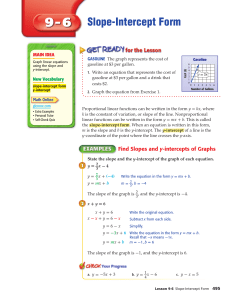
Enabling single-mode behavior over large areas with photonic Dirac
... examples include ultralow-threshold lasers (25–27) and singlephoton sources (28, 29) based on PhC cavities]. The dependence of the β-factor on the particular electromagnetic environment in which the considered emitter is embedded can be elucidated by examining its link with the corresponding ^ ωÞ. F ...
... examples include ultralow-threshold lasers (25–27) and singlephoton sources (28, 29) based on PhC cavities]. The dependence of the β-factor on the particular electromagnetic environment in which the considered emitter is embedded can be elucidated by examining its link with the corresponding ^ ωÞ. F ...
Solutions to Exercises, Section 2.1
... x−2 Multiplying both sides of this equation by x − 2 and then adding 1 gives the equation y = 4x − 7. Now we can find a number c such that the point (c, −19) is on the line given by the equation above. To do this, in the equation above replace x by c and y by −19, getting −19 = 4c − 7. Solving this e ...
... x−2 Multiplying both sides of this equation by x − 2 and then adding 1 gives the equation y = 4x − 7. Now we can find a number c such that the point (c, −19) is on the line given by the equation above. To do this, in the equation above replace x by c and y by −19, getting −19 = 4c − 7. Solving this e ...
Lectures on Atomic Physics
... A(MHz) for states in Na (µI = 2.2176, I = 3/2) with experimental data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.4 Contributions to the reduced matrix element of the electric dipole transition operator ωr in length-form and in velocity form for the 3s − 3p1/2 transition in Na ...
... A(MHz) for states in Na (µI = 2.2176, I = 3/2) with experimental data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.4 Contributions to the reduced matrix element of the electric dipole transition operator ωr in length-form and in velocity form for the 3s − 3p1/2 transition in Na ...
Paul A.M. Dirac`sThe Principles of Quantum Mechanics | SpringerLink
... stage, the tone, and much of the language of the quantum-mechanical revolution, was published three-quarters of a century ago in 1930.1 Abdus Salam and Eugene P. Wigner declared in their preface of a book commemorating Dirac’s seventieth birthday that: Posterity will rate Dirac [figure 1] as one of ...
... stage, the tone, and much of the language of the quantum-mechanical revolution, was published three-quarters of a century ago in 1930.1 Abdus Salam and Eugene P. Wigner declared in their preface of a book commemorating Dirac’s seventieth birthday that: Posterity will rate Dirac [figure 1] as one of ...