Principles of Macroeconomics
... largest increase in aggregate demand? (A)A $30 billion increase in military expenditure and a $30 billion open market purchase of government securities (B)A $30 billion increase in military expenditure and a $30 billion open market sale of government securities (C)A $30 billion tax decrease and a $3 ...
... largest increase in aggregate demand? (A)A $30 billion increase in military expenditure and a $30 billion open market purchase of government securities (B)A $30 billion increase in military expenditure and a $30 billion open market sale of government securities (C)A $30 billion tax decrease and a $3 ...
Output and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run
... Assume a 75% depreciation of a country’s currency in one week Demand for foreign exchange has increased and supply has decreased Exchange rate goes from XRe to XR’’ Could have been capital flight out of country due to domestic crisis or due to exchange rate being fixed at inappropriate level for lon ...
... Assume a 75% depreciation of a country’s currency in one week Demand for foreign exchange has increased and supply has decreased Exchange rate goes from XRe to XR’’ Could have been capital flight out of country due to domestic crisis or due to exchange rate being fixed at inappropriate level for lon ...
Topic 3: Fiscal Policy
... Interest Rates Suppose interest rate i = 5%. Buy a 1-year $1000 bond. At the end of the year, the bond pays out $1000 x 1.05 = $1050 ...
... Interest Rates Suppose interest rate i = 5%. Buy a 1-year $1000 bond. At the end of the year, the bond pays out $1000 x 1.05 = $1050 ...
The dual nature of public goods and congestion: the role of fiscal
... utility benefits to users. This argument holds for traditionally defined public consumption goods as well, such as law and order, national parks, defence. While these goods might directly affect the utility consumers derive from them, they can also have significant productivity benefits (by providin ...
... utility benefits to users. This argument holds for traditionally defined public consumption goods as well, such as law and order, national parks, defence. While these goods might directly affect the utility consumers derive from them, they can also have significant productivity benefits (by providin ...
Do Deficits Matter? And, If So, How?
... 1 percent increase in the projected budget deficit raises longterm interest rates by 25 to 35 basis points. Another element that bears on whether deficits affect the conversion of available savings into investment capital also happens to be one of the most controversial. It comes from the assumption ...
... 1 percent increase in the projected budget deficit raises longterm interest rates by 25 to 35 basis points. Another element that bears on whether deficits affect the conversion of available savings into investment capital also happens to be one of the most controversial. It comes from the assumption ...
Energy Economics – II Jeffrey Frankel Harpel
... (10) Chile’s official forecasts are not overly optimistic. It has apparently avoided the problem of forecasts that unrealistically extrapolate in boom times. ...
... (10) Chile’s official forecasts are not overly optimistic. It has apparently avoided the problem of forecasts that unrealistically extrapolate in boom times. ...
"Laying the Foundation for Inclusive Prosperity"
... reach for many working families, which ultimately impacts the economy. We believe the most efficient and fair way to deliver high-quality child care to young children is through a tax benefit delivered directly from the government to certified high-quality child care providers. This would be availab ...
... reach for many working families, which ultimately impacts the economy. We believe the most efficient and fair way to deliver high-quality child care to young children is through a tax benefit delivered directly from the government to certified high-quality child care providers. This would be availab ...
Japan`s Fiscal Policy and Fiscal Reconstruction October 22, 2004 by
... whether it is appropriate to lump together government- and private-sector balance. The integrated approach may be useful in determining the limits of the government ability to pay debt, because the government – which has the right to taxation – can tap private resources through higher taxes. ...
... whether it is appropriate to lump together government- and private-sector balance. The integrated approach may be useful in determining the limits of the government ability to pay debt, because the government – which has the right to taxation – can tap private resources through higher taxes. ...
Nominal GDP
... • Nominal GDP increases because production increases and because prices increase (Inflation). • Use the GDP deflator to take out the effect of inflation and reveal real GDP. • The Base year for current SNA is 2000. • Inflation rate = rate of change of price level, 130% = (230-100)/100*100 ...
... • Nominal GDP increases because production increases and because prices increase (Inflation). • Use the GDP deflator to take out the effect of inflation and reveal real GDP. • The Base year for current SNA is 2000. • Inflation rate = rate of change of price level, 130% = (230-100)/100*100 ...
Unit 6 The Phillips Curve
... ● The unemployment rate tends to shift towards its normal rate ○ Natural Rate of Unemployment- 5% ○ The natural unemployment rate is where the economy tends to gravitate towards in the long run. However, the natural rate may not be socially ...
... ● The unemployment rate tends to shift towards its normal rate ○ Natural Rate of Unemployment- 5% ○ The natural unemployment rate is where the economy tends to gravitate towards in the long run. However, the natural rate may not be socially ...
Chapter 10 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... 1. In the long run the aggregate supply curve is vertical at the economy’s full-employment output. 2. The curve is vertical because in the long run resources prices adjust to changes in the price level, leaving no incentive for firms to change their output. B. Aggregate supply in the short run (Figu ...
... 1. In the long run the aggregate supply curve is vertical at the economy’s full-employment output. 2. The curve is vertical because in the long run resources prices adjust to changes in the price level, leaving no incentive for firms to change their output. B. Aggregate supply in the short run (Figu ...
6. Rolling the hoop .Banks will take a long time to recover. So will
... unexploited innovations. But when the recovery arrives, Friedman suggested, it is all the more forceful because these resources have been lying idle, waiting to be brought back into production. The economy can grow faster than normal for a period until it reaches the point where it would have been w ...
... unexploited innovations. But when the recovery arrives, Friedman suggested, it is all the more forceful because these resources have been lying idle, waiting to be brought back into production. The economy can grow faster than normal for a period until it reaches the point where it would have been w ...
Download pdf | 88 KB |
... range of obstacles that can delay new infrastructure. Planning is most often cited. That’s going to change. Under our plans, if a development is sustainable, the starting point is: it will go through. Socially sustainable, economically sustainable, and environmentally sustainable. Those reforms are ...
... range of obstacles that can delay new infrastructure. Planning is most often cited. That’s going to change. Under our plans, if a development is sustainable, the starting point is: it will go through. Socially sustainable, economically sustainable, and environmentally sustainable. Those reforms are ...
Practice Final Exam Economics 503 Fundamentals of Economic
... Inflation rate is 3.5% and nominal interest rate is 6%. ...
... Inflation rate is 3.5% and nominal interest rate is 6%. ...
OSP9: Fiscal policy 1971-1979
... Operational Selection Policies are intended to be working tools for those involved in the selection of public records. This policy may therefore be reviewed and revised in the light of comments from users of the records or from archive professionals, HM Treasury’s experience of using the policy, or ...
... Operational Selection Policies are intended to be working tools for those involved in the selection of public records. This policy may therefore be reviewed and revised in the light of comments from users of the records or from archive professionals, HM Treasury’s experience of using the policy, or ...
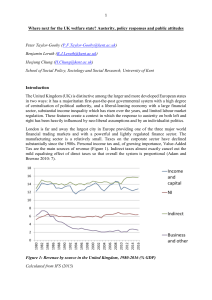
United Kingdom - Kent Blogs
... economy improved. The introduction of the national minimum wage and of Tax Credits in 1999 reduced poverty among children and working families to a moderate extent. Increases in the basic state pension plus the introduction of means-tested Pension Credit cut poverty among pensioners faster. Pensione ...
... economy improved. The introduction of the national minimum wage and of Tax Credits in 1999 reduced poverty among children and working families to a moderate extent. Increases in the basic state pension plus the introduction of means-tested Pension Credit cut poverty among pensioners faster. Pensione ...
Economics 302
... Homework will be graded for content as well as neatness, sloppy or illegible work will not receive full credit. This homework requires the use of Microsoft Excel. 1. Keynesian Cross Consider a closed economy with consumption given by the following equation. C 100 2 (Y T ) ...
... Homework will be graded for content as well as neatness, sloppy or illegible work will not receive full credit. This homework requires the use of Microsoft Excel. 1. Keynesian Cross Consider a closed economy with consumption given by the following equation. C 100 2 (Y T ) ...
Economic Base Model - University of Utah
... importing of products from a basic industry. Cross-hauling (the importing of products for local consumption in an export industry) leads to: – an overstatement of the local area’s consumption of the product of industry i and – an underestimate of the local area’s basic employment in the industry ...
... importing of products from a basic industry. Cross-hauling (the importing of products for local consumption in an export industry) leads to: – an overstatement of the local area’s consumption of the product of industry i and – an underestimate of the local area’s basic employment in the industry ...
Chapter 10 Federal Reserve System
... bonds pay a fixed interest payment each year (coupon pmt) bond prices are determined by the relationship between current interest rates and the bond’s rate ...
... bonds pay a fixed interest payment each year (coupon pmt) bond prices are determined by the relationship between current interest rates and the bond’s rate ...
Income Inequality: Evidence and Policy Implications
... Pre-tax top US incomes have surged in recent decades: top 1% income share increased from 9% in 1970 to 20% in 2010 In 2010, top 1% income earners paid average Federal individual tax rate of 22% = 2.6 GDP points Increasing the Federal individual tax rate on top 1% from 22% to 33% would raise revenue ...
... Pre-tax top US incomes have surged in recent decades: top 1% income share increased from 9% in 1970 to 20% in 2010 In 2010, top 1% income earners paid average Federal individual tax rate of 22% = 2.6 GDP points Increasing the Federal individual tax rate on top 1% from 22% to 33% would raise revenue ...
Topics_and_schedule
... we calculate real GDP? Tasks What is the difference between micro and macro economics? What are the main approaches to calculation of GDP? What do we need the GDP indicator for? What is the difference between real and nominal GDP indicators? What is inflation? What types of inflation do you know? Wh ...
... we calculate real GDP? Tasks What is the difference between micro and macro economics? What are the main approaches to calculation of GDP? What do we need the GDP indicator for? What is the difference between real and nominal GDP indicators? What is inflation? What types of inflation do you know? Wh ...
330KB - NZQA
... tourism industry; with references to the stimulus material. Eg, the investment in irrigation will increase farm production, which means that I and X are likely to rise. C may also rise as an effect of higher incomes for business employees and therefore AD and growth increase. On the other hand, poor ...
... tourism industry; with references to the stimulus material. Eg, the investment in irrigation will increase farm production, which means that I and X are likely to rise. C may also rise as an effect of higher incomes for business employees and therefore AD and growth increase. On the other hand, poor ...