Chapter 4 A Review of .M. Keynes SECTION 2 MONETARY
... frequency theory, developed an ingenious theory of decision-making under uncertainty. Each managerial decision is a unique event, he pOSited, and this calls the choice-theoretic basis of reductionism into question. Without a stable basiS in choice logic the concept of market eqUilibrium collapses. B ...
... frequency theory, developed an ingenious theory of decision-making under uncertainty. Each managerial decision is a unique event, he pOSited, and this calls the choice-theoretic basis of reductionism into question. Without a stable basiS in choice logic the concept of market eqUilibrium collapses. B ...
Gauging the Impact of the Fed on Inequality During the Great
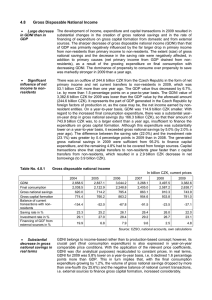
... the fact that in May President George W. Bush signed into law the Economic Stimulus Act of 2008 (which Congress had already passed) to provide $160 billion in fiscal stimulus. The second round of LSAPs (QE2) began in November 2010 with an announcement that the Fed would purchase an additional $600 b ...
... the fact that in May President George W. Bush signed into law the Economic Stimulus Act of 2008 (which Congress had already passed) to provide $160 billion in fiscal stimulus. The second round of LSAPs (QE2) began in November 2010 with an announcement that the Fed would purchase an additional $600 b ...
Monetary Policy 1: Transmission Mechanism
... monetary policy cannot be pegged to lower the interest rate or the unemployment. Is so it only raises inflationary expectation and increase in price level. There will be no impact on real magnitudes. Monetary authority can control nominal quantities such as it liabilities, M0, M3 or M4. By controlli ...
... monetary policy cannot be pegged to lower the interest rate or the unemployment. Is so it only raises inflationary expectation and increase in price level. There will be no impact on real magnitudes. Monetary authority can control nominal quantities such as it liabilities, M0, M3 or M4. By controlli ...
Consumers Into Customers
... Consumer USA 2000. (Euromonitor International). Annual. This reference book provides data on over 300 consumer product sectors (food and drink, household cleaners, leisure, cosmetics, appliances, etc.) Data elements include market volume, market value, per capita volume and per capita value and also ...
... Consumer USA 2000. (Euromonitor International). Annual. This reference book provides data on over 300 consumer product sectors (food and drink, household cleaners, leisure, cosmetics, appliances, etc.) Data elements include market volume, market value, per capita volume and per capita value and also ...
Transport Infrastructure Investments as Means to
... countries due to investment in infrastructure increased on average by 1.6% between 1991-95 and 2001-05. • Particularly large impact in South Asia where it reached to 2.5% • If each Latin American country could match the average level of infrastructure among nonLatin American middle income country, g ...
... countries due to investment in infrastructure increased on average by 1.6% between 1991-95 and 2001-05. • Particularly large impact in South Asia where it reached to 2.5% • If each Latin American country could match the average level of infrastructure among nonLatin American middle income country, g ...
Phillips Curve FRQs answers
... (i) The short-run Phillips curve. Explain. 1) SRPC shifts left because inflation expectations decrease…remember that the AD shift left will be followed by an SRAS curve shift right when wages fall (ii) The natural rate of unemployment unchanged 3. The unemployment rate is an important indicator of t ...
... (i) The short-run Phillips curve. Explain. 1) SRPC shifts left because inflation expectations decrease…remember that the AD shift left will be followed by an SRAS curve shift right when wages fall (ii) The natural rate of unemployment unchanged 3. The unemployment rate is an important indicator of t ...
Chapter 6Understanding business cycles
... - The purchasing power of money decreases. - The liability of the borrower decreases if the loan has fixed monetary terms. • Deflation is a sustained decrease in the aggregate price level (negative inflation rate). - The purchasing power of money increases. - The liability of the borrower increases ...
... - The purchasing power of money decreases. - The liability of the borrower decreases if the loan has fixed monetary terms. • Deflation is a sustained decrease in the aggregate price level (negative inflation rate). - The purchasing power of money increases. - The liability of the borrower increases ...
“
... Given the difficulty of amending the Constitution, statutory changes to budget rules can provide a way forward to control spending. In particular, a cap should be placed on the overall annual growth in federal outlays. While the Budget Enforcement Act imposed multiyear caps on discretionary spending ...
... Given the difficulty of amending the Constitution, statutory changes to budget rules can provide a way forward to control spending. In particular, a cap should be placed on the overall annual growth in federal outlays. While the Budget Enforcement Act imposed multiyear caps on discretionary spending ...
Global economic conditions survey report: Q2, 2011 AccountAnts for business
... 4. Respondents to the survey are not asked directly whether they think governments will get spending wrong. Instead they are asked how they expect the level of public spending to change over the next five years and how they would like for it to change. Both questions are coded as fivepoint scales (f ...
... 4. Respondents to the survey are not asked directly whether they think governments will get spending wrong. Instead they are asked how they expect the level of public spending to change over the next five years and how they would like for it to change. Both questions are coded as fivepoint scales (f ...
Homework 2 Answer Key
... the household with an after-tax income stream equal to Y0 =50 and Y1 = 143. Calculate the present value and annuity value of this after tax income stream. If the household consumes the annuity value, what is consumption and saving? ii. In the second tax plan, the government will collect a tax of 22 ...
... the household with an after-tax income stream equal to Y0 =50 and Y1 = 143. Calculate the present value and annuity value of this after tax income stream. If the household consumes the annuity value, what is consumption and saving? ii. In the second tax plan, the government will collect a tax of 22 ...
G - University of Southampton
... 10) Here is what we know about a household: wages $25,000, unemployment insurance benefits $3,000, dividend income $4,000, income tax $5,000. What is the contribution to GDP of this household following the expenditure approach? A) $24,000 B) $29,000 C) $25,000 D) $28,000 ...
... 10) Here is what we know about a household: wages $25,000, unemployment insurance benefits $3,000, dividend income $4,000, income tax $5,000. What is the contribution to GDP of this household following the expenditure approach? A) $24,000 B) $29,000 C) $25,000 D) $28,000 ...
policy designed to change the money supply, credit availability, and
... economy is decreased and credit becomes harder to obtain and more expensive © 2012 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited ...
... economy is decreased and credit becomes harder to obtain and more expensive © 2012 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited ...
LAPORDE 2014
... Growth and Distribution • Growth and distribution were two key topics in classical political economy (capital accumulation and the rate of profit) • But in neoclassical theory income distribution became a nonissue on the assumption that factor prices equal their marginal productivities • The classi ...
... Growth and Distribution • Growth and distribution were two key topics in classical political economy (capital accumulation and the rate of profit) • But in neoclassical theory income distribution became a nonissue on the assumption that factor prices equal their marginal productivities • The classi ...
Interdependence, Exchange Rate Flexibility, And National Economies
... account deficit. That is because, if imports are a reasonably stable proportion of income, the trade deficit would be limited by the size of the rise in income. On the other hand, when capital markets are fully integrated, the tendency toward higher interest rates will call forth a flood of incoming ...
... account deficit. That is because, if imports are a reasonably stable proportion of income, the trade deficit would be limited by the size of the rise in income. On the other hand, when capital markets are fully integrated, the tendency toward higher interest rates will call forth a flood of incoming ...
V hospodářském cyklu USA a EU se prosazují odlišnosti
... foreign factors of production or, as the case may be, the net income earned by nonresident entities. On a year-to-year basis, GDNI was 114.9 billion CZK smaller. With regard to the increased final consumption expenditure, there was a substantial yearon-year drop in gross national savings (by 166.3 b ...
... foreign factors of production or, as the case may be, the net income earned by nonresident entities. On a year-to-year basis, GDNI was 114.9 billion CZK smaller. With regard to the increased final consumption expenditure, there was a substantial yearon-year drop in gross national savings (by 166.3 b ...
ROMANIA – EUROPEAN UNION’S MEMBER MACROECONOMIC TENDENCIES AND PROGNOSIS
... the theory of GDP increasing of 6% for the year 2007. Tendencies of relaxing the monetary policy Disinflation process continued successfully in the first three months of the year 2007. Inflation rate recorded the level 3.66% in March, the disinflation tendency for the last months remaining so unmodi ...
... the theory of GDP increasing of 6% for the year 2007. Tendencies of relaxing the monetary policy Disinflation process continued successfully in the first three months of the year 2007. Inflation rate recorded the level 3.66% in March, the disinflation tendency for the last months remaining so unmodi ...
Bank of England - Speech by Mark Carney at the Roscoe Lecture
... investments in equities and real estate are low relative to the level of interest rates because investors are valuing safety much more than they are expecting faster growth. Said differently, since pensions are future claims on the economy, there isn’t a parallel universe of higher interest rates, h ...
... investments in equities and real estate are low relative to the level of interest rates because investors are valuing safety much more than they are expecting faster growth. Said differently, since pensions are future claims on the economy, there isn’t a parallel universe of higher interest rates, h ...
Chapter 7
... Measures average price level of consumers goods actually bought EXAMPLE using “Market basket of goods” ...
... Measures average price level of consumers goods actually bought EXAMPLE using “Market basket of goods” ...
Microeconomics In Pictures
... Capital inflows help finance domestic investment and the government’s deficit ...
... Capital inflows help finance domestic investment and the government’s deficit ...
Module History and Alternative Views of
... Important difference: SRAS is vertical (CT) so a shift in AD changes PL but not output. In Keynesian view, a shift affects both PL and output. ...
... Important difference: SRAS is vertical (CT) so a shift in AD changes PL but not output. In Keynesian view, a shift affects both PL and output. ...
BLOOD, SWEAT AND TEARS: BRITISH MOBILISATION FOR
... wartime taxes could be treated as forced savings or deferred pay to be repaid after the war. This had the additional advantage of building up potential purchasing power that could be released in the event of a postwar slump, as well as financing the war effort. To the extent that the government fail ...
... wartime taxes could be treated as forced savings or deferred pay to be repaid after the war. This had the additional advantage of building up potential purchasing power that could be released in the event of a postwar slump, as well as financing the war effort. To the extent that the government fail ...
Projections of Domestic Resources
... Health spending on average has tended to increase with economic ...
... Health spending on average has tended to increase with economic ...
Presentation to the University of California at Berkeley Boalt School... San Francisco, California
... actions. Before that, Fed watchers had to infer policy changes from the Fed’s behavior in the open market. Over time, the amount of information in that statement has also gradually increased. For example, the Committee introduced language in 2000 describing its assessment of the balance of risks wi ...
... actions. Before that, Fed watchers had to infer policy changes from the Fed’s behavior in the open market. Over time, the amount of information in that statement has also gradually increased. For example, the Committee introduced language in 2000 describing its assessment of the balance of risks wi ...
Impact of Arms Production on Income Distribution Looney, R.E.
... The negative impact of the military burden in the producing countries clearly invalidates the forced savings explanation offalling private consumption and increa~~d investment found with increased military burdens. The income distributional demand profile alternation and resource shift mechanism out ...
... The negative impact of the military burden in the producing countries clearly invalidates the forced savings explanation offalling private consumption and increa~~d investment found with increased military burdens. The income distributional demand profile alternation and resource shift mechanism out ...