Syllabus : Advanced Quantum Mechanics (Prof
... Quantum Field Theory (Revised Edition) by F. Mandl and G. Shaw (Wiley ISBN 0-471-94186-7) This graduate level course is an introduction to quantum field theory using canonical quantization. The emphasis is on the application of field theoretic concepts and methods to understand and be able to calcul ...
... Quantum Field Theory (Revised Edition) by F. Mandl and G. Shaw (Wiley ISBN 0-471-94186-7) This graduate level course is an introduction to quantum field theory using canonical quantization. The emphasis is on the application of field theoretic concepts and methods to understand and be able to calcul ...
Document
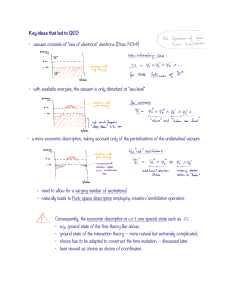
... the parameter that gives the infinitesimal change is a vector field. Hence these constraints must multiply a vector field, without using a metric. Thus these constraints are the components of a one form. It should also be invariant under ordinary gauge transformations, as they commute with differomo ...
... the parameter that gives the infinitesimal change is a vector field. Hence these constraints must multiply a vector field, without using a metric. Thus these constraints are the components of a one form. It should also be invariant under ordinary gauge transformations, as they commute with differomo ...
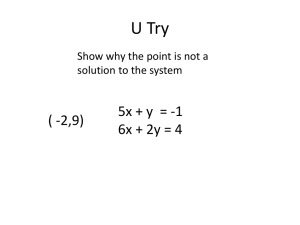
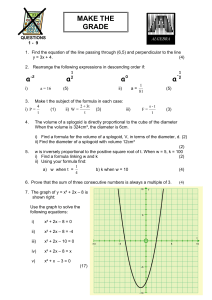
7.2 and 7.3 Quadratic Formula and Discriminant Printable
... The Discriminant & Quadratic Formula Learning goal Solve quadratic equations by inspection (e.g., for x² = 49), taking square roots, completing the square, the quadratic formula and factoring, as appropriate to the initial form of the equation. Recognize when the quadratic formula gives complex solu ...
... The Discriminant & Quadratic Formula Learning goal Solve quadratic equations by inspection (e.g., for x² = 49), taking square roots, completing the square, the quadratic formula and factoring, as appropriate to the initial form of the equation. Recognize when the quadratic formula gives complex solu ...
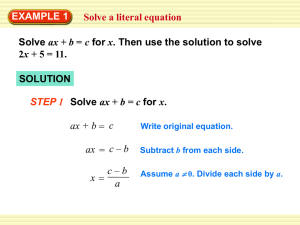
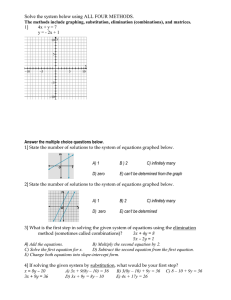
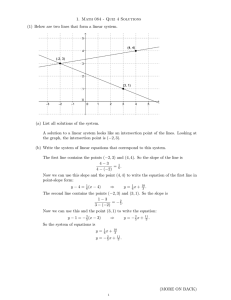
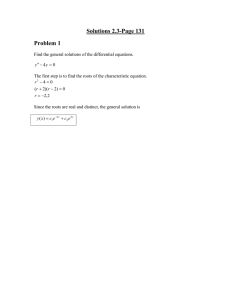
Solution - UFL MAE
... The general solution is y = c1e 3 x + c 2 e x . The initial conditions are used to find the constants. y ′ = 3c1e 3 x + c 2 e x . Substituting the initial conditions gives: y (0) = 7 = c1 + c 2 y ′(0) = 11 = 3c1 + c 2 ...
... The general solution is y = c1e 3 x + c 2 e x . The initial conditions are used to find the constants. y ′ = 3c1e 3 x + c 2 e x . Substituting the initial conditions gives: y (0) = 7 = c1 + c 2 y ′(0) = 11 = 3c1 + c 2 ...