AS Macro: Assess the extent to which a rise in imports may
... 4. Imports of cheaper products can help to keep inflation under control 5. Rising demand for imports provide a short term boost to consumers’ standard of living 6. Providing that the economy can achieve a higher value of exports, the rising demand for imports need not necessarily cause a much bigger ...
... 4. Imports of cheaper products can help to keep inflation under control 5. Rising demand for imports provide a short term boost to consumers’ standard of living 6. Providing that the economy can achieve a higher value of exports, the rising demand for imports need not necessarily cause a much bigger ...
December 17, 2012
... of medical costs rising faster than the growth rate of GDP, some do make a sizable dent in the deficit. For example, the Bowles-Simpson budget commission noted that by combining several of the changes noted above, Medicare spending could be reduced by $110 billion over the next 10 years. But this po ...
... of medical costs rising faster than the growth rate of GDP, some do make a sizable dent in the deficit. For example, the Bowles-Simpson budget commission noted that by combining several of the changes noted above, Medicare spending could be reduced by $110 billion over the next 10 years. But this po ...
Year-End Talking Points - Front Barnett Associates LLC
... Investors’ new-found attraction to equities is based upon the view the new administration’s fiscal policies, combined with regulation reduction, will lead to a more robust economy. Expect: ...
... Investors’ new-found attraction to equities is based upon the view the new administration’s fiscal policies, combined with regulation reduction, will lead to a more robust economy. Expect: ...
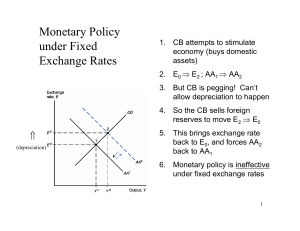
Fixed Exchange Rates and Macroeconomic Policy
... use monetary policy to target domestic inflation or to try to smooth out the domestic business cycle • The only hope for independent monetary policy is capital controls to prevent traders buying or selling domestic currency • But capital controls reduce trade and foreign direct investment, and prese ...
... use monetary policy to target domestic inflation or to try to smooth out the domestic business cycle • The only hope for independent monetary policy is capital controls to prevent traders buying or selling domestic currency • But capital controls reduce trade and foreign direct investment, and prese ...
The government`s fiscal rules - Institute for Fiscal Studies
... will already be reflected in public sector net debt as a result of the contracted payments from the public sector to the private sector. In addition recent changes to the measurement of public sector net debt made by the by the Office for National Statistics in respect of the finance lease component ...
... will already be reflected in public sector net debt as a result of the contracted payments from the public sector to the private sector. In addition recent changes to the measurement of public sector net debt made by the by the Office for National Statistics in respect of the finance lease component ...
The Use of Fiscal Policy at the National Level Miron DUMITRESCU
... fixed exchange rate regime, because the Central Bank intervention counteracts the crowding out of net exports. There is also the possibility that fiscal policy does not lead to higher prices for exports because appreciation may reduce inflation. So, expansionary fiscal policy can also be effective f ...
... fixed exchange rate regime, because the Central Bank intervention counteracts the crowding out of net exports. There is also the possibility that fiscal policy does not lead to higher prices for exports because appreciation may reduce inflation. So, expansionary fiscal policy can also be effective f ...
response lag
... If a government is trying to stimulate the economy through tax cuts or spending increases, this, other things being equal, will increase the government deficit. One thus expects deficits in recessions—cyclical deficits, which are temporary and do not impose any long-run problems, especially if modes ...
... If a government is trying to stimulate the economy through tax cuts or spending increases, this, other things being equal, will increase the government deficit. One thus expects deficits in recessions—cyclical deficits, which are temporary and do not impose any long-run problems, especially if modes ...
Lecture 6 and 7:
... which presents historical evidence). a. What is not spent is called saving. b.Therefore, DI – C = S or C + I = DI ...
... which presents historical evidence). a. What is not spent is called saving. b.Therefore, DI – C = S or C + I = DI ...
Public goods
... wages in the long run will tend to the minimum value needed to keep workers alive. The justification for the theory is that when wages are higher, more workers will be produced, and when wages are lower, some workers will die, in each case bringing supply back to a subsistence-level equilibrium. • T ...
... wages in the long run will tend to the minimum value needed to keep workers alive. The justification for the theory is that when wages are higher, more workers will be produced, and when wages are lower, some workers will die, in each case bringing supply back to a subsistence-level equilibrium. • T ...
Macroeconomics Final Exam Study Guide – Fall 2007
... c. Explain the appropriate fiscal policy responses according to the Keynesians. d. Name and define the three tools of the Fed and explain how each will be used in response to output being below the potential level. e. Explain the impact of the monetary policy that you just recommended. 5. Repeat the ...
... c. Explain the appropriate fiscal policy responses according to the Keynesians. d. Name and define the three tools of the Fed and explain how each will be used in response to output being below the potential level. e. Explain the impact of the monetary policy that you just recommended. 5. Repeat the ...
AP Macroeconomics - Valley View High School
... to GDP, income approach to GDP, nominal versus real GDP, phases of the business cycle, types of unemployment, full employment, measurements of inflation, types of inflation, effects of inflation ...
... to GDP, income approach to GDP, nominal versus real GDP, phases of the business cycle, types of unemployment, full employment, measurements of inflation, types of inflation, effects of inflation ...
Is Fiscal Austerity Good for the Economy?
... the crucial long-run benefits of austerity through maintaining intertemporal budget balance, which could outweigh the short-run costs. Few studies on the effects of fiscal policy consider the short-run effects and the long-run effects together. One exception is recent work by Harald Uhlig.11 He find ...
... the crucial long-run benefits of austerity through maintaining intertemporal budget balance, which could outweigh the short-run costs. Few studies on the effects of fiscal policy consider the short-run effects and the long-run effects together. One exception is recent work by Harald Uhlig.11 He find ...
Chapter 2
... • 4. Consumption: spending by domestic households on final goods and services (including those produced abroad) • 5. Investment: spending for new capital goods (fixed investment) plus inventory investment • 6. Government purchases of goods and services: • 7. Net exports: exports minus imports • pur ...
... • 4. Consumption: spending by domestic households on final goods and services (including those produced abroad) • 5. Investment: spending for new capital goods (fixed investment) plus inventory investment • 6. Government purchases of goods and services: • 7. Net exports: exports minus imports • pur ...
The Global Economic and Financial Crisis
... Even the principle that spending provides more stimulus than tax cuts has returned; not just from Larry Summers, e.g., but also from Martin Feldstein. ...
... Even the principle that spending provides more stimulus than tax cuts has returned; not just from Larry Summers, e.g., but also from Martin Feldstein. ...
Aggregate Supply and Unemployment
... Aggregate supply (AS) measures the output of goods and services than an economy can supply at a given price level in a given time period. The output potential of the economy depends on (a) the stock of factor inputs available (b) the productivity of factor inputs (c) the pace of technological progre ...
... Aggregate supply (AS) measures the output of goods and services than an economy can supply at a given price level in a given time period. The output potential of the economy depends on (a) the stock of factor inputs available (b) the productivity of factor inputs (c) the pace of technological progre ...
America`s Innovation and Jobs
... • The government is not effective in creating jobs • Additional public sector jobs cost more money to taxpayers and are rarely effective • Additional private sector jobs can only be created by private sector, but government can play a useful role in facilitating that by improving business environmen ...
... • The government is not effective in creating jobs • Additional public sector jobs cost more money to taxpayers and are rarely effective • Additional private sector jobs can only be created by private sector, but government can play a useful role in facilitating that by improving business environmen ...
The Underfunded Pentagon 2 m a r c h
... that point, these three programs plus the interest on the national debt would use up almost all federal tax revenues (if tax rates remained where they are now). Of course, this will not be allowed to happen. A political solution will be found to the problem of funding these important programs throug ...
... that point, these three programs plus the interest on the national debt would use up almost all federal tax revenues (if tax rates remained where they are now). Of course, this will not be allowed to happen. A political solution will be found to the problem of funding these important programs throug ...
Darwin, The Market Whiz
... would save more and spend less on luxury goods, leading to greater investment and economic growth, without any need for government to micromanage anyone’s behavior. Consumers in the tier just below, influenced by those at the top, would also spend less, and so on, all the way down the income ladder. ...
... would save more and spend less on luxury goods, leading to greater investment and economic growth, without any need for government to micromanage anyone’s behavior. Consumers in the tier just below, influenced by those at the top, would also spend less, and so on, all the way down the income ladder. ...
aggregate supply curve
... The relationship between the level of income and consumption spending is called the consumption function: C = Ca + by Ca = autonomous consumption, or the amount of consumption spending that does not depend on the level of income. by = the part of consumption that is dependent on income, where: b = m ...
... The relationship between the level of income and consumption spending is called the consumption function: C = Ca + by Ca = autonomous consumption, or the amount of consumption spending that does not depend on the level of income. by = the part of consumption that is dependent on income, where: b = m ...
S = 1
... Supplier deliveries/Vendor performance (15%) – speed of supplier delivery Inventories (10%) – the rate of liquidating manufacturers’ inventories ...
... Supplier deliveries/Vendor performance (15%) – speed of supplier delivery Inventories (10%) – the rate of liquidating manufacturers’ inventories ...
Chapter 15 A Critical Assessment of the ... Budget Jonathan Wright (Adapted from a paper given by the
... disincentive effects to work effort are likely. at a theoretical level to be strongest in the poverty trap. most obviously. because it is here that the highest marginal rates occur; but also. and perhaps more Significantly. because providing benefits and then withdrawing them has an unambiguous net ...
... disincentive effects to work effort are likely. at a theoretical level to be strongest in the poverty trap. most obviously. because it is here that the highest marginal rates occur; but also. and perhaps more Significantly. because providing benefits and then withdrawing them has an unambiguous net ...
Gross Domestic Product
... of resident producer units for the reporting period. Methods: In Georgia GDP is calculated by following methods: The production approach is a concept of value added. As an aggregate measure of production, the GDP of a country is equal to the sum of the gross value added of all resident institutional ...
... of resident producer units for the reporting period. Methods: In Georgia GDP is calculated by following methods: The production approach is a concept of value added. As an aggregate measure of production, the GDP of a country is equal to the sum of the gross value added of all resident institutional ...
Government Spending & Fiscal Policy
... happened because the government was obliged to reduce its spending. Government spending changes not only as a response to changes in economic policy, but also as a response to structural changes in the economy. ...
... happened because the government was obliged to reduce its spending. Government spending changes not only as a response to changes in economic policy, but also as a response to structural changes in the economy. ...
US Election one week on: will President Trump`s administration be
... social issues, the largest threat to economic growth could well be his promise to “put America first” through controlling imports. Historically, such policies have not been successful and a similar policy led to a deepening of the 1930 US depression. Herbert Hoover, the 31st President of the US, had ...
... social issues, the largest threat to economic growth could well be his promise to “put America first” through controlling imports. Historically, such policies have not been successful and a similar policy led to a deepening of the 1930 US depression. Herbert Hoover, the 31st President of the US, had ...