Exam 3
... b. a recession will not occur c. inflationary expectations will fall d. the natural rate of unemployment will rise e. structural unemployment will start to decrease ____ 20. A zero inflation rate is not the Fed's objective because a. that would cause prices to rise b. that would cause price to fall ...
... b. a recession will not occur c. inflationary expectations will fall d. the natural rate of unemployment will rise e. structural unemployment will start to decrease ____ 20. A zero inflation rate is not the Fed's objective because a. that would cause prices to rise b. that would cause price to fall ...
lecture notes
... Aggregate demand is a schedule or curve that shows the various amounts of real domestic output that domestic and foreign buyers will want to purchase at each possible price level. A. The aggregate demand curve is shown in Figure 10.1. 1. It shows an inverse relationship between price level and real ...
... Aggregate demand is a schedule or curve that shows the various amounts of real domestic output that domestic and foreign buyers will want to purchase at each possible price level. A. The aggregate demand curve is shown in Figure 10.1. 1. It shows an inverse relationship between price level and real ...
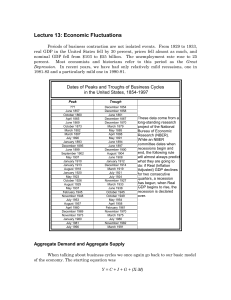
3. Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand. Internal Balance
... For example, the economy may be in short-run equilibrium at point A in our graph. But it will not remain there. The actual output is less than potential output, the recessionary gap exists. Firms are not selling as much as they would like to and so they slow down the rate at which they increase the ...
... For example, the economy may be in short-run equilibrium at point A in our graph. But it will not remain there. The actual output is less than potential output, the recessionary gap exists. Firms are not selling as much as they would like to and so they slow down the rate at which they increase the ...
Unit 3 PPT
... – A high inflation rate forces firms to change prices more often than they would if the price level was more or less stable. – The changing of a listed price has a “real” cost. ...
... – A high inflation rate forces firms to change prices more often than they would if the price level was more or less stable. – The changing of a listed price has a “real” cost. ...
Economics 302 Spring 2007 Homework #5 Homework will be
... be higher or lower than 1,500? If you expect equilibrium Y to be different, explain the mechanism by which you would expect Y to change in this economy. Planned expenditure is 1,600. Inventory deculmulation is 100. Equilibrium Y should be higher than 1,500. Finally, since planned expenditure is grea ...
... be higher or lower than 1,500? If you expect equilibrium Y to be different, explain the mechanism by which you would expect Y to change in this economy. Planned expenditure is 1,600. Inventory deculmulation is 100. Equilibrium Y should be higher than 1,500. Finally, since planned expenditure is grea ...
Economic Policies for the 1980`s - Scholarly Commons
... Accordingly, this paper is devoted to issues of macroeconomic stabilization, highlighting the twin problems of unemployment and inflation. While the policy objective is to attain both full employment and price stability, these two targets are not jointly attainable. Price stability can be achieved, ...
... Accordingly, this paper is devoted to issues of macroeconomic stabilization, highlighting the twin problems of unemployment and inflation. While the policy objective is to attain both full employment and price stability, these two targets are not jointly attainable. Price stability can be achieved, ...
BB111_fme_lnt_008_Ma..
... economy’s production capabilities. • Improvements in and greater stocks of land, labor, and capital can shift out the production possibilities ...
... economy’s production capabilities. • Improvements in and greater stocks of land, labor, and capital can shift out the production possibilities ...
Lecture 13
... aggregate demand curve is a downward sloping function of price. The higher the level of P, the lower the level of aggregate demand. Why is the aggregate supply curve not a function of price? Long proofs that supply curves slope upward are generally a sure-fire cure for insomnia. However, the total a ...
... aggregate demand curve is a downward sloping function of price. The higher the level of P, the lower the level of aggregate demand. Why is the aggregate supply curve not a function of price? Long proofs that supply curves slope upward are generally a sure-fire cure for insomnia. However, the total a ...
Marco Casiraghi and Giuseppe Ferrero
... between inflation and its target (i.e. the inflation gap) as close as possible to zero (Woodford, 2003). Typically, the target is slightly positive because positive and negative shocks to inflation that are equal in terms of absolute deviation from the target may imply very different welfare costs. ...
... between inflation and its target (i.e. the inflation gap) as close as possible to zero (Woodford, 2003). Typically, the target is slightly positive because positive and negative shocks to inflation that are equal in terms of absolute deviation from the target may imply very different welfare costs. ...
The AD curve shows the relationship between the inflation rate and
... 1. What two variables are related by the aggregate demand (AD) curve? Explain how real balances (i.e., the purchasing power of people’s holdings of money) are related to movements along the curve. List and discuss two other factors that lead the curve to have a negative slope. ...
... 1. What two variables are related by the aggregate demand (AD) curve? Explain how real balances (i.e., the purchasing power of people’s holdings of money) are related to movements along the curve. List and discuss two other factors that lead the curve to have a negative slope. ...
unit 4 review
... Which of the following explains the slope of the aggregate demand curve? I. the wealth effect of a change in the aggregate price level II. the interest rate effect of a change in the aggregate price level III. the product-substitution effect of a change in the aggregate price level a. I only b. II ...
... Which of the following explains the slope of the aggregate demand curve? I. the wealth effect of a change in the aggregate price level II. the interest rate effect of a change in the aggregate price level III. the product-substitution effect of a change in the aggregate price level a. I only b. II ...
Bank of England Inflation Report August 2009
... purchased assets financed by the issuance of central bank reserves reaches £175 billion and remains there throughout the forecast period. The coloured bands have a similar interpretation to those on the fan charts. Like the fan charts, they portray the central 90% of the probability distribution. If ...
... purchased assets financed by the issuance of central bank reserves reaches £175 billion and remains there throughout the forecast period. The coloured bands have a similar interpretation to those on the fan charts. Like the fan charts, they portray the central 90% of the probability distribution. If ...
Document
... between the old one and the new target. The economy must now move to its new steady state by the principle of transition dynamics. The change in the rate of inflation causes the AS curve to shift during the following period. Firms adjust their expectation for inflation to account for the new l ...
... between the old one and the new target. The economy must now move to its new steady state by the principle of transition dynamics. The change in the rate of inflation causes the AS curve to shift during the following period. Firms adjust their expectation for inflation to account for the new l ...
Fan charts - Bank of England
... to lie within each pair of the lighter coloured areas on 10 (narrow bands) and 30 (wide bands) occasions. In any particular quarter of the forecast period, GDP growth, CPI inflation or the unemployment rate are therefore expected to lie somewhere within the fan on 90 out of 100 occasions. And on the ...
... to lie within each pair of the lighter coloured areas on 10 (narrow bands) and 30 (wide bands) occasions. In any particular quarter of the forecast period, GDP growth, CPI inflation or the unemployment rate are therefore expected to lie somewhere within the fan on 90 out of 100 occasions. And on the ...
29 INFLATION, JOBS, AND THE BUSINESS CYCLE**
... initial rise in the price level and the money wage rate response to a one-time rise in the price level. Figure 12.3 shows the effect of a one-time increase in the price level that results from a onetime increase in aggregate demand. The aggregate demand curve shifts rightward from AD0 to AD1 and ini ...
... initial rise in the price level and the money wage rate response to a one-time rise in the price level. Figure 12.3 shows the effect of a one-time increase in the price level that results from a onetime increase in aggregate demand. The aggregate demand curve shifts rightward from AD0 to AD1 and ini ...
Interactive Tool
... with no money, or in a world where money sharply lost its value. 18. A nation's overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the interaction of spending and production decisions made by all households, firms, government agencies, and others in the economy. Students will be able ...
... with no money, or in a world where money sharply lost its value. 18. A nation's overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the interaction of spending and production decisions made by all households, firms, government agencies, and others in the economy. Students will be able ...
Effect of Inflation on the Growth and Development
... Ojo (2000) and Melberg (1992) the term inflation describes a general and persistent increase in the prices of goods and services in an economy. Inflation rate is measured as the percentage change in the price index (consumer price index, wholesale price index, producer price index etc). Essien (2002 ...
... Ojo (2000) and Melberg (1992) the term inflation describes a general and persistent increase in the prices of goods and services in an economy. Inflation rate is measured as the percentage change in the price index (consumer price index, wholesale price index, producer price index etc). Essien (2002 ...
syllabus
... Course description The Introductory Economics (Macroeconomics) is a one and a half semester (threemodule) course for the first-year students. The course gives the introduction to the macroeconomic fundamentals and to the main concepts and principles of macroeconomic theory and policy. The course dea ...
... Course description The Introductory Economics (Macroeconomics) is a one and a half semester (threemodule) course for the first-year students. The course gives the introduction to the macroeconomic fundamentals and to the main concepts and principles of macroeconomic theory and policy. The course dea ...
chapter 4 - MCNEIL ECONOMICS
... to raise the price level. Business cycles are shorter-term events that occur (1) Demand-pull inflation is the result of exaround that long-term upward trend and keep that cess total spending in the economy. trend from being a straight, upward-sloping line. (2) Cost-push inflation is the result of fa ...
... to raise the price level. Business cycles are shorter-term events that occur (1) Demand-pull inflation is the result of exaround that long-term upward trend and keep that cess total spending in the economy. trend from being a straight, upward-sloping line. (2) Cost-push inflation is the result of fa ...
Phillips curve

In economics, the Phillips curve is a historical inverse relationship between rates of unemployment and corresponding rates of inflation that result in an economy. Stated simply, decreased unemployment, (i.e., increased levels of employment) in an economy will correlate with higher rates of inflation.While there is a short run tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, it has not been observed in the long run. In 1968, Milton Friedman asserted that the Phillips Curve was only applicable in the short-run and that in the long-run, inflationary policies will not decrease unemployment. Friedman then correctly predicted that, in the upcoming years after 1968, both inflation and unemployment would increase. The long-run Phillips Curve is now seen as a vertical line at the natural rate of unemployment, where the rate of inflation has no effect on unemployment. Accordingly, the Phillips curve is now seen as too simplistic, with the unemployment rate supplanted by more accurate predictors of inflation based on velocity of money supply measures such as the MZM (""money zero maturity"") velocity, which is affected by unemployment in the short but not the long term.