • The potential functions ...
... entirely on the electric and magnetic fields that are present. • These fields can be represented as derivatives of scalar and vector potential functions that are often mathematically convenient, but are actually only auxiliary quantities. (Each such set is called a gauge.) • The potential functions ...
2. Free Fields
... is deceptively simple: if you were to write the wavefunction in quantum field theory, it would be a functional, that is a function of every possible configuration of the field φ. The typical information we want to know about a quantum theory is the spectrum of the Hamiltonian H. In quantum field the ...
... is deceptively simple: if you were to write the wavefunction in quantum field theory, it would be a functional, that is a function of every possible configuration of the field φ. The typical information we want to know about a quantum theory is the spectrum of the Hamiltonian H. In quantum field the ...
shp_09 - Nevis Laboratories
... anything. It’s just that our choice of a ground state “hides” or “breaks” the obvious reflection symmetry of the original Lagrangian. What about the spontaneous part? If you think about it, the choice of a ground state is completely arbitrary in this system. There is no external agency that favors o ...
... anything. It’s just that our choice of a ground state “hides” or “breaks” the obvious reflection symmetry of the original Lagrangian. What about the spontaneous part? If you think about it, the choice of a ground state is completely arbitrary in this system. There is no external agency that favors o ...
CHAPTER 2. LAGRANGIAN QUANTUM FIELD THEORY §2.1
... so that we may impose the quantum mechanical commutation relations between them. Hence we would like to Legendre transform our Lagrangian system to a Hamiltonian formulation. We can see how to introduce the appropriate dynamical variables for this transformation by exhibiting the classical mechanica ...
... so that we may impose the quantum mechanical commutation relations between them. Hence we would like to Legendre transform our Lagrangian system to a Hamiltonian formulation. We can see how to introduce the appropriate dynamical variables for this transformation by exhibiting the classical mechanica ...
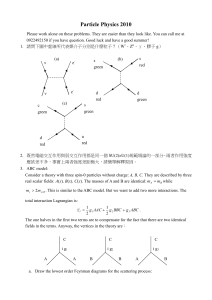
Euler Lagrange Equation
... - Gluons do carry colour charge,so to solve the QCD theory, approximations are proposed (e.g. Lattice calculation method ). - There is a fermion doubling problem in lattice which can be solved by various methods. - In order to obtain light quark properties, we need bigger computers and the calculati ...
... - Gluons do carry colour charge,so to solve the QCD theory, approximations are proposed (e.g. Lattice calculation method ). - There is a fermion doubling problem in lattice which can be solved by various methods. - In order to obtain light quark properties, we need bigger computers and the calculati ...
What black holes teach about strongly coupled particles
... panel typically have a short mean free path and mean free travel time τ before they interact with others. The system of weakly interacting particles illustrated in the left panel is amenable to traditional perturbative calculational techniques, but as τ decreases, particles begin to lose their indiv ...
... panel typically have a short mean free path and mean free travel time τ before they interact with others. The system of weakly interacting particles illustrated in the left panel is amenable to traditional perturbative calculational techniques, but as τ decreases, particles begin to lose their indiv ...
algebraic quantization and t
... various others. These techniques have led to important insights concerning the existence of various 'inequivalent' quantum theories corresponding to a given classical system, which appear to go hand in hand with certain 'topological' terms in the action (or Hamiltonian). Thus kinematical and dynamic ...
... various others. These techniques have led to important insights concerning the existence of various 'inequivalent' quantum theories corresponding to a given classical system, which appear to go hand in hand with certain 'topological' terms in the action (or Hamiltonian). Thus kinematical and dynamic ...
Progress In N=2 Field Theory - Rutgers Physics
... U.B. 2: Find the space of BPS states for other theories. U.B. 3: Find exact results for path integrals – including insertions of ``defects’’ such as ``line operators,’’ ``surface operators’’, ….. ...
... U.B. 2: Find the space of BPS states for other theories. U.B. 3: Find exact results for path integrals – including insertions of ``defects’’ such as ``line operators,’’ ``surface operators’’, ….. ...
this PDF file - e
... In the same era, the theory that tries to understand the behaviour of small objects (or particle) emerges, known as the quantum theory. Then, because subatomic particle travel with speed close to light speed (c = 3 x 108 m/s), the special theory of relativity is considered to play a role in quantum ...
... In the same era, the theory that tries to understand the behaviour of small objects (or particle) emerges, known as the quantum theory. Then, because subatomic particle travel with speed close to light speed (c = 3 x 108 m/s), the special theory of relativity is considered to play a role in quantum ...
Heavy gravitons on-shell decay of the Higgs boson at high
... space-time is always flat and space-time metric is always Minkowski metric, so gαβ is no longer space-time metric [41]. Equation (4) gives the mass term in gravitational gauge fields. To obtain the eigenstates of mass matrix the following rotation is needed C 3 co s C sin C 2 ...
... space-time is always flat and space-time metric is always Minkowski metric, so gαβ is no longer space-time metric [41]. Equation (4) gives the mass term in gravitational gauge fields. To obtain the eigenstates of mass matrix the following rotation is needed C 3 co s C sin C 2 ...
The Klein-Gordon equation
... physical quantities can be calculated from the qi and pi after some prescription for the order of the qi and pi in the operators. In particular, the Hamiltonian is given by the Legendre transform ...
... physical quantities can be calculated from the qi and pi after some prescription for the order of the qi and pi in the operators. In particular, the Hamiltonian is given by the Legendre transform ...