Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Economics Syllabus code 9708
... Meaning of scarcity and the inevitability of choices at all levels ...
... Meaning of scarcity and the inevitability of choices at all levels ...
Social Security Cash Deficits
... CBO March 2010 Baseline The Concord Coalition Plausible Baseline adds in the effects of the new Health Care Reform law and assumes that discretionary spending grows at the rate of nominal GDP, that war costs slow gradually, that Medicare physician payment cuts are postponed, and that all expiring ta ...
... CBO March 2010 Baseline The Concord Coalition Plausible Baseline adds in the effects of the new Health Care Reform law and assumes that discretionary spending grows at the rate of nominal GDP, that war costs slow gradually, that Medicare physician payment cuts are postponed, and that all expiring ta ...
analysing uk fiscal policy - UK Government Web Archive
... economic cycle. As the economy strengthens, incomes and expenditure tend to rise, resulting in higher tax receipts, while falling unemployment reduces social security spending. As the economy weakens, the opposite effect occurs. So government borrowing will be relatively low when the economy is oper ...
... economic cycle. As the economy strengthens, incomes and expenditure tend to rise, resulting in higher tax receipts, while falling unemployment reduces social security spending. As the economy weakens, the opposite effect occurs. So government borrowing will be relatively low when the economy is oper ...
The Role of Expectations in the FRB/US Macroeconomic Model
... The lack of adequate data has meant that builders of macroeconomic models have had to specify a priori how individuals form expectations (see box ‘‘Assumptions about the Ways in Which Expectations Are Formed’’). Most models developed in the 1960s and 1970s, including MPS, incorporated the simplifyin ...
... The lack of adequate data has meant that builders of macroeconomic models have had to specify a priori how individuals form expectations (see box ‘‘Assumptions about the Ways in Which Expectations Are Formed’’). Most models developed in the 1960s and 1970s, including MPS, incorporated the simplifyin ...
Policy Biases when the Monetary and Fiscal Authorities
... the control of inflation (see Cukierman, 1992; Walsh, 1993). In fact, in recent years several central banks around the world have adopted inflation targeting as the cornerstone of their monetary policy (see Bernanke and others, 1999). For their part, fiscal authorities in many countries have also co ...
... the control of inflation (see Cukierman, 1992; Walsh, 1993). In fact, in recent years several central banks around the world have adopted inflation targeting as the cornerstone of their monetary policy (see Bernanke and others, 1999). For their part, fiscal authorities in many countries have also co ...
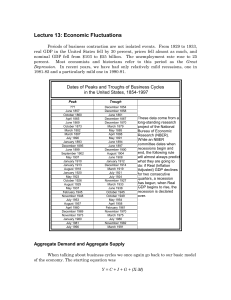
Lecture 13
... And, adjusting for the price level, Real Aggregate Demand = Y = MV/P If we want to see the slope of the aggregate demand curve, the second equation is more convenient. Holding both the money supply and velocity constant, aggregate demand curve is a downward sloping function of price. The higher the ...
... And, adjusting for the price level, Real Aggregate Demand = Y = MV/P If we want to see the slope of the aggregate demand curve, the second equation is more convenient. Holding both the money supply and velocity constant, aggregate demand curve is a downward sloping function of price. The higher the ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research
... program at the beginning of 1990. The measures introduced at that time produced a nearly 10 percent budgetary correction that year (see app. table 11A.1) and resulted in a surplus of about 3 percent of GDP. This stabilization correction resulted mainly from the following four aspects of the program. ...
... program at the beginning of 1990. The measures introduced at that time produced a nearly 10 percent budgetary correction that year (see app. table 11A.1) and resulted in a surplus of about 3 percent of GDP. This stabilization correction resulted mainly from the following four aspects of the program. ...
Business Economics – II (MB1B4): January 2009
... (a) Reduce Government spending and increase the taxes (b) Reduce Government spending and decrease the taxes (c) Increase Government spending and decrease the taxes (d) Increase Government spending and increase the taxes (e) Keep Government spending constant and increase the taxes. 9. The rate of int ...
... (a) Reduce Government spending and increase the taxes (b) Reduce Government spending and decrease the taxes (c) Increase Government spending and decrease the taxes (d) Increase Government spending and increase the taxes (e) Keep Government spending constant and increase the taxes. 9. The rate of int ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES FINANCING CONSUMPTION IN AN AGING JAPAN:
... the impact of aging on Japanese saving and investment rates. In our simulations, we adopt the standard small-country, open capital markets, Ramsey optimal growth model. Specifically, we follow Cutler, Poterba, Sheiner, and Summers’ (1990) modifications to the Ramsey growth model, in examining the im ...
... the impact of aging on Japanese saving and investment rates. In our simulations, we adopt the standard small-country, open capital markets, Ramsey optimal growth model. Specifically, we follow Cutler, Poterba, Sheiner, and Summers’ (1990) modifications to the Ramsey growth model, in examining the im ...
political economy of tax reforms
... them during a regular session. The constitution also strengthened the process of judicial review in Colombia, allowing the courts to determine whether laws are constitutional. The Constitutional Court has a mandate to review all laws and constitutional amendments enacted and holds veto power over t ...
... them during a regular session. The constitution also strengthened the process of judicial review in Colombia, allowing the courts to determine whether laws are constitutional. The Constitutional Court has a mandate to review all laws and constitutional amendments enacted and holds veto power over t ...
Company Name - University of Wisconsin–La Crosse
... AS-AD model uses the aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve together to ...
... AS-AD model uses the aggregate supply curve and the aggregate demand curve together to ...
Markov-Perfect Optimal Fiscal Policy: The Case of
... Our answer to the above question is in the affirmative, provided this is the policy expected by households and all successive governments. The observation of positive income taxes and, especially, of positive levels of public debt has been at odds with most neoclassical theories of optimal fiscal po ...
... Our answer to the above question is in the affirmative, provided this is the policy expected by households and all successive governments. The observation of positive income taxes and, especially, of positive levels of public debt has been at odds with most neoclassical theories of optimal fiscal po ...
Chapter 30
... New aircraft carriers, Air Force I, Presidential limo, FBI vehicles, etc. Does the government buy US products only? NX = net exports = eXports – iMports ...
... New aircraft carriers, Air Force I, Presidential limo, FBI vehicles, etc. Does the government buy US products only? NX = net exports = eXports – iMports ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES OPTIMAL TIME—CONSISTENT FISCAL POLICY WITH UNCERTAIN LIFETIMES
... was the first to study utilitarian planning in an economy with finitely— lived overlapping generations. In the model of Samuelson (1968), a generation lives for two periods and a new generation is born each period until a known date T in the future. Thus, the last generation is born on date 1—1.. If ...
... was the first to study utilitarian planning in an economy with finitely— lived overlapping generations. In the model of Samuelson (1968), a generation lives for two periods and a new generation is born each period until a known date T in the future. Thus, the last generation is born on date 1—1.. If ...
Testing stabilisation policy limits in a small open economy: Editors’ summary of a macroeconomic policy forum
... prices, particularly if accompanied by a significant increase in unemployment levels. If large enough, in combination these shocks could potentially pose a systematic risk to the ...
... prices, particularly if accompanied by a significant increase in unemployment levels. If large enough, in combination these shocks could potentially pose a systematic risk to the ...
The AD-AS Model and Monetary Policy
... Just because the Bank of Canada drops interest rates, that does not necessarily mean that people or businesses will go out and borrow money. ...
... Just because the Bank of Canada drops interest rates, that does not necessarily mean that people or businesses will go out and borrow money. ...
unit #8 slides
... Today, we live in an era of GLOBAL ECONOMIC INTERDEPENDENCE, in which countries depend on one another for goods, services, & natural resources Advantages: Business can make greater PROFITS because they have more MARKETS in which to sell Greater COMPETITION can result in lower PRICES & a wide ...
... Today, we live in an era of GLOBAL ECONOMIC INTERDEPENDENCE, in which countries depend on one another for goods, services, & natural resources Advantages: Business can make greater PROFITS because they have more MARKETS in which to sell Greater COMPETITION can result in lower PRICES & a wide ...
Advanced Placement Macroeconomics
... Key Concepts: microeconomics, macroeconomics, gross domestic product (GDP), consumption, investment, government purchases, net exports, nominal GDP, real GDP, GDP deflator, consumer price index, inflation rate, indexation, nominal interest rate, real interest rate C. Identifying Unemployment Unemplo ...
... Key Concepts: microeconomics, macroeconomics, gross domestic product (GDP), consumption, investment, government purchases, net exports, nominal GDP, real GDP, GDP deflator, consumer price index, inflation rate, indexation, nominal interest rate, real interest rate C. Identifying Unemployment Unemplo ...
chapter overview
... and erases a trade deficit. The reverse is true for a tight monetary policy, which would tend to reduce net exports and worsen a trade deficit. 3. Table 15-4 illustrates these points. VI. ...
... and erases a trade deficit. The reverse is true for a tight monetary policy, which would tend to reduce net exports and worsen a trade deficit. 3. Table 15-4 illustrates these points. VI. ...
Monetary Policy Statement June 2011 Contents
... While export earnings are likely to increase further over the ...
... While export earnings are likely to increase further over the ...
A1 Technical appendix to “Income per natural: Measuring
... individuals file is matched to a household from the households file. Household income per capita for each individual is then calculated by dividing “Household Total Income in 1999” by “Number of Person Records Following This Housing Record”. All individuals born in the US are then dropped, and house ...
... individuals file is matched to a household from the households file. Household income per capita for each individual is then calculated by dividing “Household Total Income in 1999” by “Number of Person Records Following This Housing Record”. All individuals born in the US are then dropped, and house ...
Chapter 17 homework - Mr. Sadow`s History Class Website
... 1. Define long-run aggregate supply (LRAS). Why is the LRAS curve perfectly vertical? 2. Define long-run equilibrium. Create a graph showing long-run equilibrium. 3. What happens when the LRAS and AD both shift right? Create a graph showing both shifts (double-shift). 4. What does the LRAS curve com ...
... 1. Define long-run aggregate supply (LRAS). Why is the LRAS curve perfectly vertical? 2. Define long-run equilibrium. Create a graph showing long-run equilibrium. 3. What happens when the LRAS and AD both shift right? Create a graph showing both shifts (double-shift). 4. What does the LRAS curve com ...
publication - Centre for European Policy Studies
... ratios is something observed in all recessions and therefore temporary (see, for example, Schmieding, 2013). Of course, everything on earth is temporary in some sense. Given the size of the build-up of government debt ratios in the eurozone’s periphery, the temporary nature of this build-up may beco ...
... ratios is something observed in all recessions and therefore temporary (see, for example, Schmieding, 2013). Of course, everything on earth is temporary in some sense. Given the size of the build-up of government debt ratios in the eurozone’s periphery, the temporary nature of this build-up may beco ...