Learning, Memory, Amnesia, and Brain
... • Research in the role of the hippocampus in episodic memory shows damage impairs abilities on two types of tasks: • Delayed matching-to-sample tasks – a subject sees an object and must later choose the object that matches. • Delayed non-matching-to-sample tasks– subject sees an object and must late ...
... • Research in the role of the hippocampus in episodic memory shows damage impairs abilities on two types of tasks: • Delayed matching-to-sample tasks – a subject sees an object and must later choose the object that matches. • Delayed non-matching-to-sample tasks– subject sees an object and must late ...
3FA3M8-C-B4-Handout
... Result: skill learning changes strength of connections in M1\ Conclusion: Proves that plasticity of cortical connections is associated with learning a new motor skill ...
... Result: skill learning changes strength of connections in M1\ Conclusion: Proves that plasticity of cortical connections is associated with learning a new motor skill ...
Neuroplasticity
... LTP: mechanisms for induction, expression and maintenance • Multiple mechanisms for induction • Increased [Ca2+ ]I • AMPA and NMDA (Hebb) • Cooperativity : strong synaptic input necessary to depolarize membrane, AMPAR) • Associativity/input selectivity: weak input in itself does not relieve Mg2+ ...
... LTP: mechanisms for induction, expression and maintenance • Multiple mechanisms for induction • Increased [Ca2+ ]I • AMPA and NMDA (Hebb) • Cooperativity : strong synaptic input necessary to depolarize membrane, AMPAR) • Associativity/input selectivity: weak input in itself does not relieve Mg2+ ...
associative memory ENG - Weizmann Institute of Science
... • If the external inputs are constant the network may reach a stable state, but this is not guaranteed (the attractors may be limit cycles and the network may even be chaotic). • When the recurrent connections are symmetric and there is no self coupling we can write an energy function, such that at ...
... • If the external inputs are constant the network may reach a stable state, but this is not guaranteed (the attractors may be limit cycles and the network may even be chaotic). • When the recurrent connections are symmetric and there is no self coupling we can write an energy function, such that at ...
What is working memory? Definitions
... suppressing interference from irrelevant information and distractors. ...
... suppressing interference from irrelevant information and distractors. ...
What changes in the brain when we learn?
... The problem of the biological basis of memory in the brain has many facets, and only a few were summarized above. One intriguing question is the neural basis for emotional learning and memory. A specific brain region called the amygdala is known to be involved in emotional responses and, in particul ...
... The problem of the biological basis of memory in the brain has many facets, and only a few were summarized above. One intriguing question is the neural basis for emotional learning and memory. A specific brain region called the amygdala is known to be involved in emotional responses and, in particul ...
Ingestive Behavior - Shoreline Community College
... Spatial-Memory Task (parietal lobe more active) ...
... Spatial-Memory Task (parietal lobe more active) ...
The ventral striatum in goal-directed behavior and - UvA-DARE
... will be spared. The ‘multiple trace’ theory posits that episodic memories exhibit a life-long dependency on the hippocampus (Nadel and Moscovitch, 1997). This theory states that the memory gains strength each time an episodic memory is retrieved and re-encoded, leading to the formation of multiple t ...
... will be spared. The ‘multiple trace’ theory posits that episodic memories exhibit a life-long dependency on the hippocampus (Nadel and Moscovitch, 1997). This theory states that the memory gains strength each time an episodic memory is retrieved and re-encoded, leading to the formation of multiple t ...
synaptic transmission worksheet
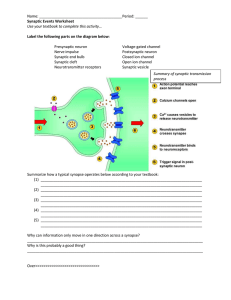
... Name: ________________________________________ Period: ______ Synaptic Events Worksheet Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
... Name: ________________________________________ Period: ______ Synaptic Events Worksheet Use your textbook to complete this activity… Label the following parts on the diagram below: Presynaptic neuron Nerve impulse Synaptic end bulb Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter receptors ...
Neural Basis of Emotion
... cortex in temporal lobe of monkeys and found that they could no longer perform in recognition memory tests • Later showed that perirhinal cortex is most important for new memory; temporary storage? Memory consolidation? ...
... cortex in temporal lobe of monkeys and found that they could no longer perform in recognition memory tests • Later showed that perirhinal cortex is most important for new memory; temporary storage? Memory consolidation? ...
Lecture Presentation for Chapter 17
... characterized as reliving and being preoccupied by traumatic events), memories produce stress hormones that further reinforce the memory. GABA, ACh, and opioid transmission can also enhance memory formation in animal models. Treatments that can block chemicals acting on the basolateral amygdala may ...
... characterized as reliving and being preoccupied by traumatic events), memories produce stress hormones that further reinforce the memory. GABA, ACh, and opioid transmission can also enhance memory formation in animal models. Treatments that can block chemicals acting on the basolateral amygdala may ...
Lecture 12
... However, this unstable state can also have negative consequences. In Figure 12.14, a brief rehearsal of sequence 1(B) makes it unstable and now a practice of sequence 2 (C) disrupts one's skill in sequence 1 (D). The observation that practice makes old memories unstable again, applies not only to pr ...
... However, this unstable state can also have negative consequences. In Figure 12.14, a brief rehearsal of sequence 1(B) makes it unstable and now a practice of sequence 2 (C) disrupts one's skill in sequence 1 (D). The observation that practice makes old memories unstable again, applies not only to pr ...
Cortex and Mind Chapter 5
... von Helmholtz found proof for his theory in patients with paralysis of the eye muscles. (This can also be tested experimentally by injecting curare into the eye muscles). These patients perceived that whenever they tried to move their eyes, the world would seem to jump in the same direction as the ...
... von Helmholtz found proof for his theory in patients with paralysis of the eye muscles. (This can also be tested experimentally by injecting curare into the eye muscles). These patients perceived that whenever they tried to move their eyes, the world would seem to jump in the same direction as the ...
Bauer 2006 - Ericastiftelsen
... the major ‘route in’ to the hippocampus. Less effective and efficient communication between cortical structures and the hippocampus would present challenges to consolidation, and therefore storage, of new information [34]. As these structures and connections between them develop we should see age-re ...
... the major ‘route in’ to the hippocampus. Less effective and efficient communication between cortical structures and the hippocampus would present challenges to consolidation, and therefore storage, of new information [34]. As these structures and connections between them develop we should see age-re ...
Part 2 - Kirkwood Community College
... – Entails learning explicit information – Is related to our conscious thoughts and our language ability – Is stored with the context in which it was learned • Circumstances of recall match the circumstances of learning. ...
... – Entails learning explicit information – Is related to our conscious thoughts and our language ability – Is stored with the context in which it was learned • Circumstances of recall match the circumstances of learning. ...
THE HUMAN MEMORY The human brain, one of the most complex
... well as the physical components of the computer in which such information is stored. Although there are indeed some parallels between the memory of a computer and the memory of a human being, there are also some fundamental and crucial differences, principally that the human brain is organized as a ...
... well as the physical components of the computer in which such information is stored. Although there are indeed some parallels between the memory of a computer and the memory of a human being, there are also some fundamental and crucial differences, principally that the human brain is organized as a ...
Schizophrenia is a multi-faceted disorder with highly complex p
... translate them into informing clinical and pharmacologic practice . Figure 1 provides a schematic overview of this collaborative proposal emphasizing the central role of computational models in integrating the results of animal and human studies and synthesizing the relevance of this work for schizo ...
... translate them into informing clinical and pharmacologic practice . Figure 1 provides a schematic overview of this collaborative proposal emphasizing the central role of computational models in integrating the results of animal and human studies and synthesizing the relevance of this work for schizo ...
Memory - Sinauer Associates
... PET scans made during eye-blink tests show increased activity in several brain regions, but not all may be essential. Patients with unilateral cerebellar damage can acquire the conditioned eye-blink response only on the intact side. ...
... PET scans made during eye-blink tests show increased activity in several brain regions, but not all may be essential. Patients with unilateral cerebellar damage can acquire the conditioned eye-blink response only on the intact side. ...
Integrating Mental Processes: Thinking and Problem Solving
... A fundamental question about memory and cognition concerns how information is acquired about categories and concepts as the result of encounters with specifi c instances. We describe a profoundly amnesic patient (E.P.) who cannot learn and remember specifi c instances-i.e., he has no detectable decl ...
... A fundamental question about memory and cognition concerns how information is acquired about categories and concepts as the result of encounters with specifi c instances. We describe a profoundly amnesic patient (E.P.) who cannot learn and remember specifi c instances-i.e., he has no detectable decl ...
Biopsychology of Memory
... Why does limited damage to the hippocampal subfields produce significant memory deficits whereas only minimal or no deficits occur with total removal of the hippocampus??? ...
... Why does limited damage to the hippocampal subfields produce significant memory deficits whereas only minimal or no deficits occur with total removal of the hippocampus??? ...
His conclusion: equipotentiality
... "trace") tends to induce lasting cellular changes that add to its stability.... When an axon of cell A is near enough to excite a cell B and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that A's efficiency, as one o ...
... "trace") tends to induce lasting cellular changes that add to its stability.... When an axon of cell A is near enough to excite a cell B and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that A's efficiency, as one o ...
PSYC550 Emotions and Memory
... makes the behavior become more frequent. • punishing stimulus – An aversive stimulus that follows a particular behavior and thus makes the behavior become less frequent. • motor learning – Learning to make a new response. ...
... makes the behavior become more frequent. • punishing stimulus – An aversive stimulus that follows a particular behavior and thus makes the behavior become less frequent. • motor learning – Learning to make a new response. ...
Memory Capacity of a Hebbian Learning Model with Inhibition
... model to learn a stream of uncorrelated stimuli is as low as O(log N), where N is the number of neurons in the network. If the coding level (proportion of active neurons) of the stimuli can vary with N as f ∼ log N/N, then the capacity can be raised to O(1/f ) = O(N/ log N). If transition robability ...
... model to learn a stream of uncorrelated stimuli is as low as O(log N), where N is the number of neurons in the network. If the coding level (proportion of active neurons) of the stimuli can vary with N as f ∼ log N/N, then the capacity can be raised to O(1/f ) = O(N/ log N). If transition robability ...
Exercise Enhances Brain Health
... CA1 neurons of the hippocampus while stimulation is applied to the Schaffer collaterals of CA3 neurons. The amplitudes of the EPSPs in the CA1 neurons are shown in B. For a single stimulus, the amplitude of the EPSPs is plotted at 100%. When a train of stimuli is applied instead, the amplitude of th ...
... CA1 neurons of the hippocampus while stimulation is applied to the Schaffer collaterals of CA3 neurons. The amplitudes of the EPSPs in the CA1 neurons are shown in B. For a single stimulus, the amplitude of the EPSPs is plotted at 100%. When a train of stimuli is applied instead, the amplitude of th ...
Slides - Computation and Cognition Lab
... arithmetic being particularly striking. An extensive battery failed to find any deficits in perception, abstract thinking, or reasoning ability, and his motivation remained excellent throughout.” ...
... arithmetic being particularly striking. An extensive battery failed to find any deficits in perception, abstract thinking, or reasoning ability, and his motivation remained excellent throughout.” ...
Memory consolidation

Memory consolidation is a category of processes that stabilize a memory trace after its initial acquisition. Consolidation is distinguished into two specific processes, synaptic consolidation, which is synonymous with late-phase LTP and occurs within the first few hours after learning, and systems consolidation, where hippocampus-dependent memories become independent of the hippocampus over a period of weeks to years. Recently, a third process has become the focus of research, reconsolidation, in which previously-consolidated memories can be made labile again through reactivation of the memory trace.