Solve the equation.
... To find solutions, perform inverse operations until you have isolated the variable. A variable is isolated when it appears by itself on one side of an equation, and not at all on the other side. Inverse Operations ...
... To find solutions, perform inverse operations until you have isolated the variable. A variable is isolated when it appears by itself on one side of an equation, and not at all on the other side. Inverse Operations ...
The path integral representation kernel of evolution operator in
... The path integral method was proposed by R. Feynman as a new approach [1] to the solution of quantum mechanical problems. Nowadays it became one of the most powerful methods in theoretical physics. Many applications (see [2–5]) of this method are devoted to diverse important problems. In articles [6 ...
... The path integral method was proposed by R. Feynman as a new approach [1] to the solution of quantum mechanical problems. Nowadays it became one of the most powerful methods in theoretical physics. Many applications (see [2–5]) of this method are devoted to diverse important problems. In articles [6 ...
Partial differential equations
... General analytical solutions of PDEs are available only in the simplest cases, and because of this freedom, they do not yet solve the problem. The actual form of the solution is defined by the symmetry of the problem (if it exists) and boundary conditions. If one of the variables is time, one usuall ...
... General analytical solutions of PDEs are available only in the simplest cases, and because of this freedom, they do not yet solve the problem. The actual form of the solution is defined by the symmetry of the problem (if it exists) and boundary conditions. If one of the variables is time, one usuall ...
Exact solutions of a Dirac equation with a varying CP
... quasiparticle approximation (cQPA), an approximation scheme in finite temperature field theory that enables studying non-equilibrium phenomena. Using cQPA we show that in non-translation invariant systems the phase space of the Wightman function has in general structure beyond the traditional mass-s ...
... quasiparticle approximation (cQPA), an approximation scheme in finite temperature field theory that enables studying non-equilibrium phenomena. Using cQPA we show that in non-translation invariant systems the phase space of the Wightman function has in general structure beyond the traditional mass-s ...
Quantum Field Theory I, Lecture Notes
... learn about many aspects of physics, some of which have attained a mythological status: • anti-particles, anti-matter, ...
... learn about many aspects of physics, some of which have attained a mythological status: • anti-particles, anti-matter, ...
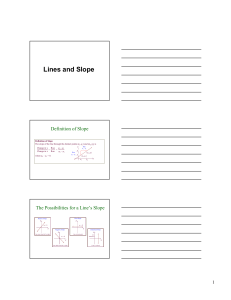
Algebra I
... Step 3- Choose one of the points Step 4- Plug in the set of points and the slope in the equation of the line. Step 5- Distribute and add or subtract like terms. Step 6- Write the final equation with slope and the y intercept. ...
... Step 3- Choose one of the points Step 4- Plug in the set of points and the slope in the equation of the line. Step 5- Distribute and add or subtract like terms. Step 6- Write the final equation with slope and the y intercept. ...
Quantum theory of many − particle systems
... This is the Lagrange equation for a particle in one dimension. We have derived it for a very simple mechanical problem, but the result can be generalized to any number of particles and any number of dimensions. If we consider a system of N particles in three dimensions, we need 3N coordinates to spe ...
... This is the Lagrange equation for a particle in one dimension. We have derived it for a very simple mechanical problem, but the result can be generalized to any number of particles and any number of dimensions. If we consider a system of N particles in three dimensions, we need 3N coordinates to spe ...







![Dirac multimode ket-bra operators` [equation]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/023088225_1-3900fa8a2c451013a9516ce21d0ecd01-300x300.png)